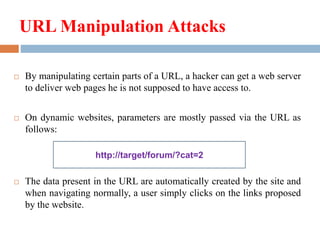
This document discusses URL manipulation and related attacks. It begins by introducing URLs and their structure. URL manipulation involves tampering with parameters passed in a URL, such as modifying account numbers or directory paths. This can allow access to restricted areas if not properly validated. Attacks like trial and error changing paths and directory traversal moving up the tree structure are described. Countermeasures include updating servers, restricting browsing below the site root, removing hidden files and directories, and accurately interpreting dynamic pages and backups.