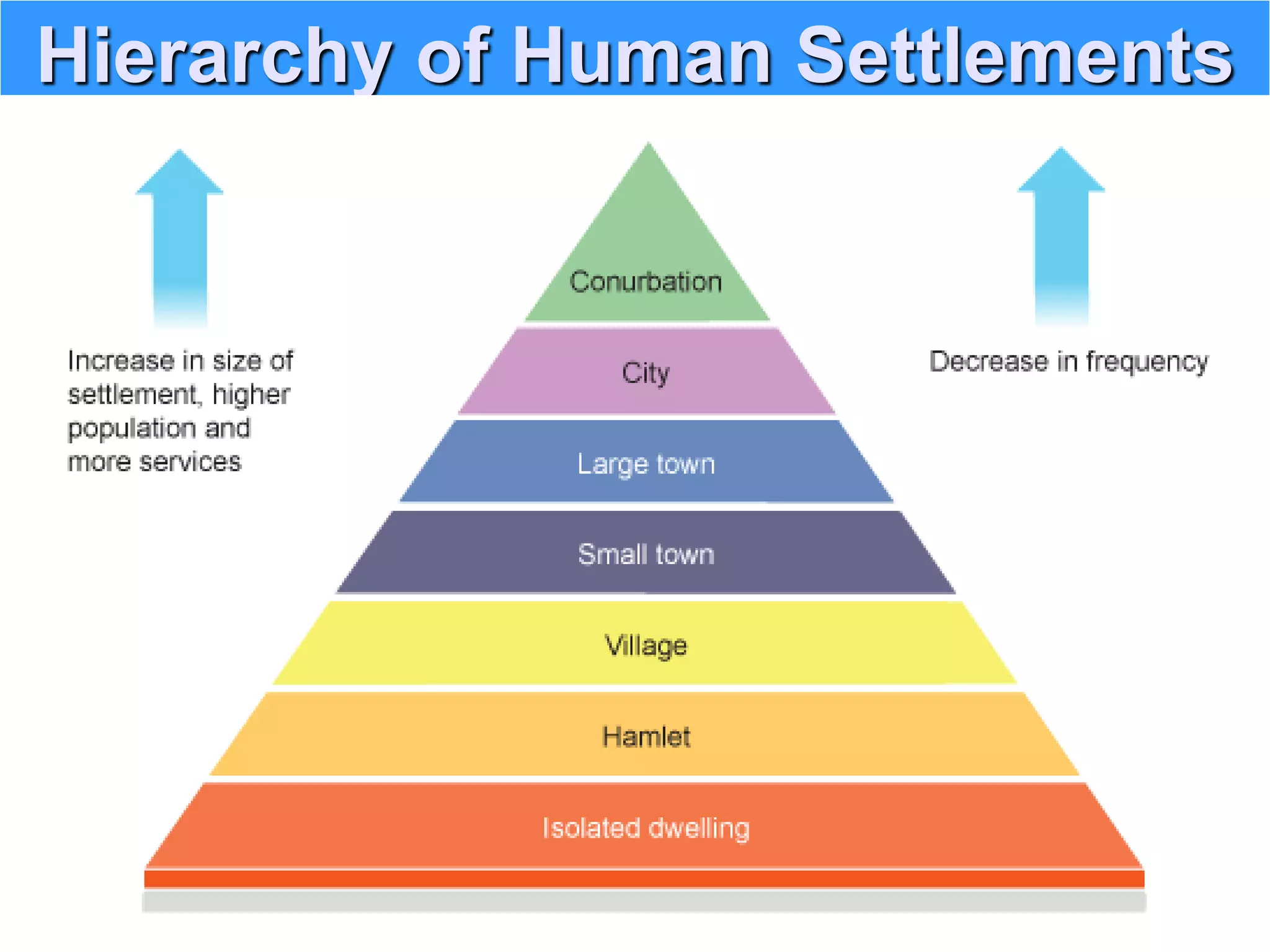
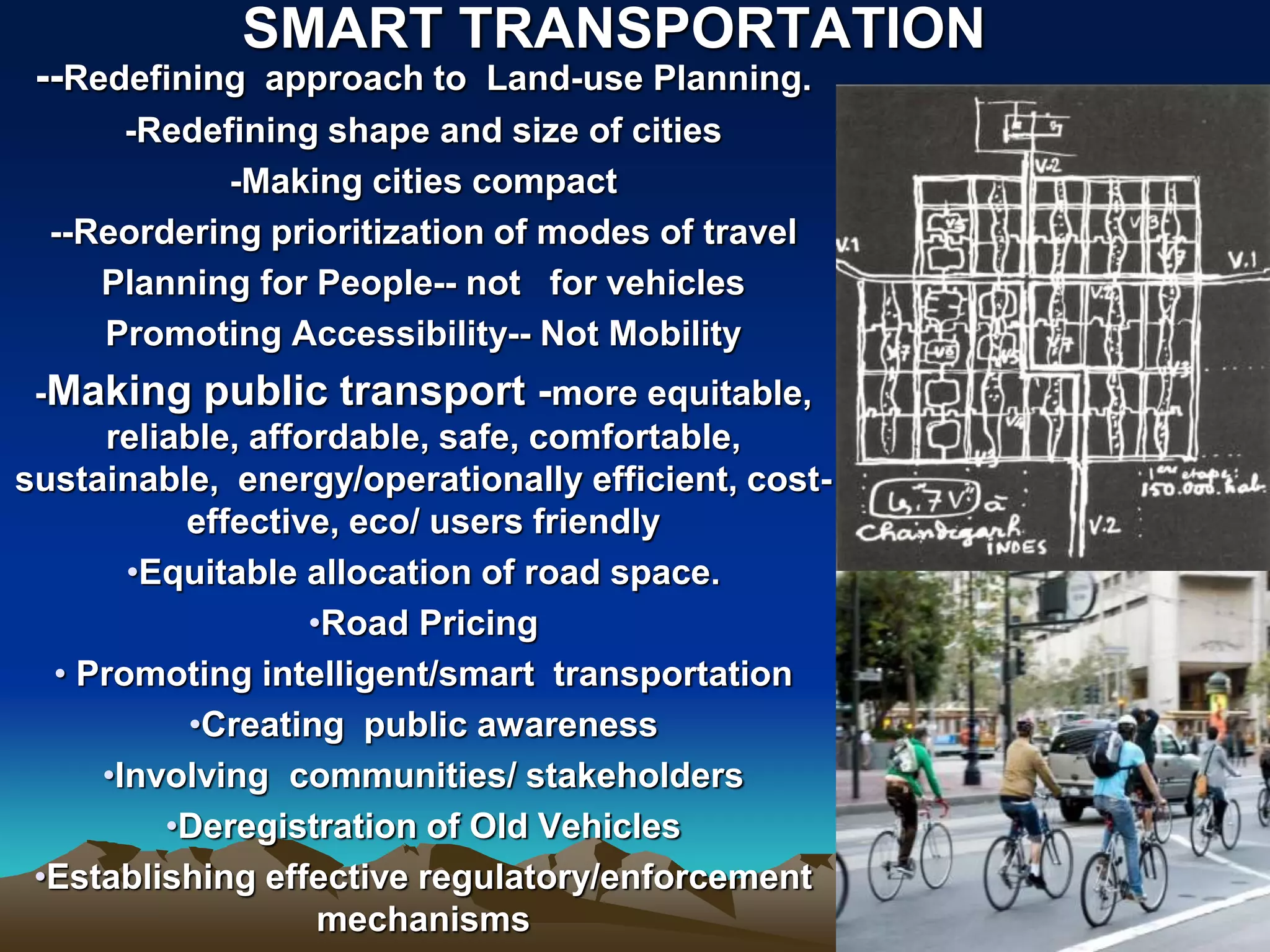
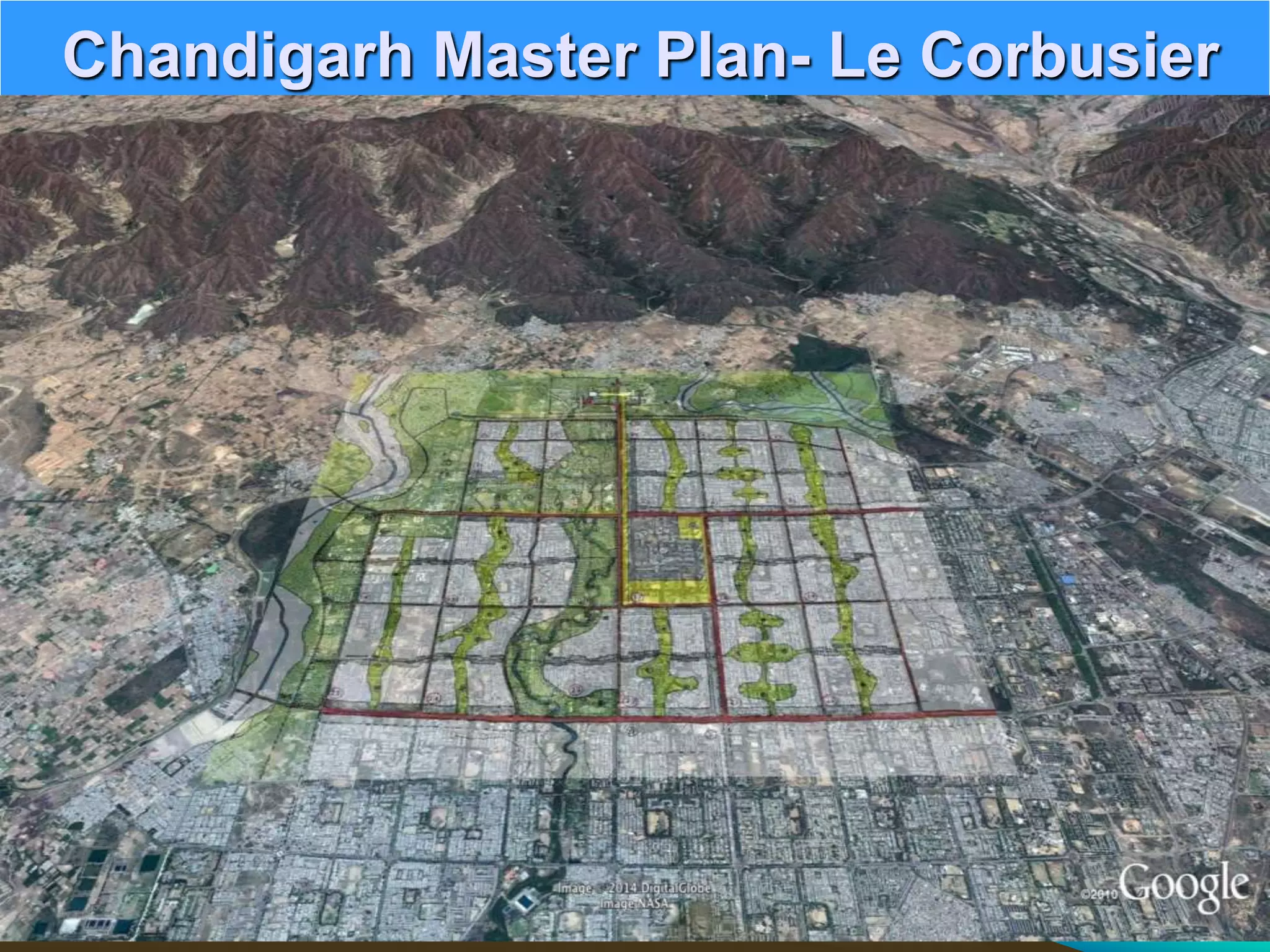
The document discusses the concept of smart cities, highlighting their importance in addressing urban challenges and promoting sustainability. It outlines the rapid urbanization in India, projected population growth, and the need for infrastructure development to accommodate urban growth. The Smart City Mission aims to create citizen-friendly, inclusive urban areas through technological solutions and sustainable planning practices.