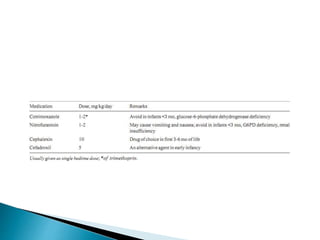
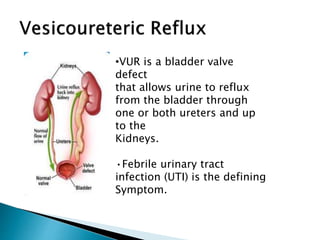
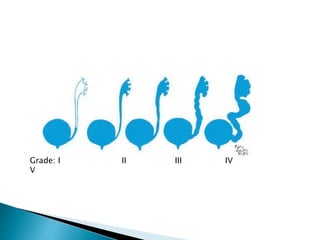
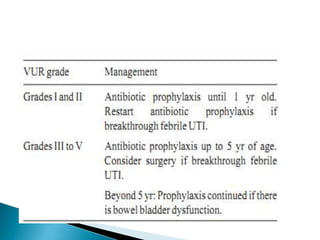
This document discusses urinary tract infections (UTIs) in children. It notes that UTIs are common in childhood and can lead to renal scarring if not treated properly. Escherichia coli is the most common cause of UTIs in children. The diagnosis of a UTI requires a positive urine culture. Treatment depends on factors like age and infection severity, but commonly involves antibiotics. Recurrent UTIs and vesicoureteral reflux increase the risk of renal damage, so preventative measures and follow-up are important.