This document discusses UX Thinking (UXT), which aims to bridge human-centered design and agile development practices. It presents UXT models and principles for building digital solutions that have business impact. The key aspects covered are:
- The 3 dimensions that shape solutions: technology, users/solutions, and trends/frameworks.
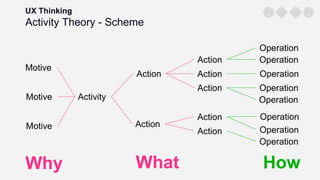
- Activity theory as a way to understand user motives and design for outcomes.
- The UXT phases from product discovery to delivery.
- The importance of shared understanding and vision statements in aligning teams.
- Psychological safety and its role in team performance based on Google's Project Aristotle research.