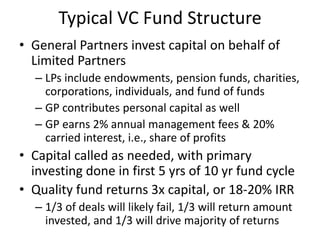
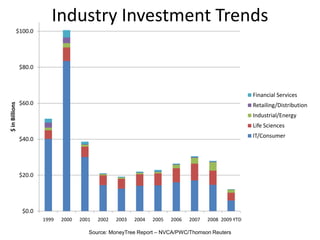
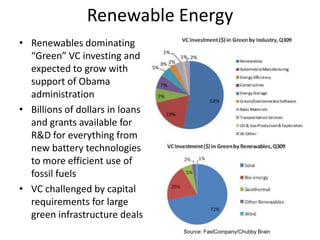
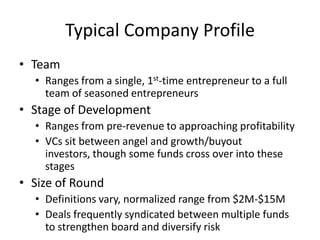
Venture capital involves private equity funding for early stage, high-growth companies. Venture capital funds are typically structured as limited partnerships with general partners investing on behalf of limited partner investors. General partners earn management fees and carried interest based on fund performance. Venture capital funding rounds involve evaluating company teams, opportunities, financial projections, and negotiating term sheets that determine share prices, liquidation preferences, and board control between investors and companies. The goal is for funds to return 3 times their capital over 10 years through a small number of highly successful portfolio company exits through acquisition or IPO.