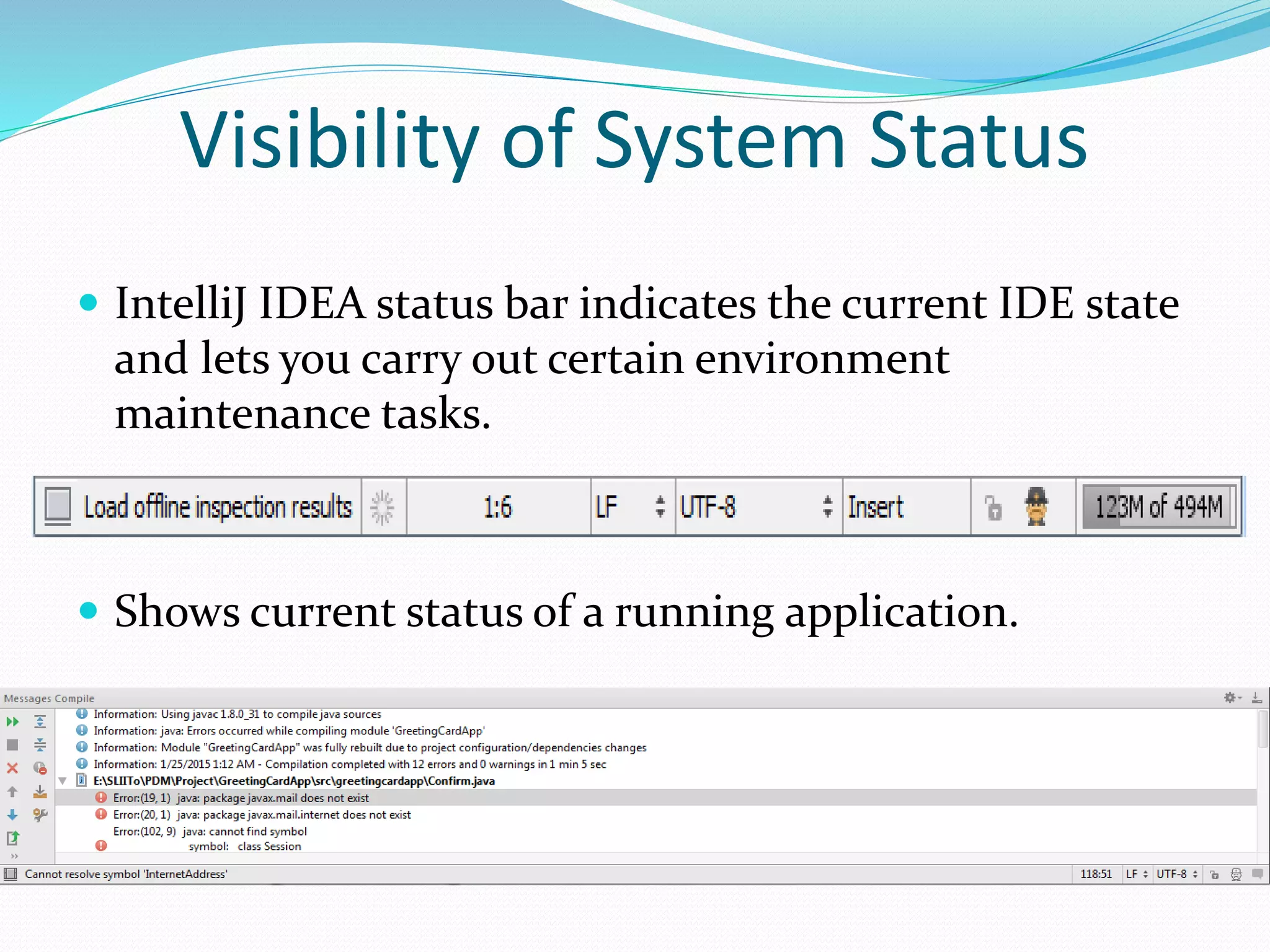
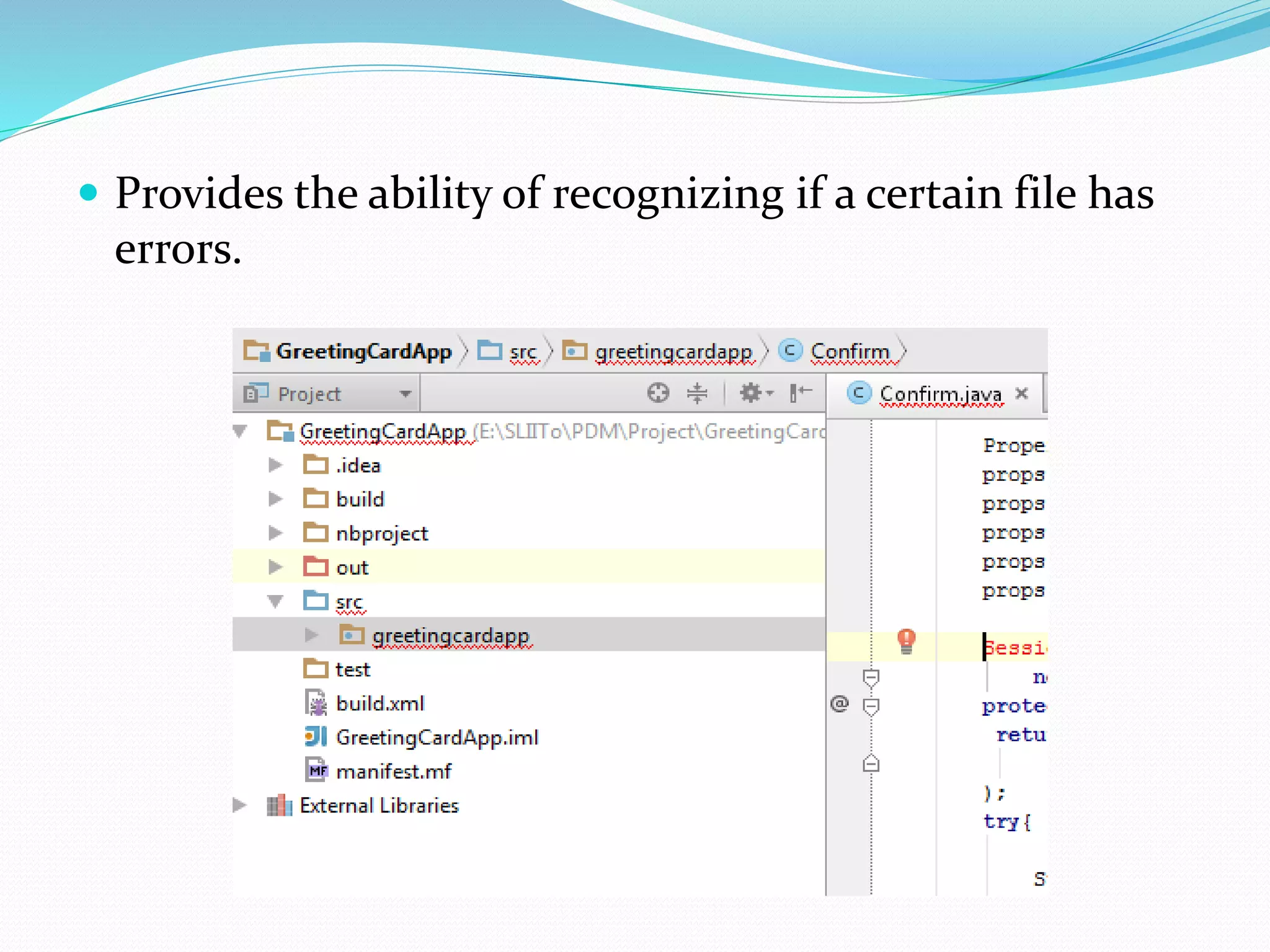
IntelliJ IDEA is an integrated development environment that provides a source code editor, build automation tools, a debugger, and supports development of desktop, mobile, and web applications. It supports several programming languages including Java, PHP, Python, and SQL. The status bar indicates the current state of the IDE and running applications, and allows maintenance tasks to be performed. Errors and warnings are displayed in a narrow area next to the code editor.