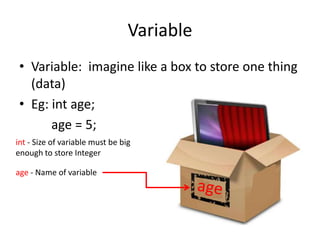
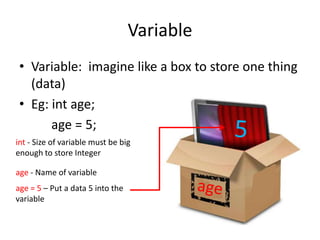
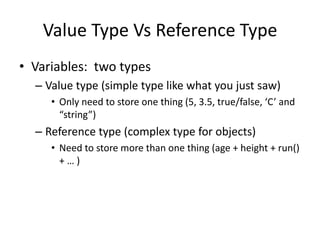
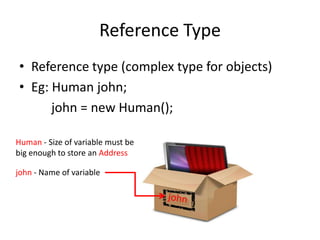
This document summarizes programming concepts covered in week 1, including variables, value types vs reference types, and static vs non-static classes. It defines variables as boxes that store data, and provides an example of an integer variable named 'age' assigned the value 5. Reference types are described as storing more complex objects with multiple fields, using a 'Human' class as an example. The document also distinguishes static classes that can be used without instantiation from non-static classes that require using 'new' to create an object instance. It recommends using console programs for basic problem solving and lists some fundamental C# language concepts and functions to use.