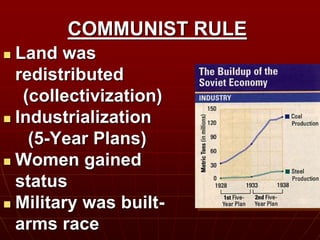
Dynastic monarchies in Russia and China faced economic and social problems in the early 20th century, leading to revolutions. In Russia, the tsar was overthrown and a provisional democratic government formed, but it failed amid World War I losses. Radicals like the Bolsheviks gained power, and their leader Lenin seized control. A civil war ensued as anti-communist forces fought back, but the Bolsheviks prevailed. Lenin established communist rule, redistributing land and industrializing through five-year plans. In China, the Qing dynasty fell in 1912 and a provisional government took over, but problems continued and communists gained victory in 1949, establishing the People's Republic of China.