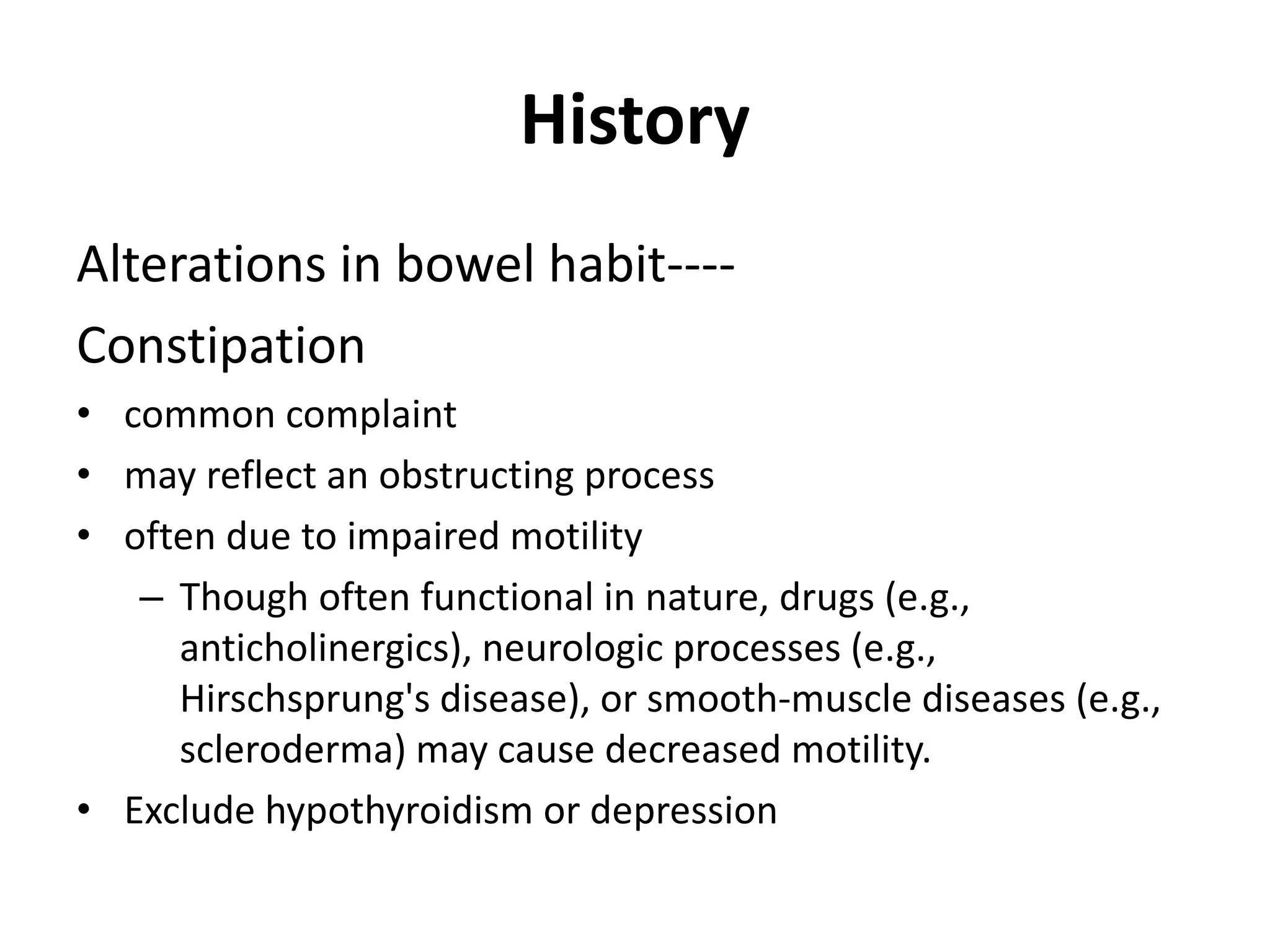
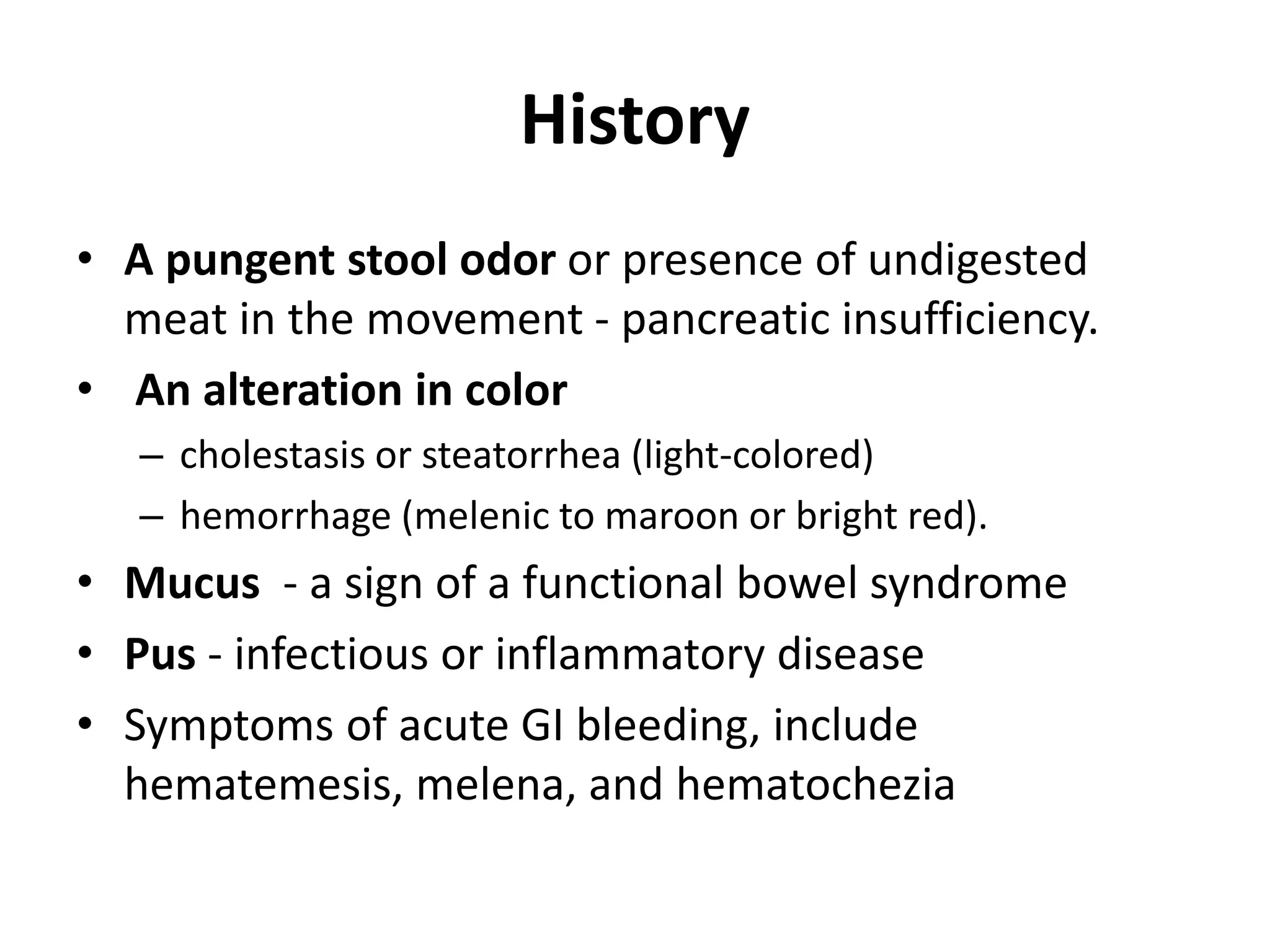
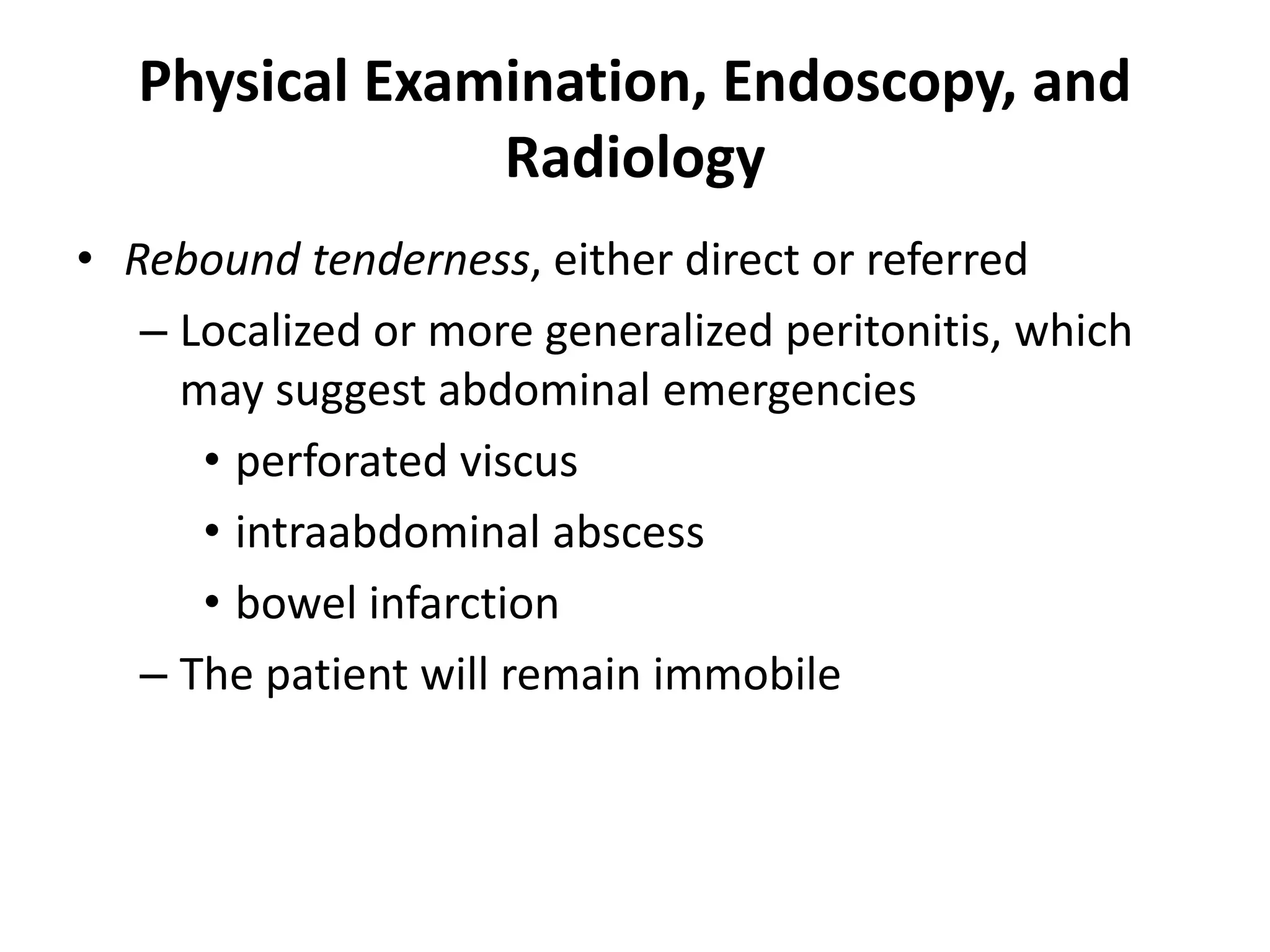
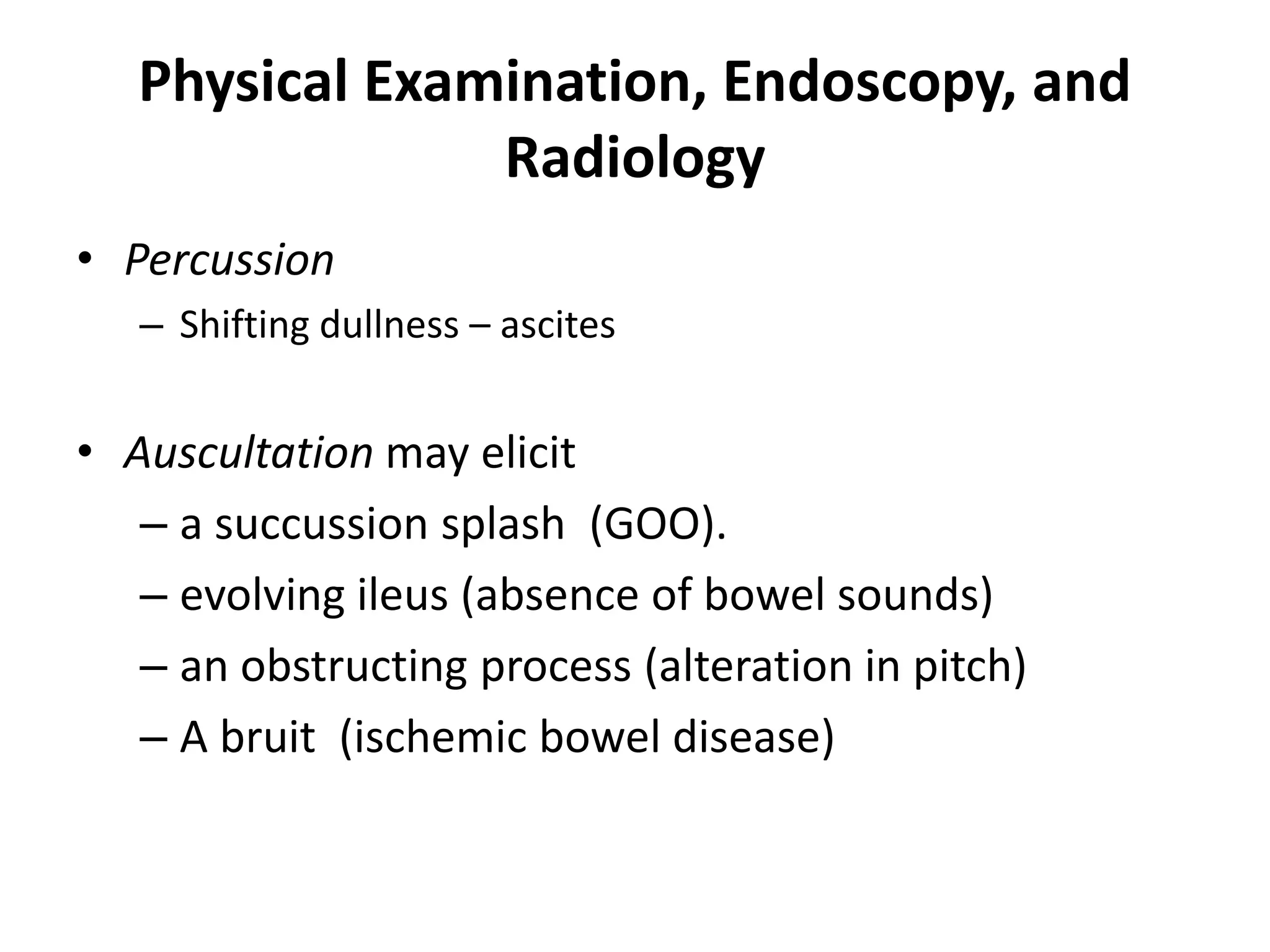
The document provides guidance on evaluating patients presenting with gastrointestinal (GI) diseases or symptoms. It outlines the following approach:
1. Take a thorough clinical history focusing on symptoms of pain, changes in bowel habits, nausea, etc. and their characteristics.
2. Perform a physical exam including inspection, palpation of the abdomen, digital rectal exam, and auscultation of bowel sounds.
3. Consider endoscopic procedures like sigmoidoscopy, upper endoscopy, or colonoscopy for direct visualization. Radiologic imaging like barium studies, ultrasound, CT and MRI can also help evaluate specific organs or abnormalities.
4. The diagnostic approach will depend on the presenting symptoms but may involve tests