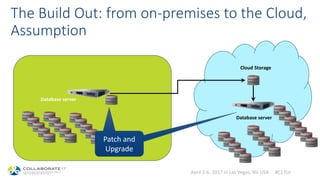
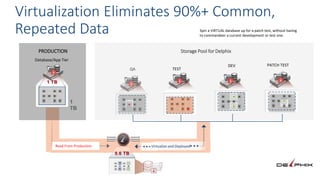
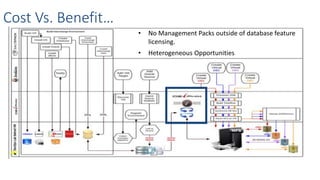
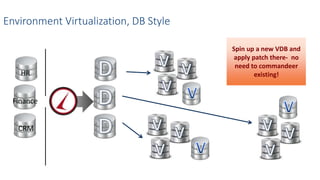
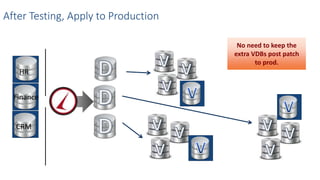
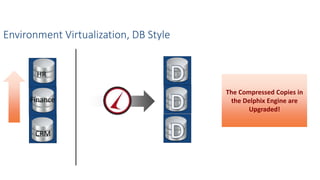
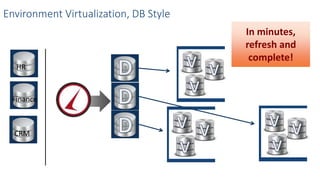
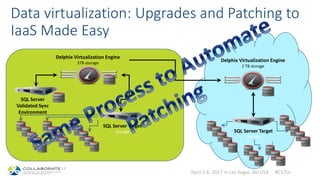
This document discusses patching and upgrading databases with virtualization. Traditionally, patching and upgrading databases requires taking databases offline in each environment, testing the patch, and then applying it to other environments. With virtualization, a virtual copy of the database can be quickly provisioned to test patches without impacting existing environments. After testing, the patch only needs to be applied once to the production environment since other environments are virtual copies automatically refreshed. This approach saves significant time spent patching each environment individually and reduces storage usage by up to 80% by eliminating redundant copies of data.