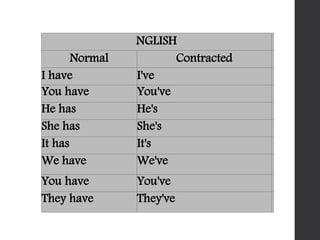
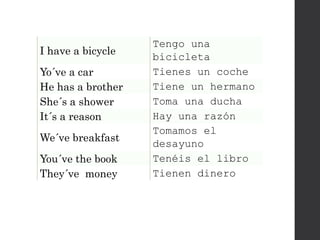
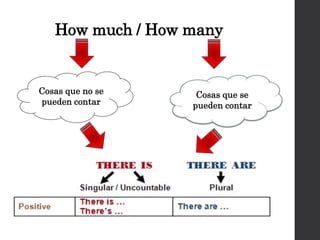
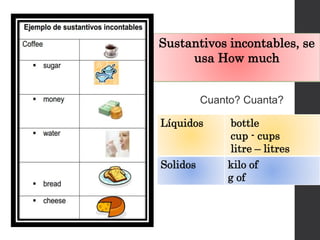
The document discusses the Mesoamerican ball game and human sacrifice practices related to it. It states that the French and Mesoamerican civilizations used to play the ball game, which was usually played by two or three teams. The players could touch the ball with their hands, feet, hips, elbows or knees. The captain or some players of the winning team were sometimes sacrificed after the game. Opinions differed on whether the Mesoamericans believed human sacrifice pleased their gods or not.


















![He was walking to work when he fell.
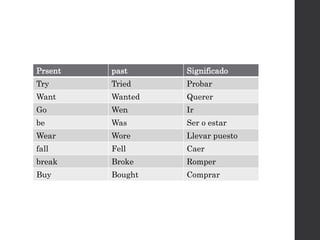
[SUJETO] + was/were + [VERBO con terminación -ing (gerundio)]
Estructura para formar oraciones en pasado
continuo
Paula wasn't living in Spain in 2005.
We were still working at 10 o'clock last night.
My son was reading while I was cooking
They were talking very loudly while we were trying to
watch the movie.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/usedto-160721045408/85/Used-to-26-320.jpg)
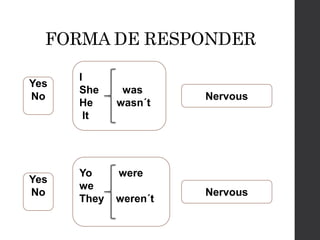
![Estructura para formar oraciones en pasado
simple
[SUJETO] + was/were + [VERBO en past tense + complemento
They were jumped in the park
I was sang in the home
Adriana was slept in the classroom
Carmela was swept the street
We were talked about the movie](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/usedto-160721045408/85/Used-to-27-320.jpg)
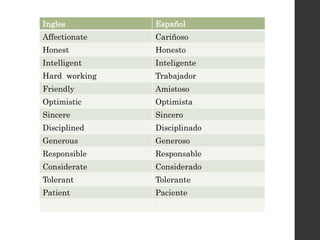
![When = cuando
[SUJETO] + was/were + [VERBO (gerundio)]+ when+ complemento
+ verbo en pasado simple (past tense)
we were running in the classroom when Maria fell
jorge was doing homework when arturo broke a glass
we were shopping at the supermarket when they raided
carlos was dancing when his mom arrived home](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/usedto-160721045408/85/Used-to-28-320.jpg)

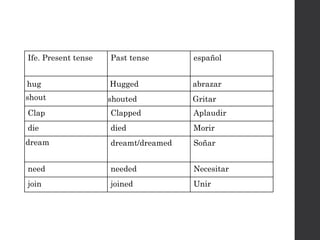







![[SUJETO] + have/has + [PARTICIPIO DEL VERBO]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/usedto-160721045408/85/Used-to-41-320.jpg)