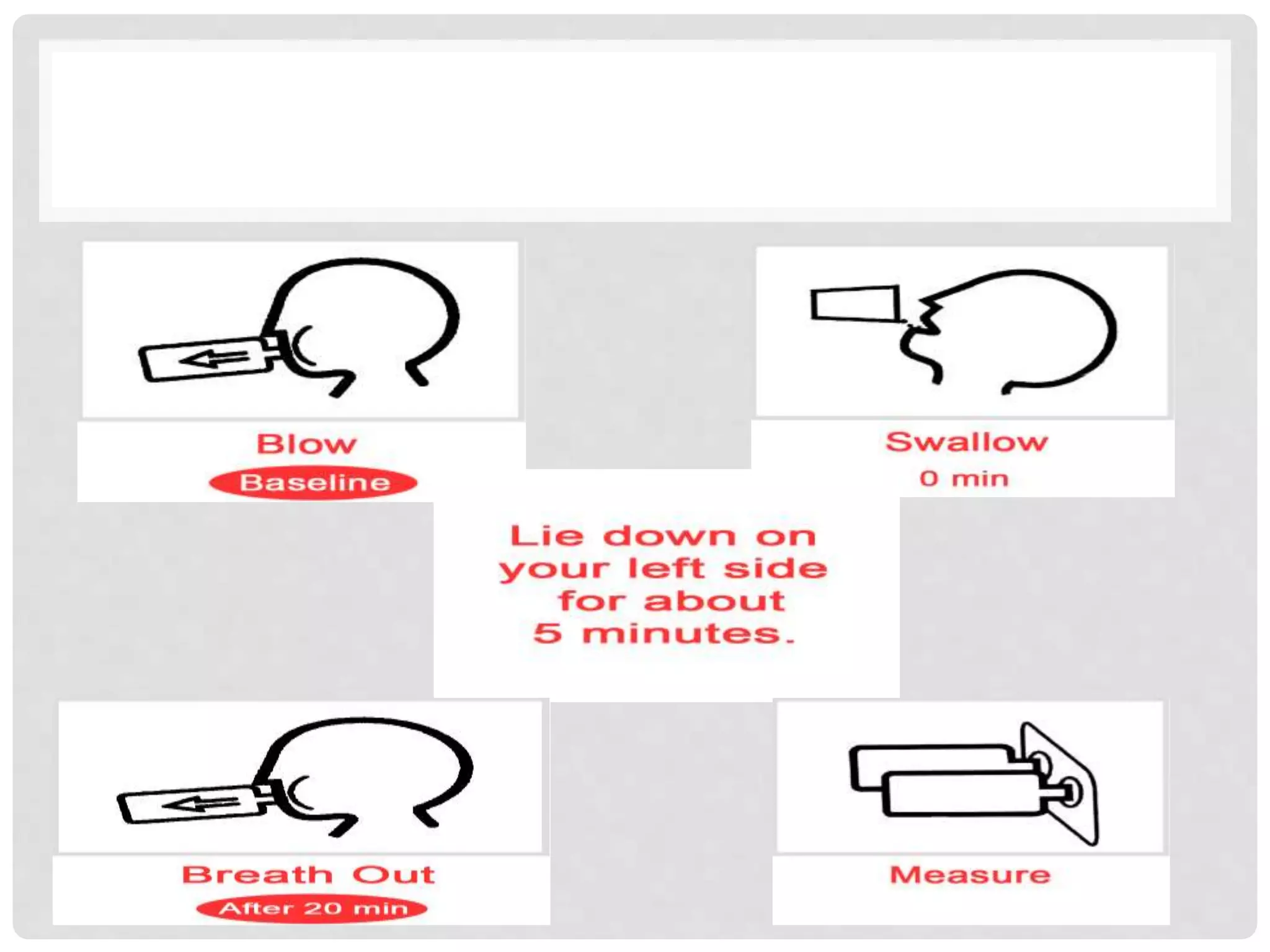
The urea breath test is a rapid, non-invasive diagnostic procedure used to identify infections of Helicobacter pylori, the bacterium linked to gastric diseases. The test works by having patients ingest urea labeled with a stable carbon isotope. H. pylori in the stomach converts the urea to carbon dioxide, which is then exhaled and detected. It provides accurate results within 25 minutes and is the best way to confirm successful eradication of H. pylori after treatment.