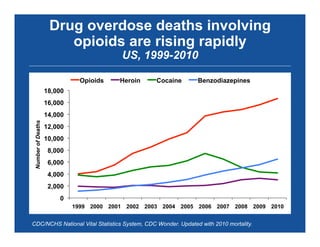
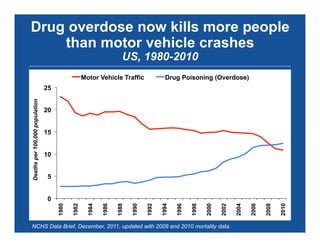
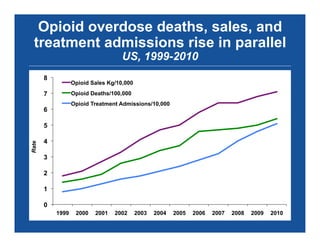
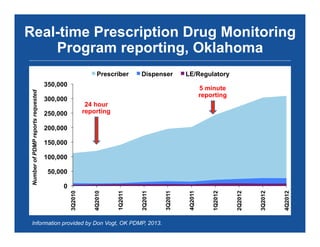
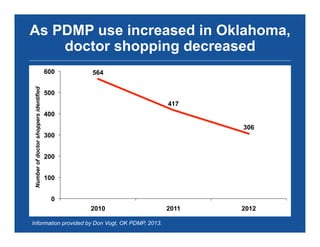
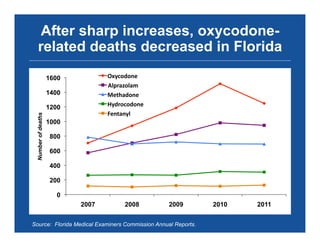
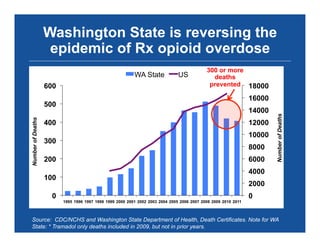
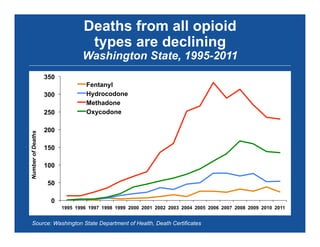
The document discusses the public health epidemic of prescription opioid abuse in the U.S., noting that over 16,500 deaths annually result from opioid-related overdoses. It emphasizes the rising trend in overdose deaths and suggests a multipronged public health approach involving better monitoring, support for states, improved clinical practices, and laws/regulations to combat the crisis. Successful state-level interventions, such as real-time prescription drug monitoring, are highlighted as effective measures in reducing overdose incidents.