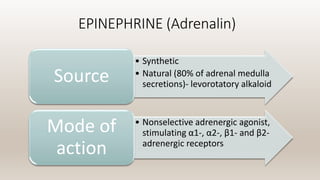
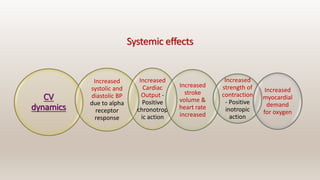
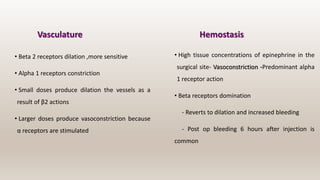
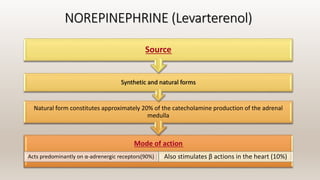
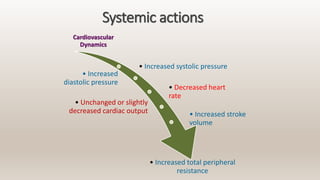
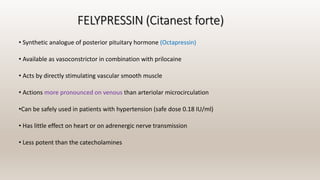
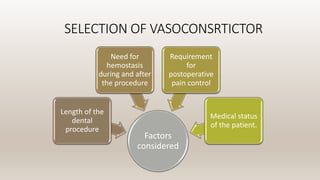
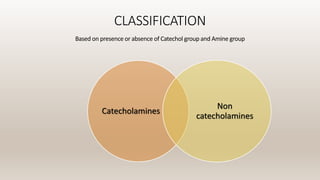
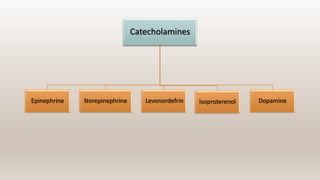
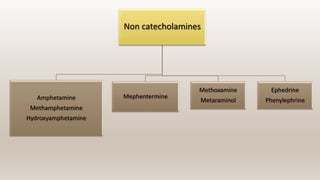
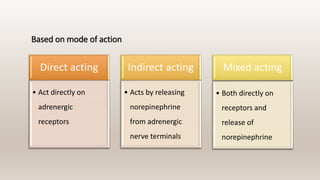
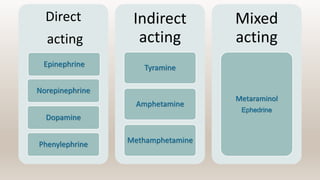
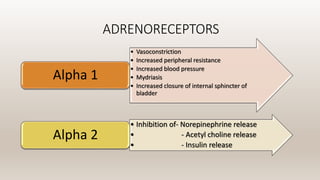
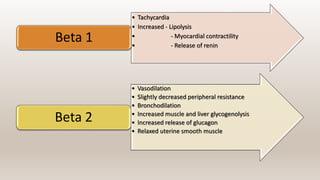
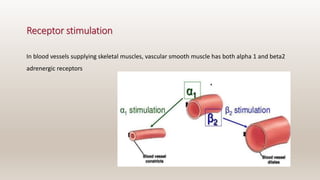
This document discusses vasoconstrictors which are drugs added to local anesthetics to prolong their duration and effectiveness. It classifies vasoconstrictors based on their chemical structure and mode of action. Epinephrine is described as the most commonly used vasoconstrictor due to its direct effects on alpha-1 and beta-2 receptors, which causes vasoconstriction and increased duration of anesthesia. Side effects are also discussed, noting the risks of hypertension, tachycardia and cardiac issues if overused. Maximum safe doses are provided for different local anesthetic solutions containing epinephrine or other vasoconstrictors like norepinephrine and phenylephrine.






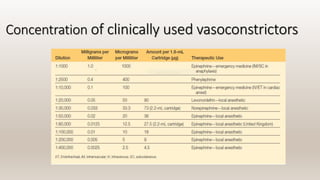
![DILUTION OF VASOCONSTRICTORS
The dilution of vasoconstrictors is commonly referred to as a ratio
( e.g : 1 to 1000 [written 1 : 1000])
Ratio of drug to carrier medium
1:1000 = 1 g in 1000 ml or 1000 mg in 1000 ml of solution
1:10,000 contains 0.1 mg/ml
1:100,000 contains 0.01 mg/ml](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationautosaved-201208053832/85/VASOCONSTRICTORS-15-320.jpg)