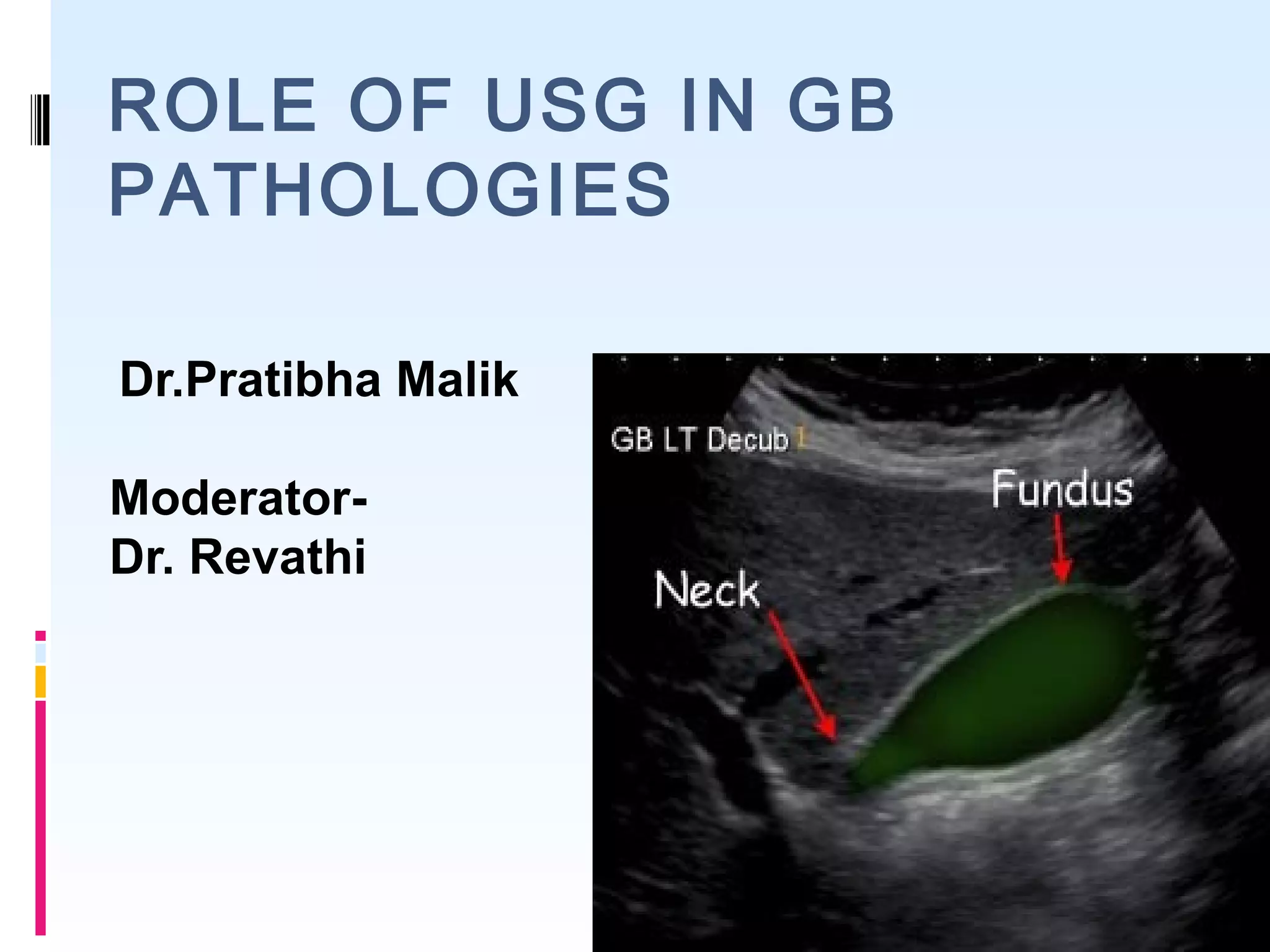
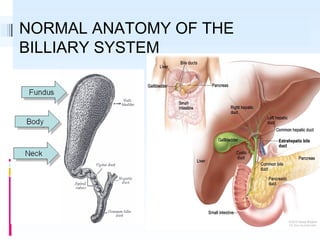
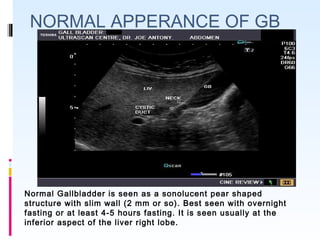
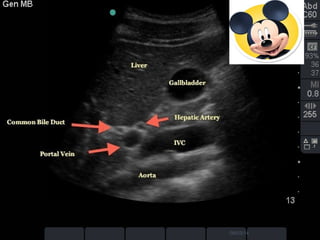
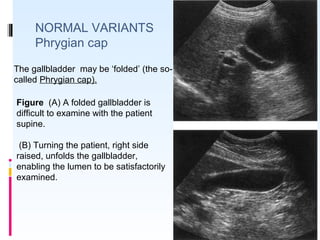
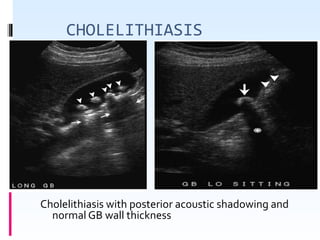
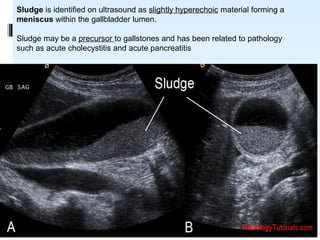
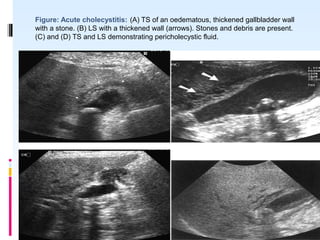
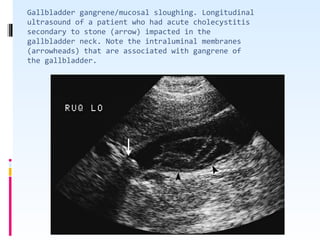
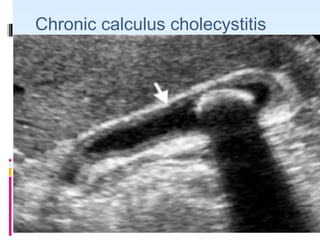
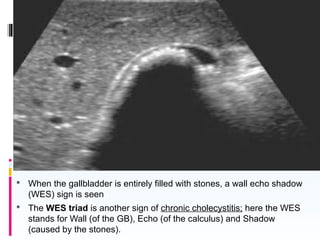
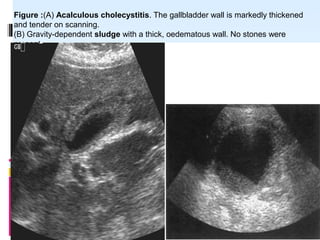
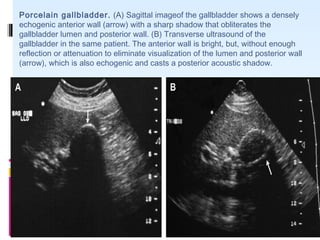
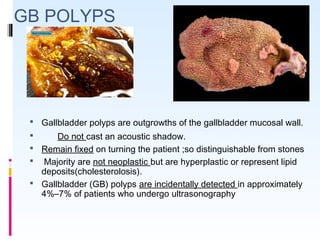
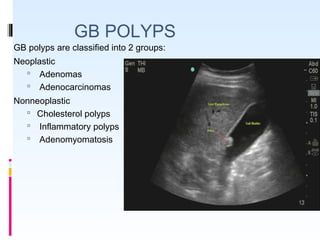
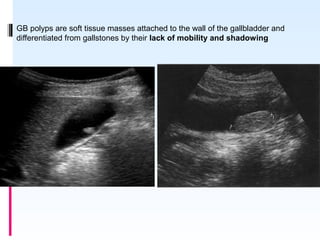
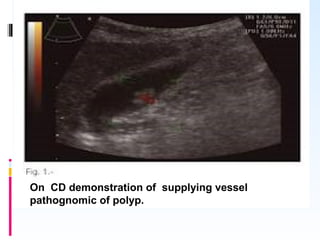
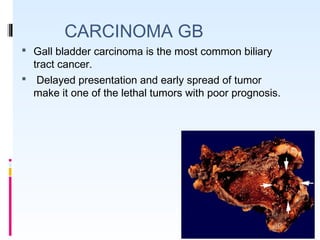
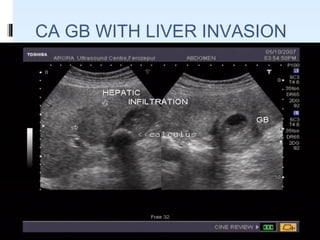
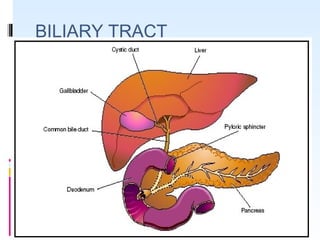
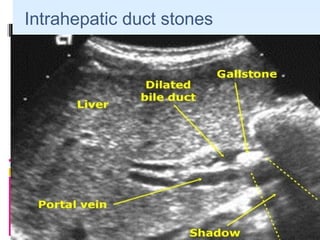
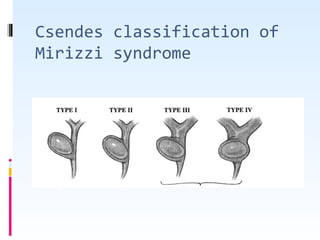
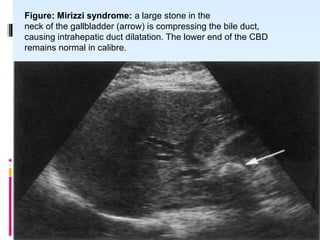
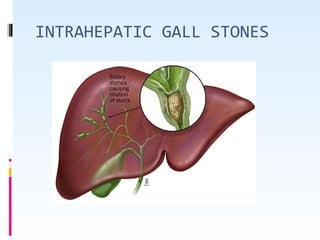
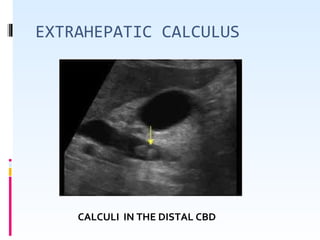
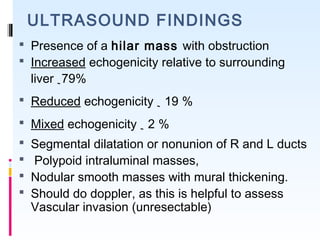
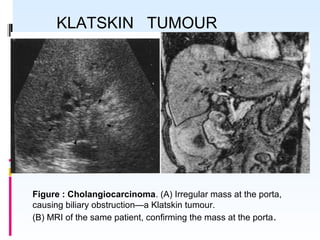
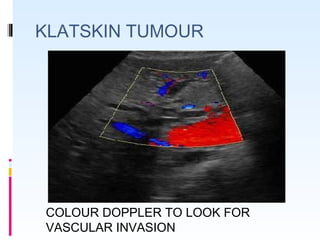
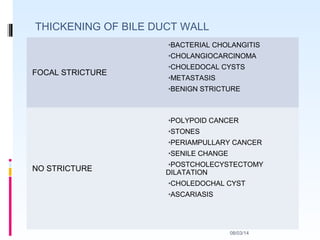
This document discusses the role of ultrasound in evaluating gallbladder pathologies. It begins by covering normal gallbladder anatomy and variants. Key pathological findings that can be identified on ultrasound include gallstones, sludge, cholecystitis, polyps, gallbladder cancer, and bile duct stones. Specific ultrasound findings that help characterize these various conditions are presented. The document also reviews ultrasound evaluation of the biliary tract, including assessment of the bile ducts and conditions like Mirizzi syndrome.