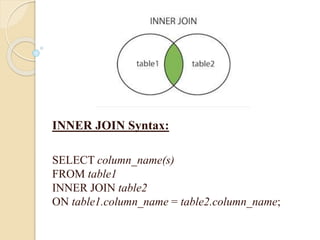
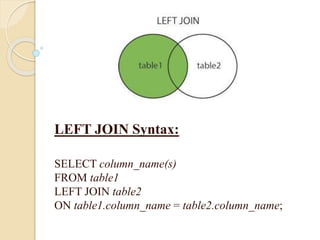
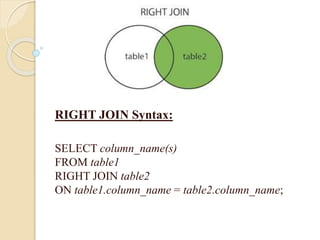
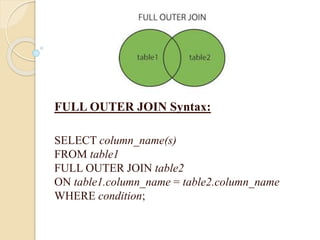
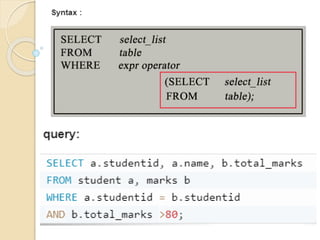
This document discusses joins and subqueries in SQL for big data analysis. It defines different types of SQL joins such as inner, left, right, and full outer joins. It explains that joins combine rows from two or more tables based on related columns. It also defines subqueries as queries nested within other SQL statements, most commonly in the WHERE clause, and notes they must be enclosed in parentheses and placed on the right side of a comparison operator.