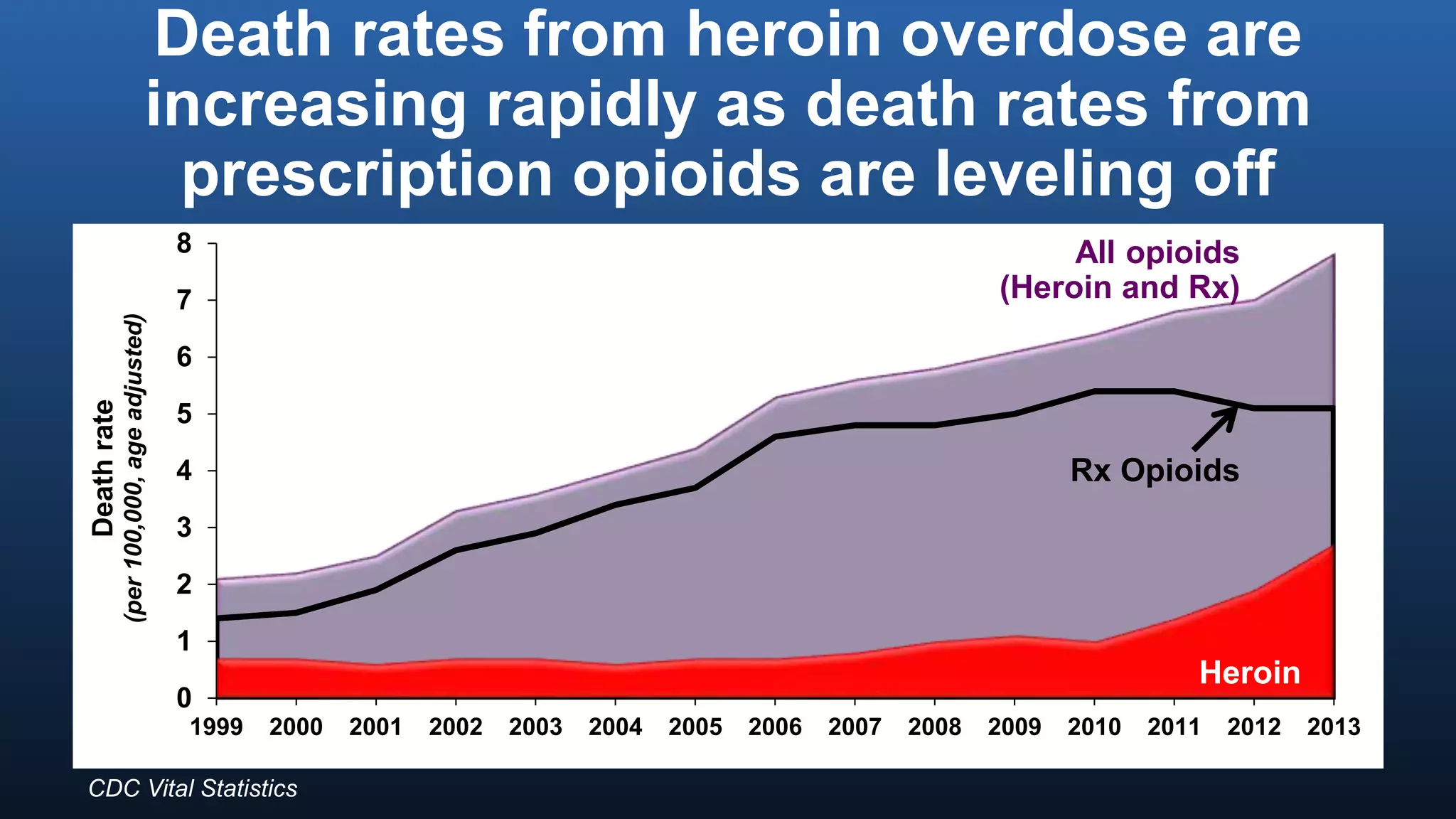
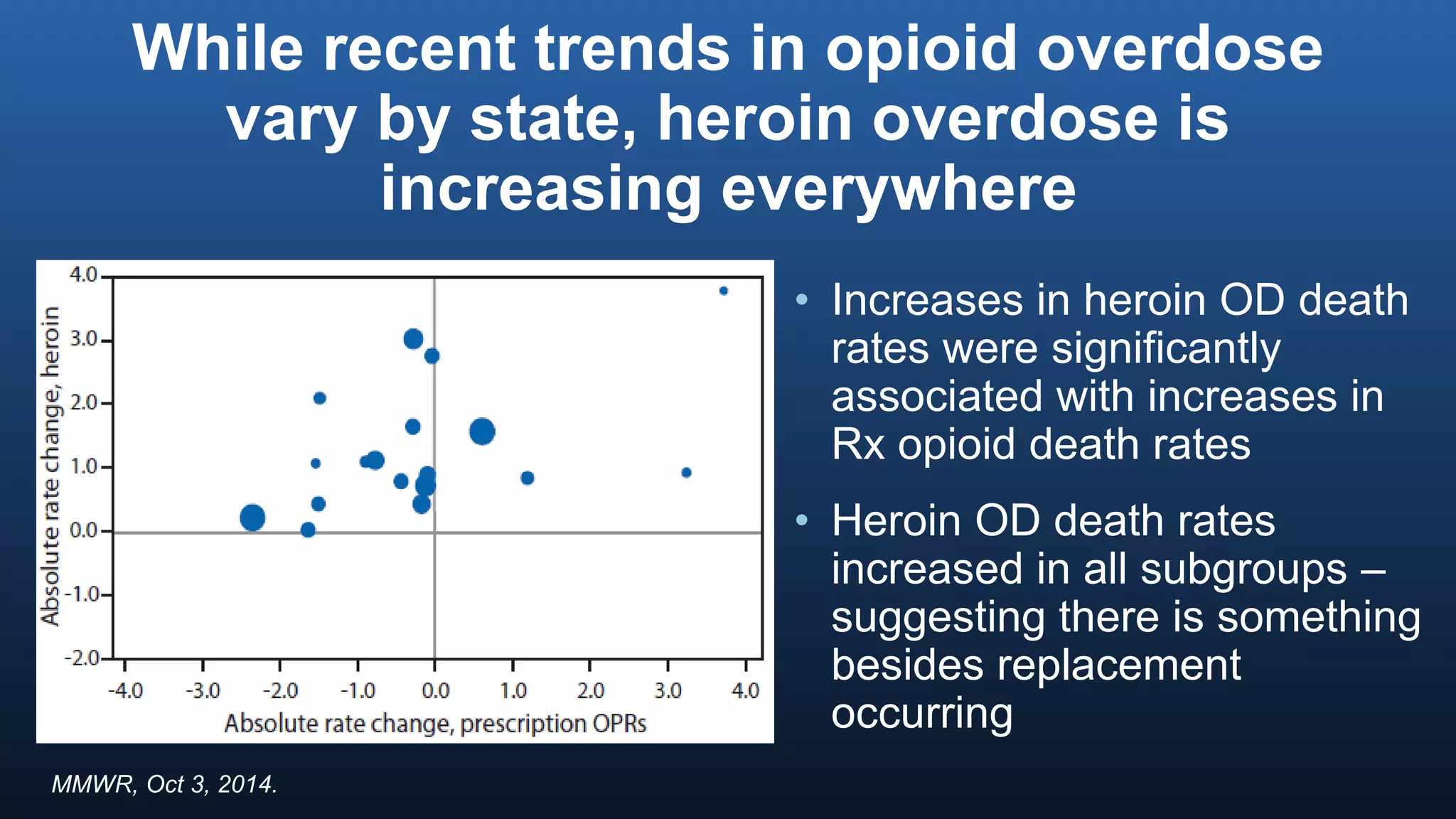
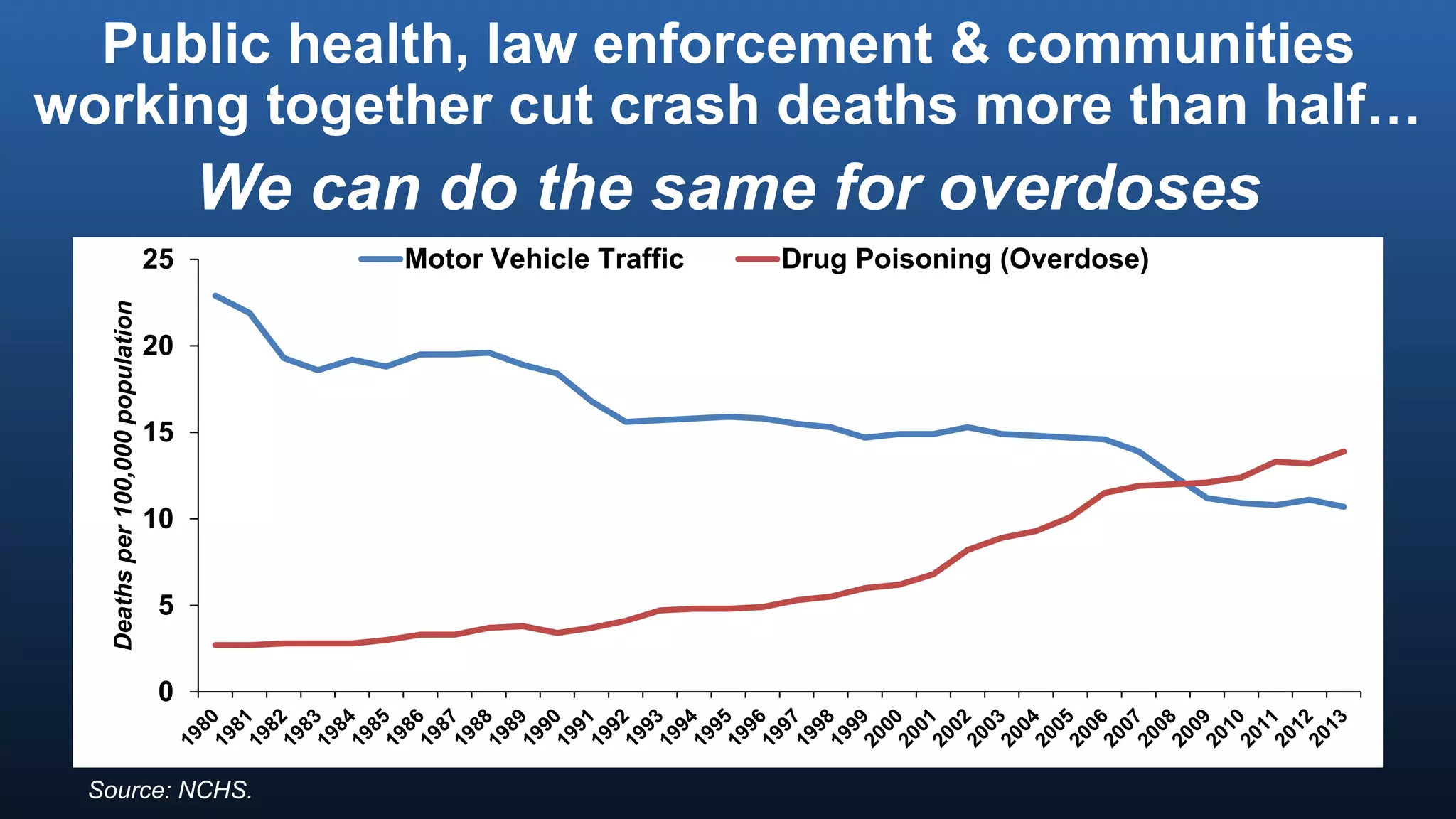
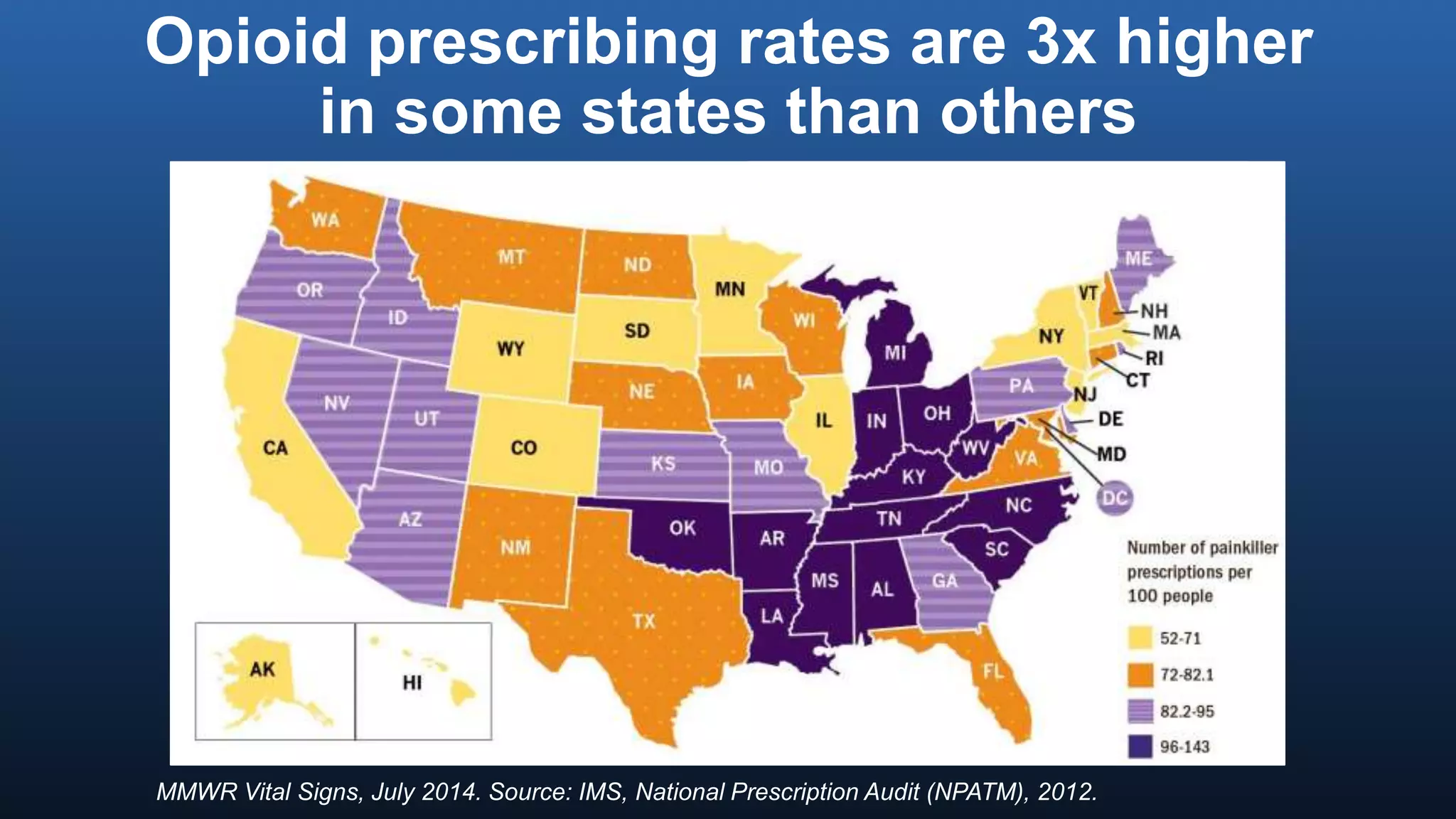
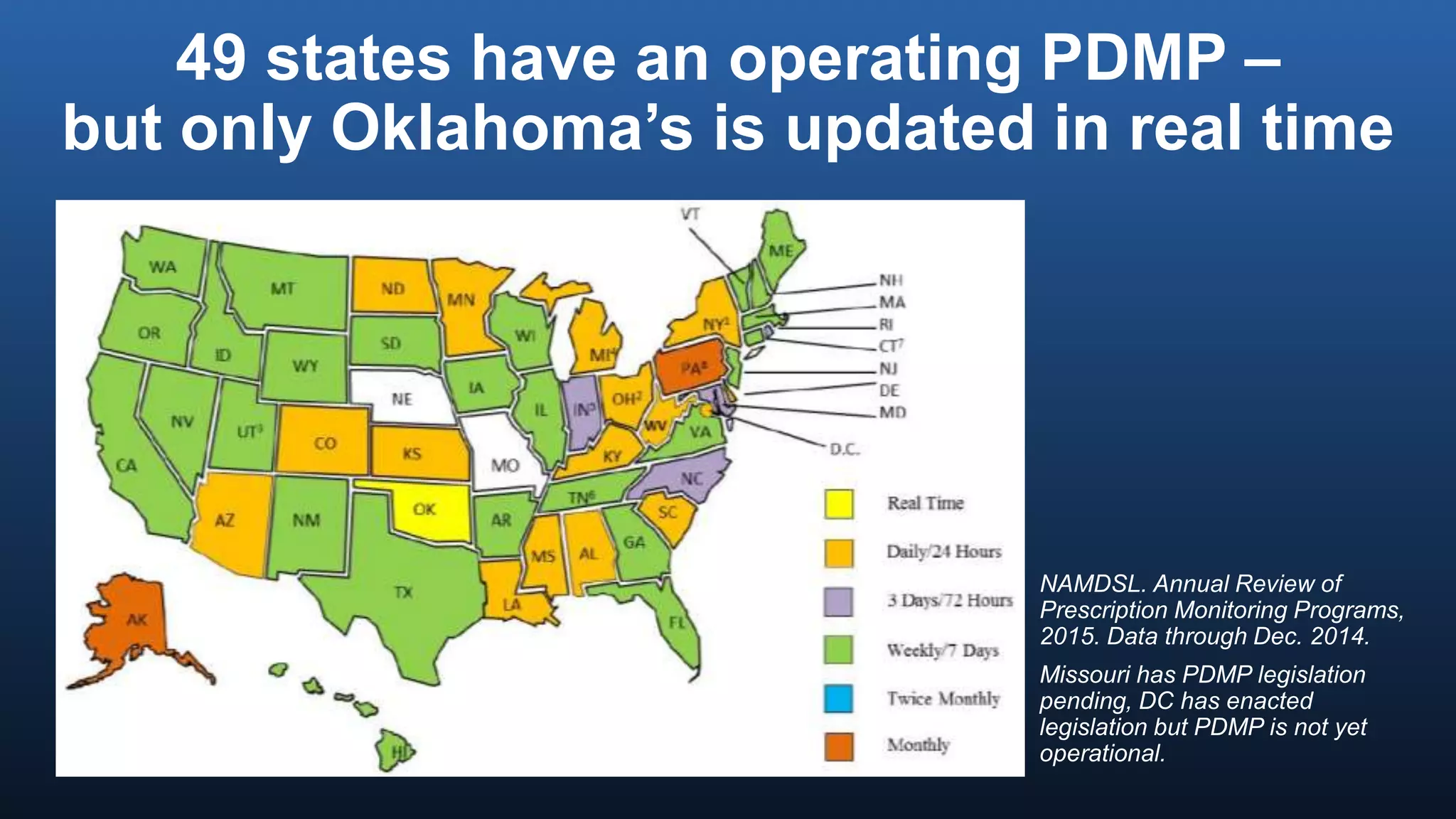
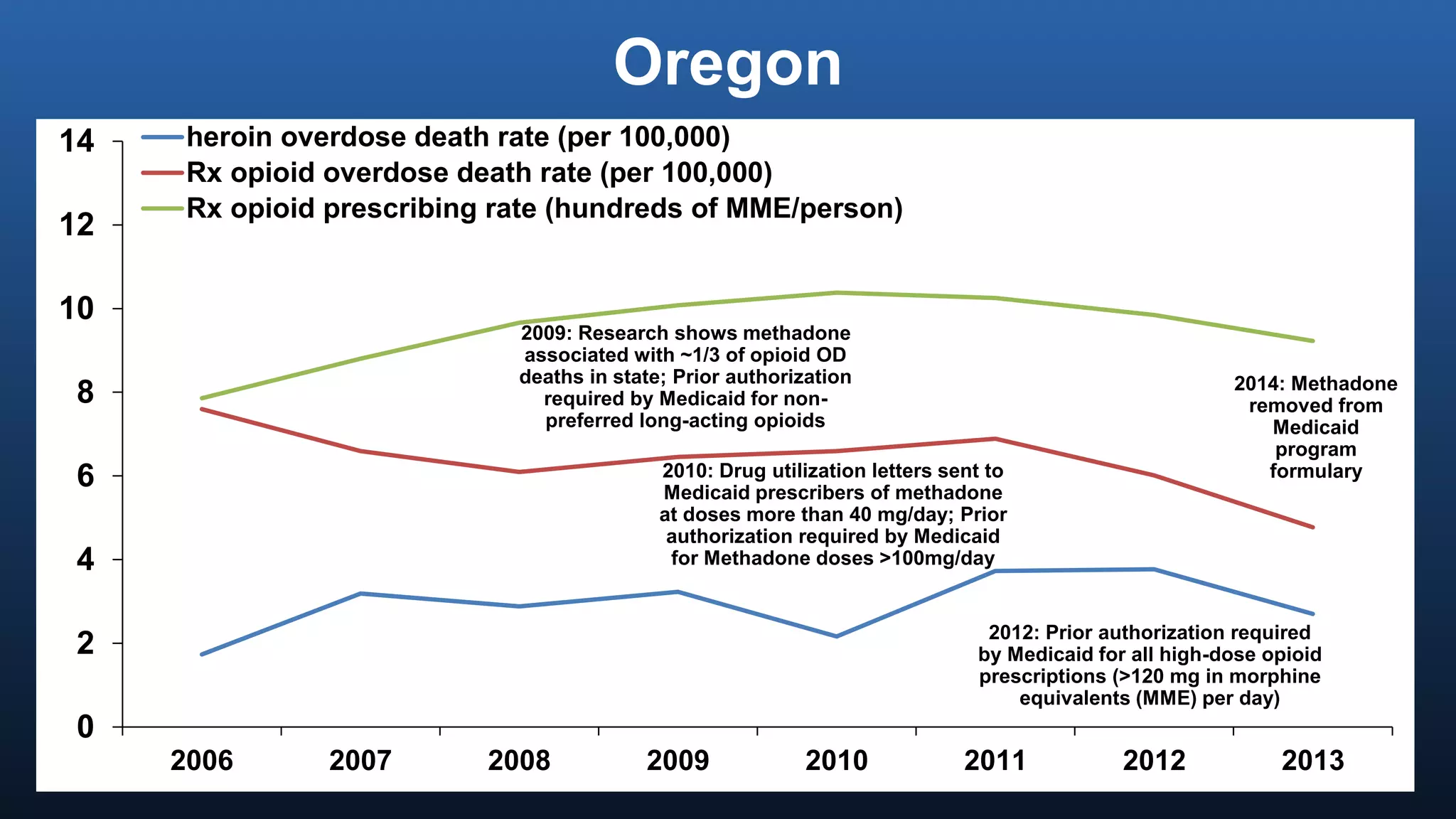
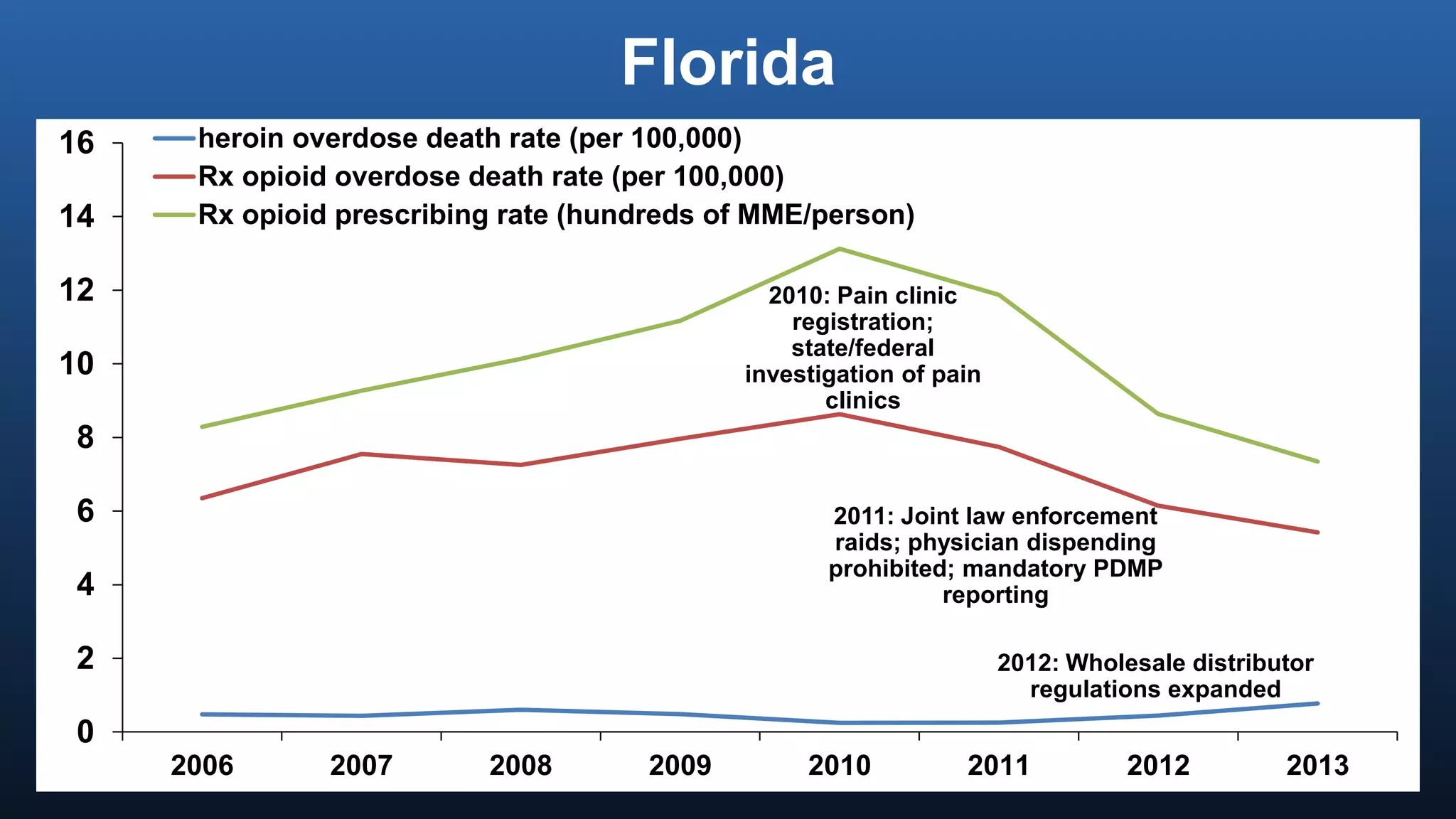
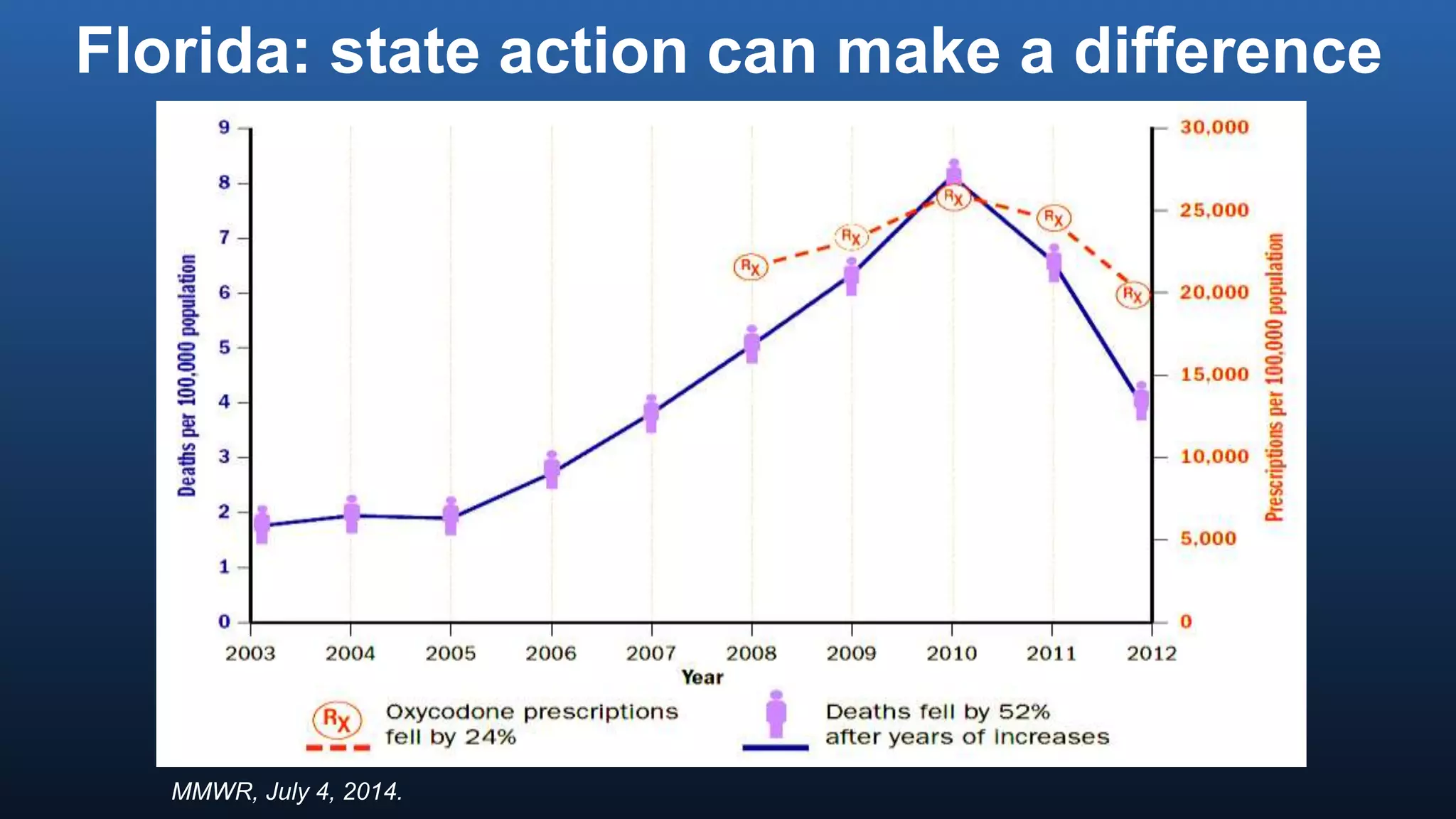
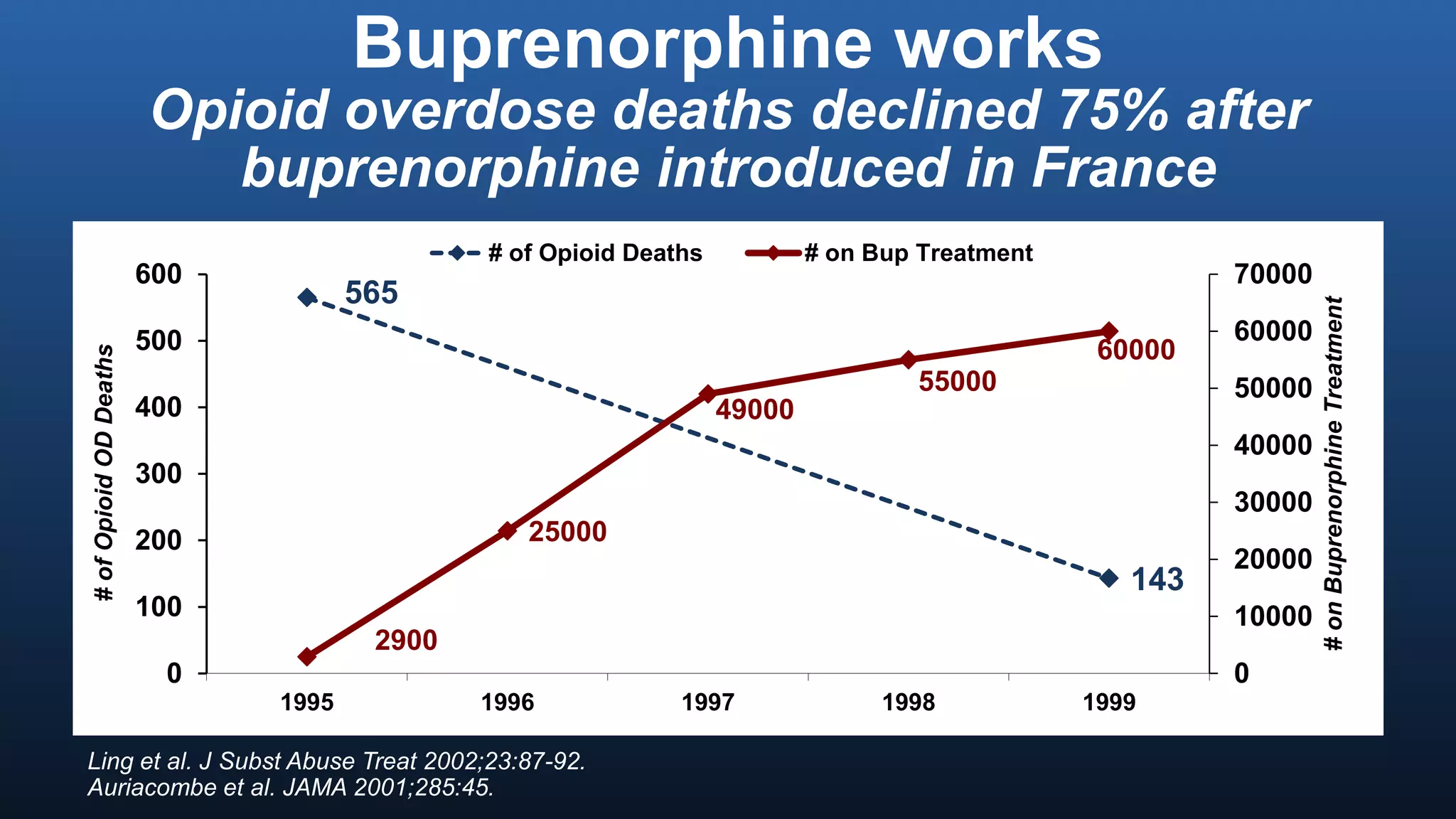
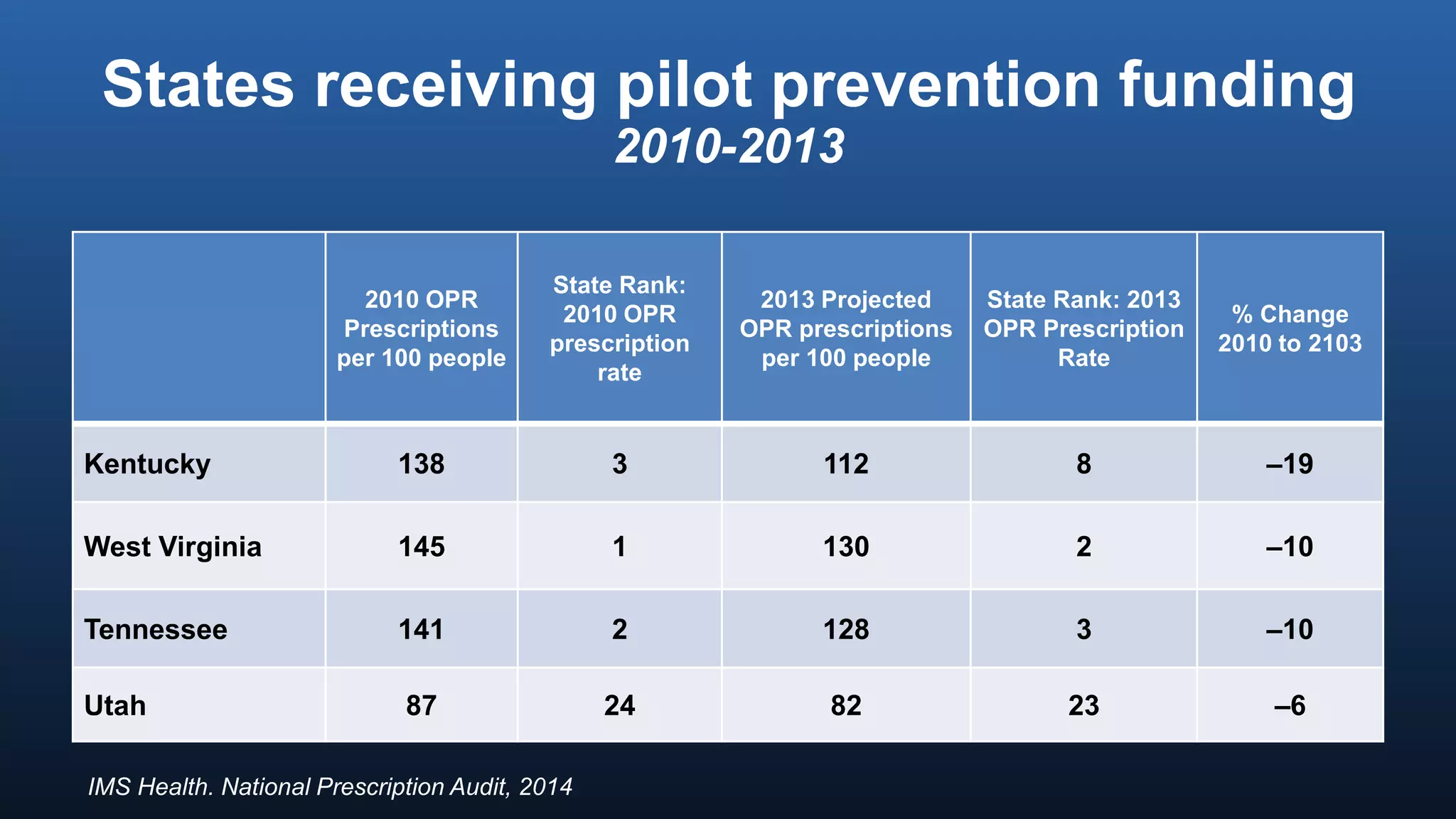
The director of the CDC discussed the prescription drug and opioid overdose epidemic in the United States. He noted that over 145,000 lives have been lost to prescription opioid overdoses in the past decade as opioid prescribing has increased 4-fold since 1999. The CDC is working with multiple states experiencing outbreaks of HIV linked to injection drug use. The director outlined a potential "technical package" of interventions including improving prescribing practices, increasing access to treatment, reducing drug availability, and public awareness campaigns. Progress requires a comprehensive, evidence-based public health approach with law enforcement and community involvement.