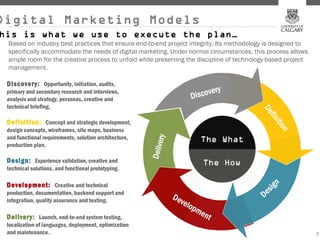
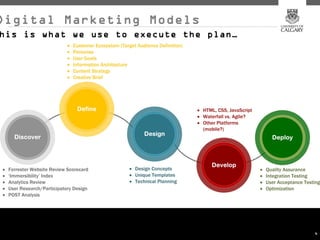
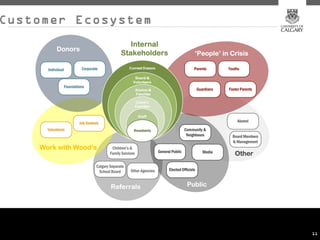
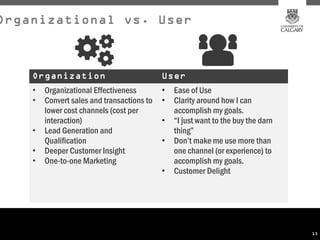
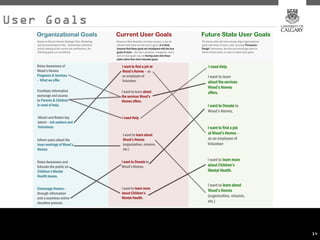
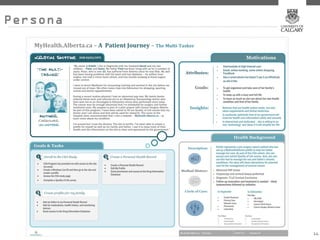
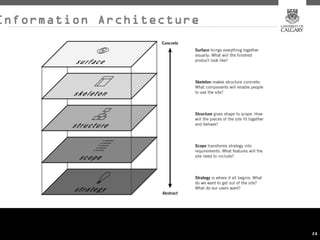
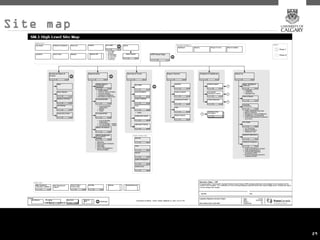
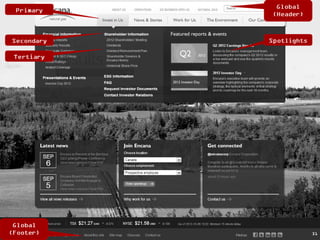
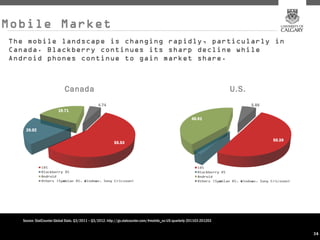
This document provides an overview of key concepts for digital marketing including how to frame a digital marketing plan, common digital marketing models, using analytics to understand website usage, defining target audiences, understanding user goals through personas, mapping the customer journey, and developing an effective content strategy. The digital marketing models section outlines the discovery, definition, design, development, and delivery phases commonly used to execute digital marketing plans. Analytics, target audiences, personas, customer journeys, and content strategy are discussed as important elements for informing digital marketing strategies and optimizing the customer experience.