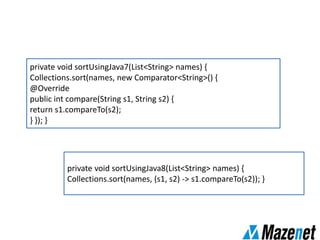
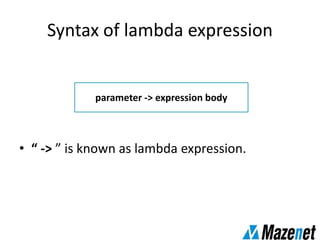
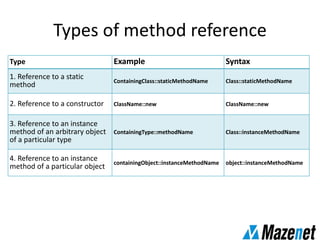
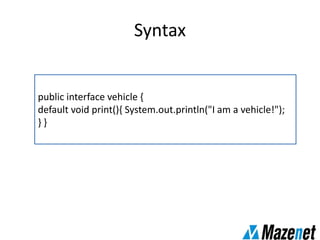
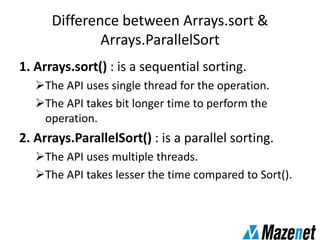
This document summarizes the new features in Java 8, including lambda expressions, method references, functional interfaces, default methods, Optional class, parallel sorting, and Calendar.Builder class. Key changes are more concise coding of sorting and comparison using lambda expressions instead of anonymous classes, ability to reference methods by name, default interface methods to add functionality without changing existing classes, and parallel sorting to improve performance on large arrays.