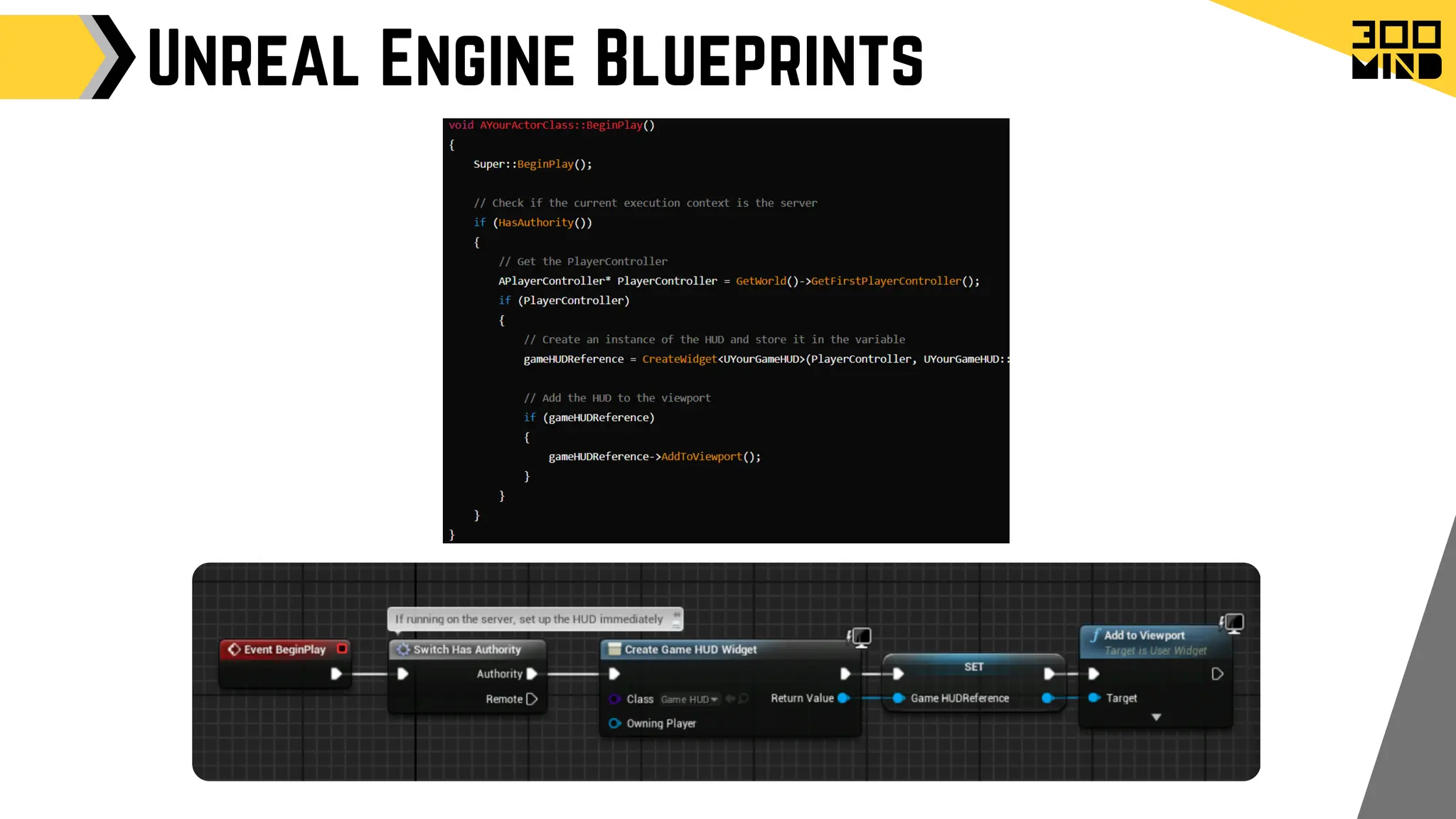
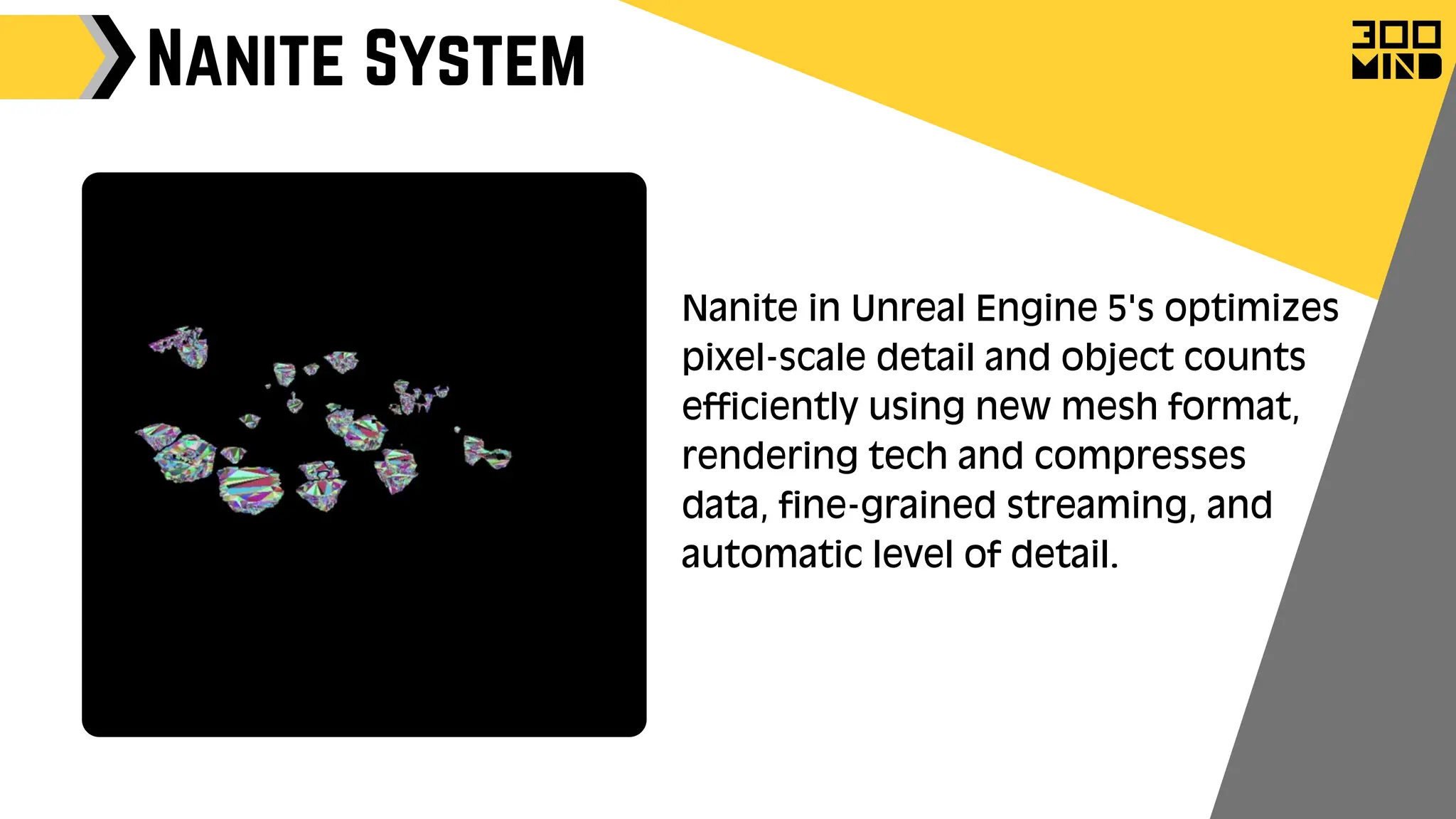
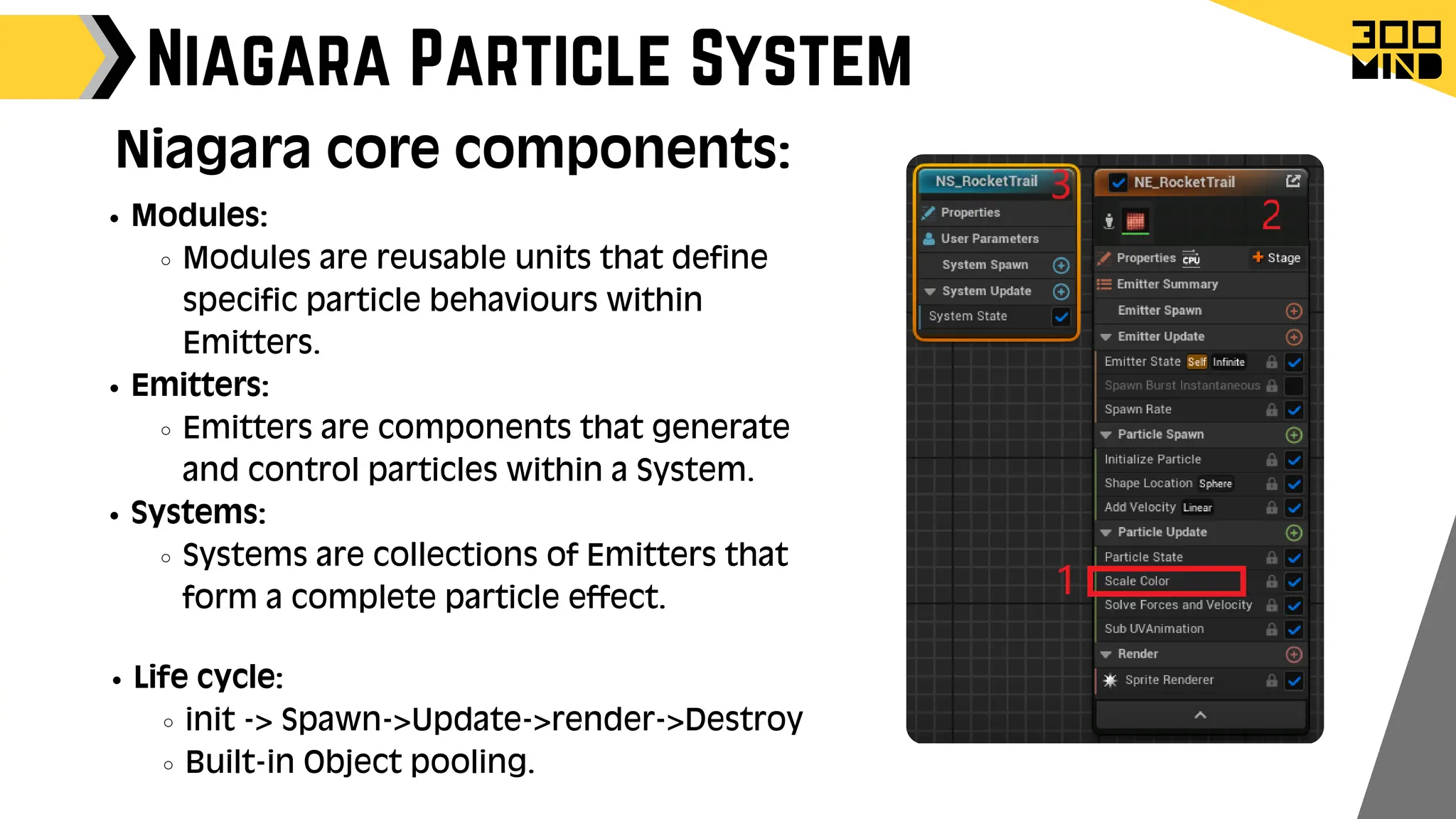
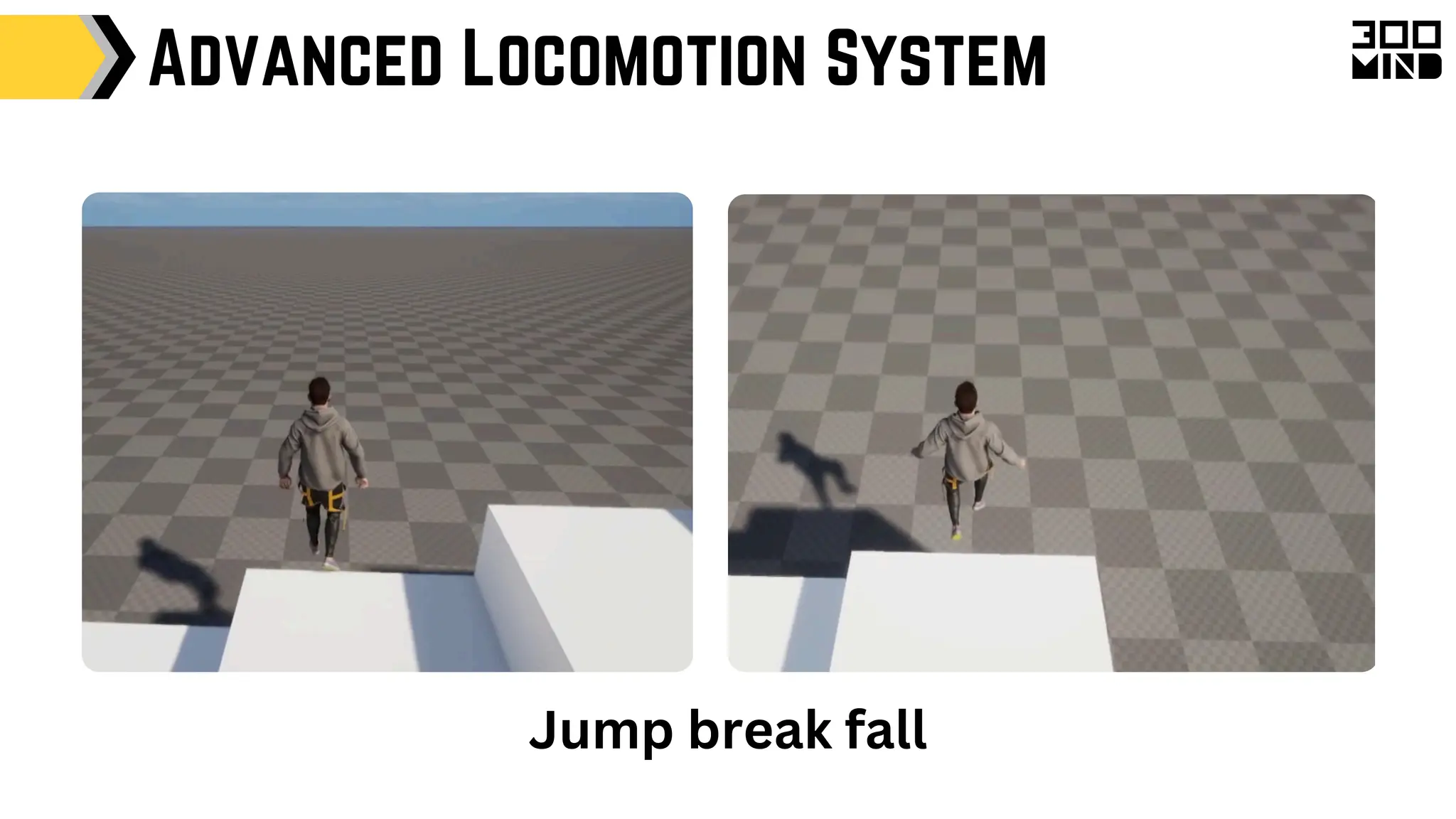
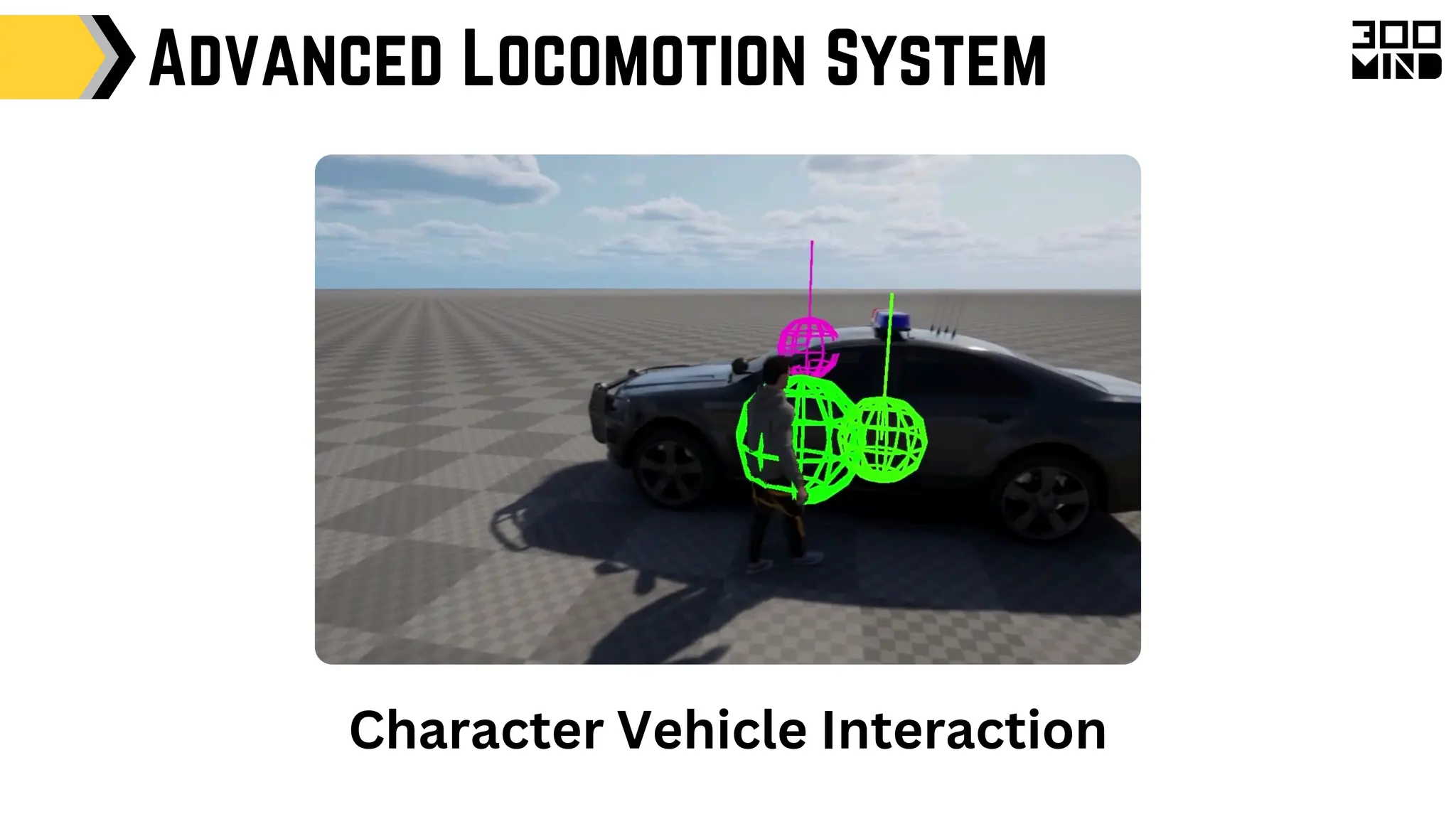
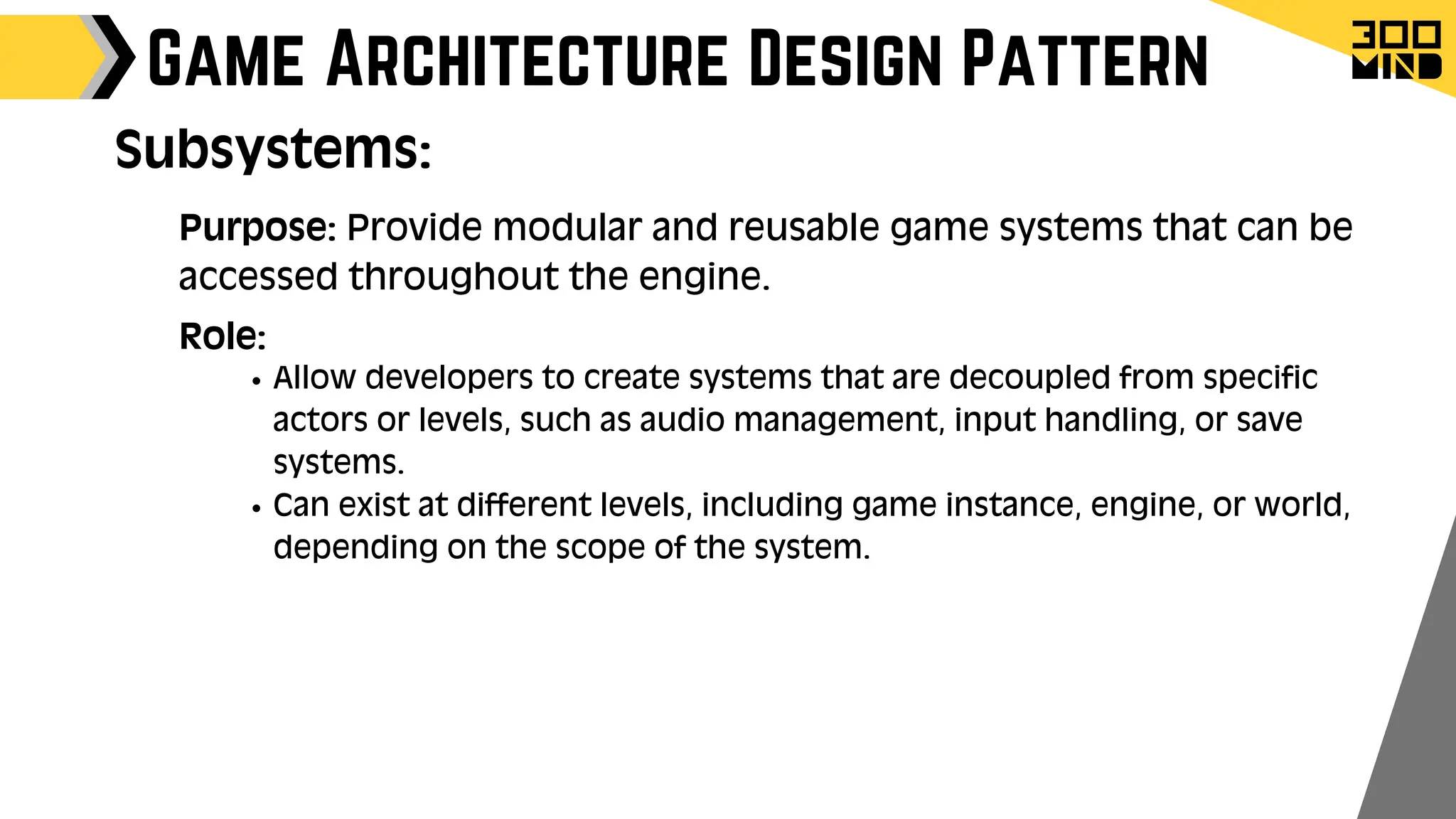
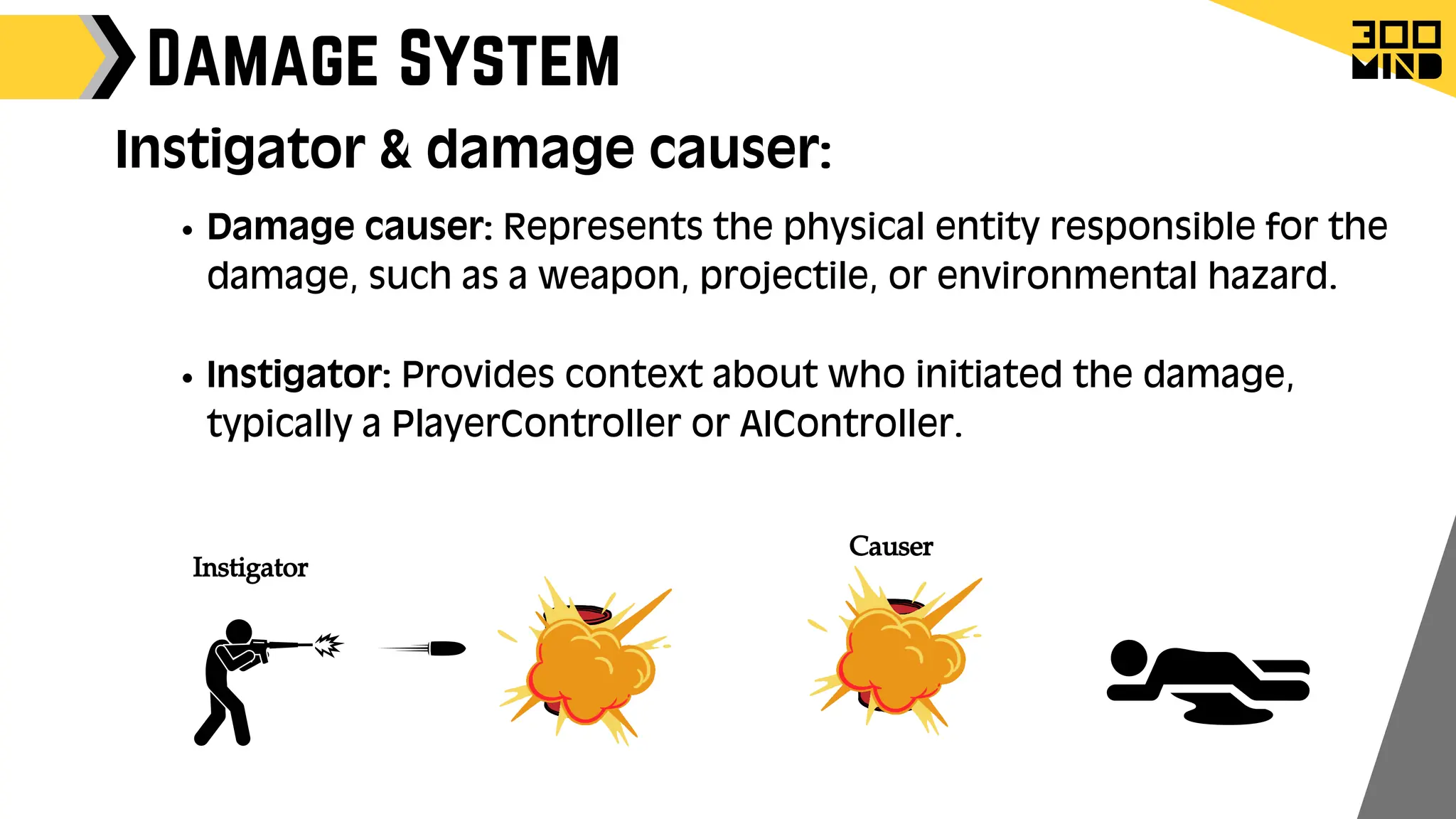
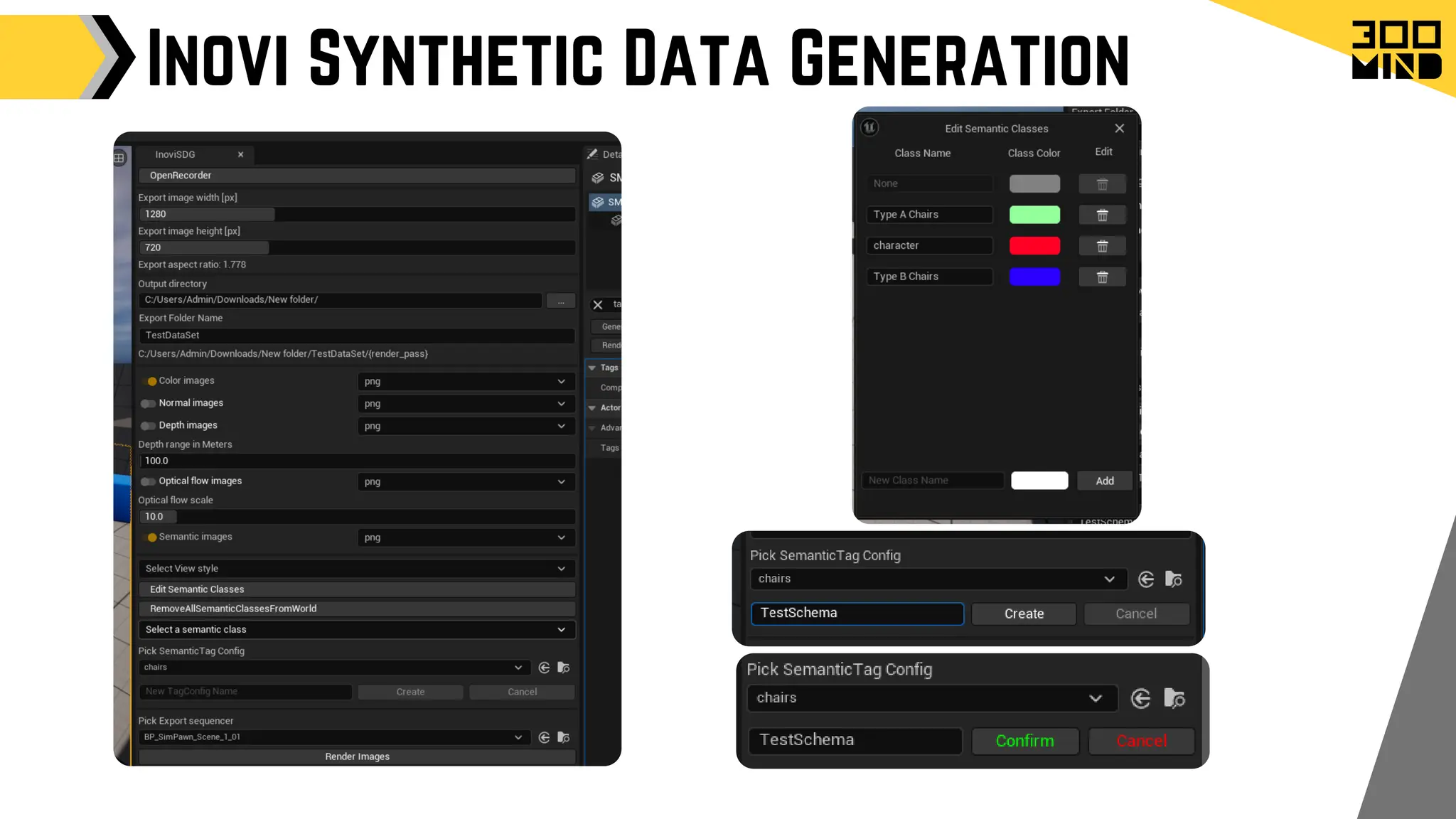
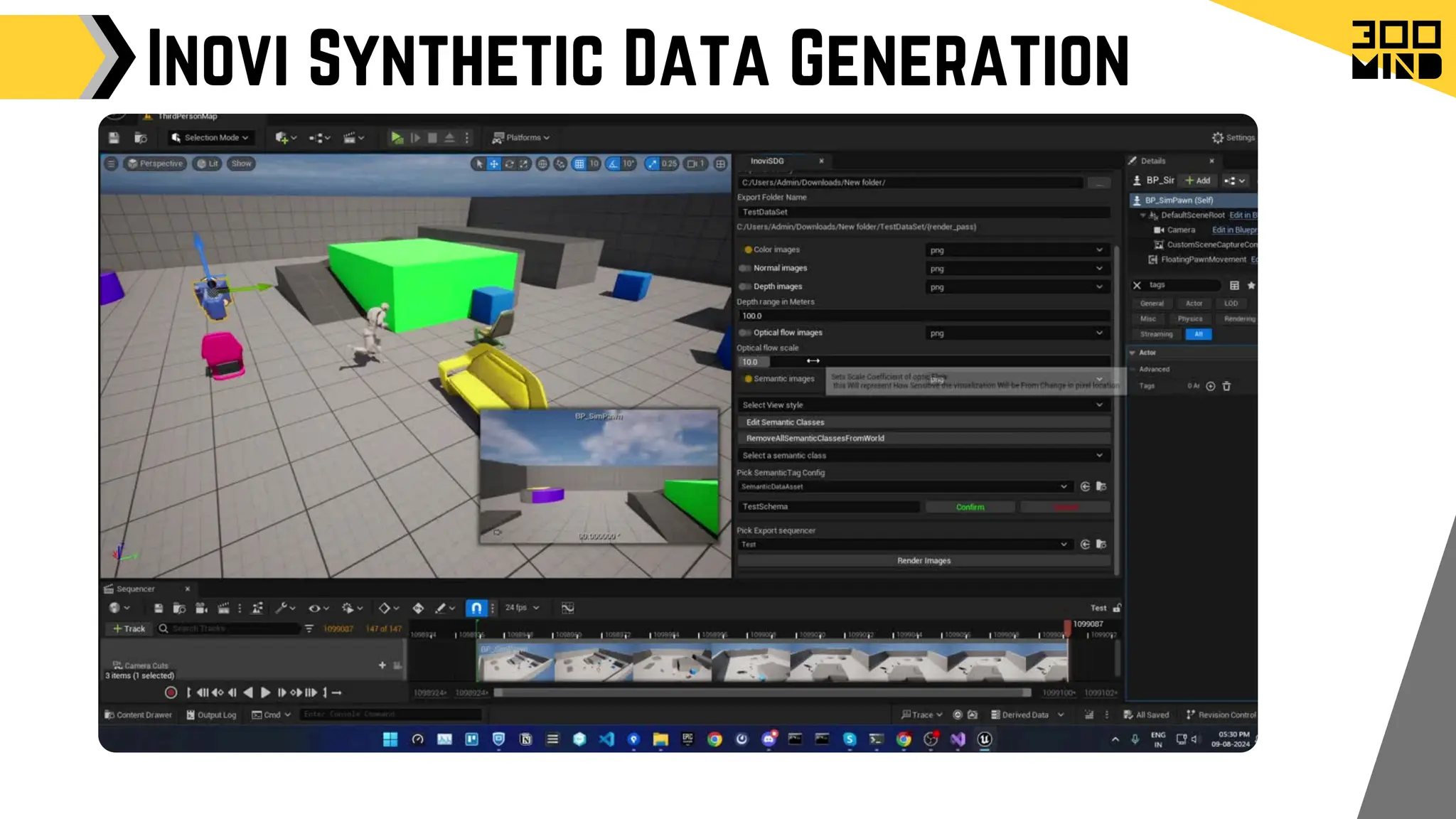
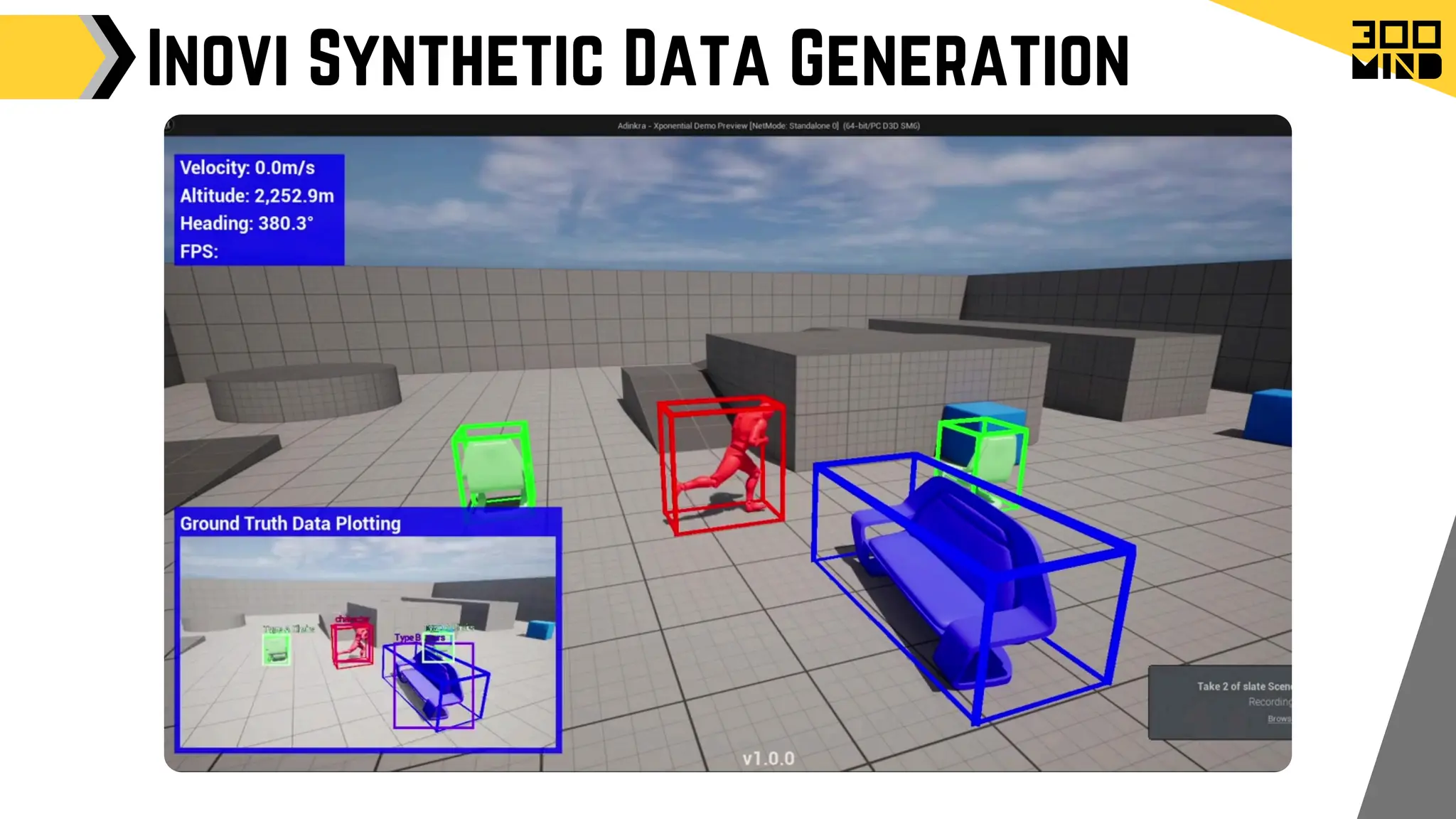
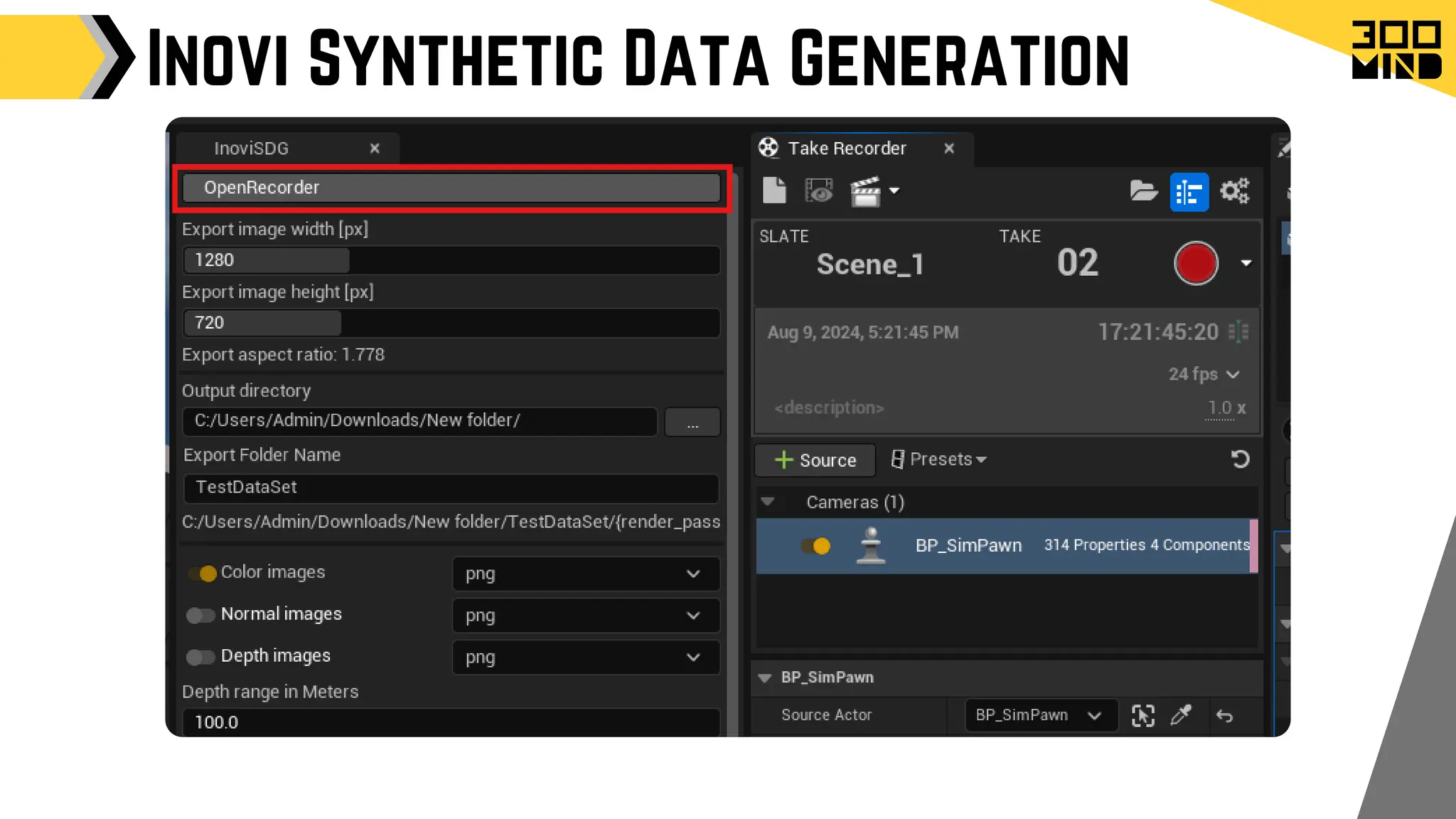
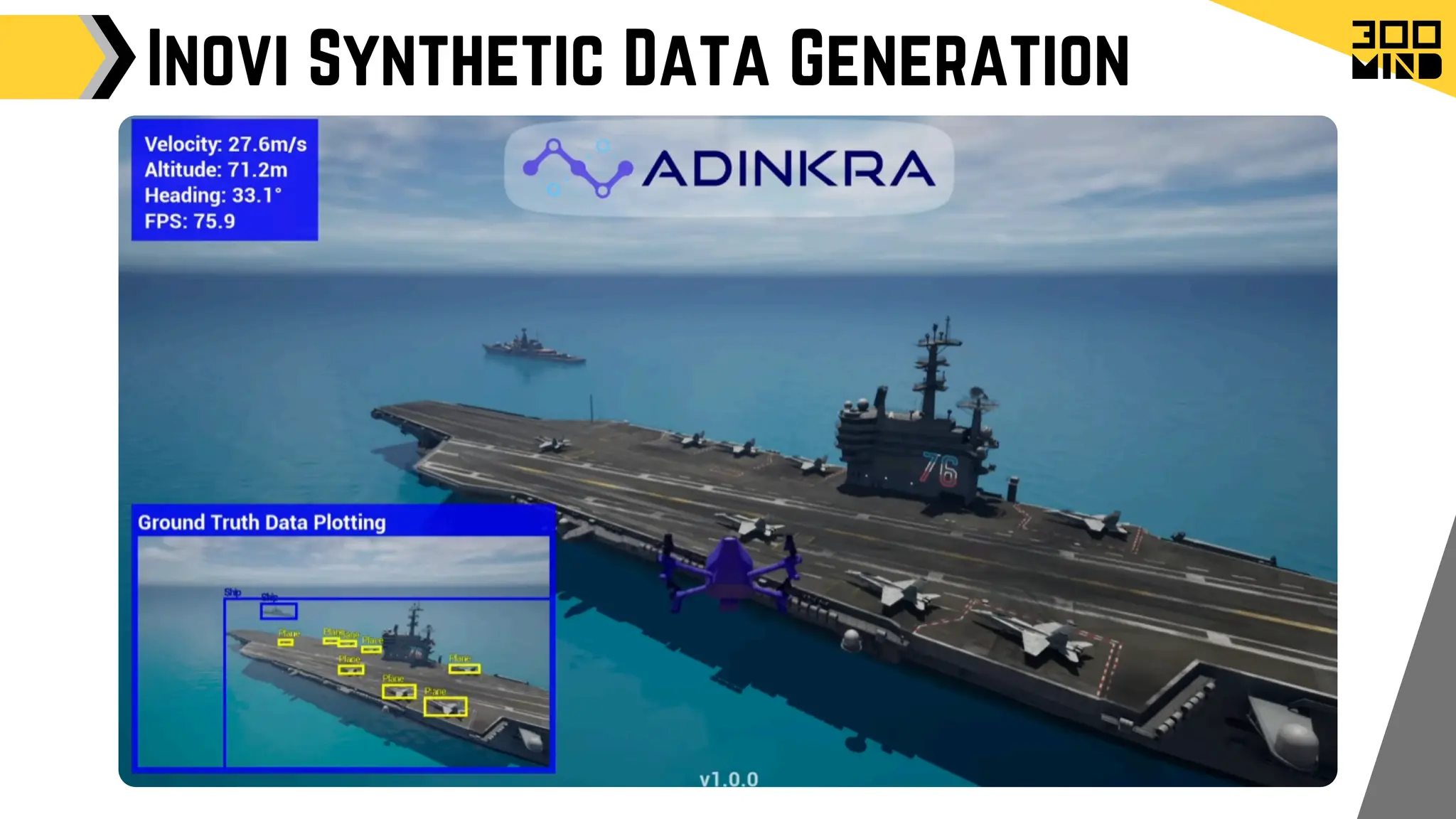
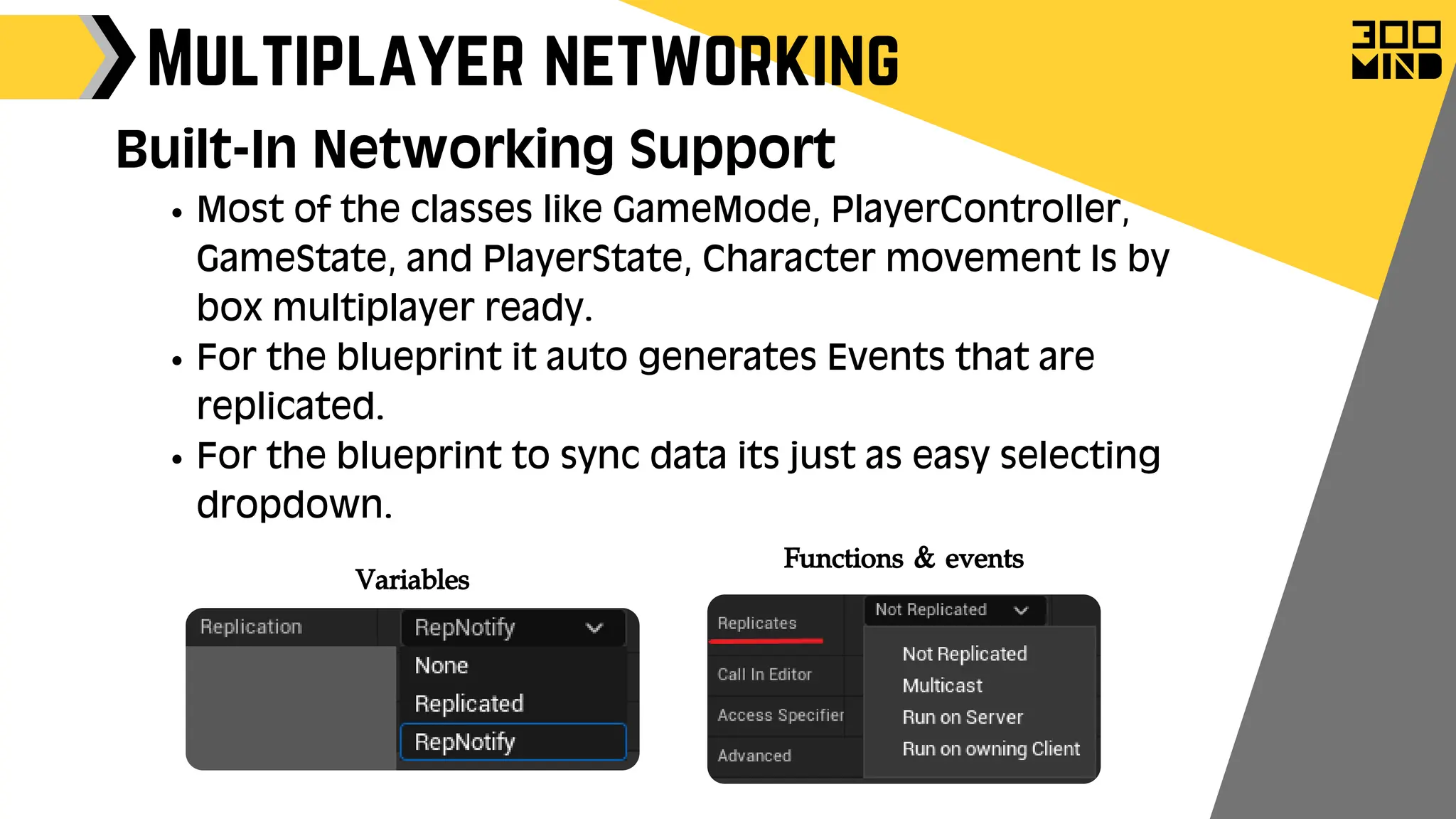
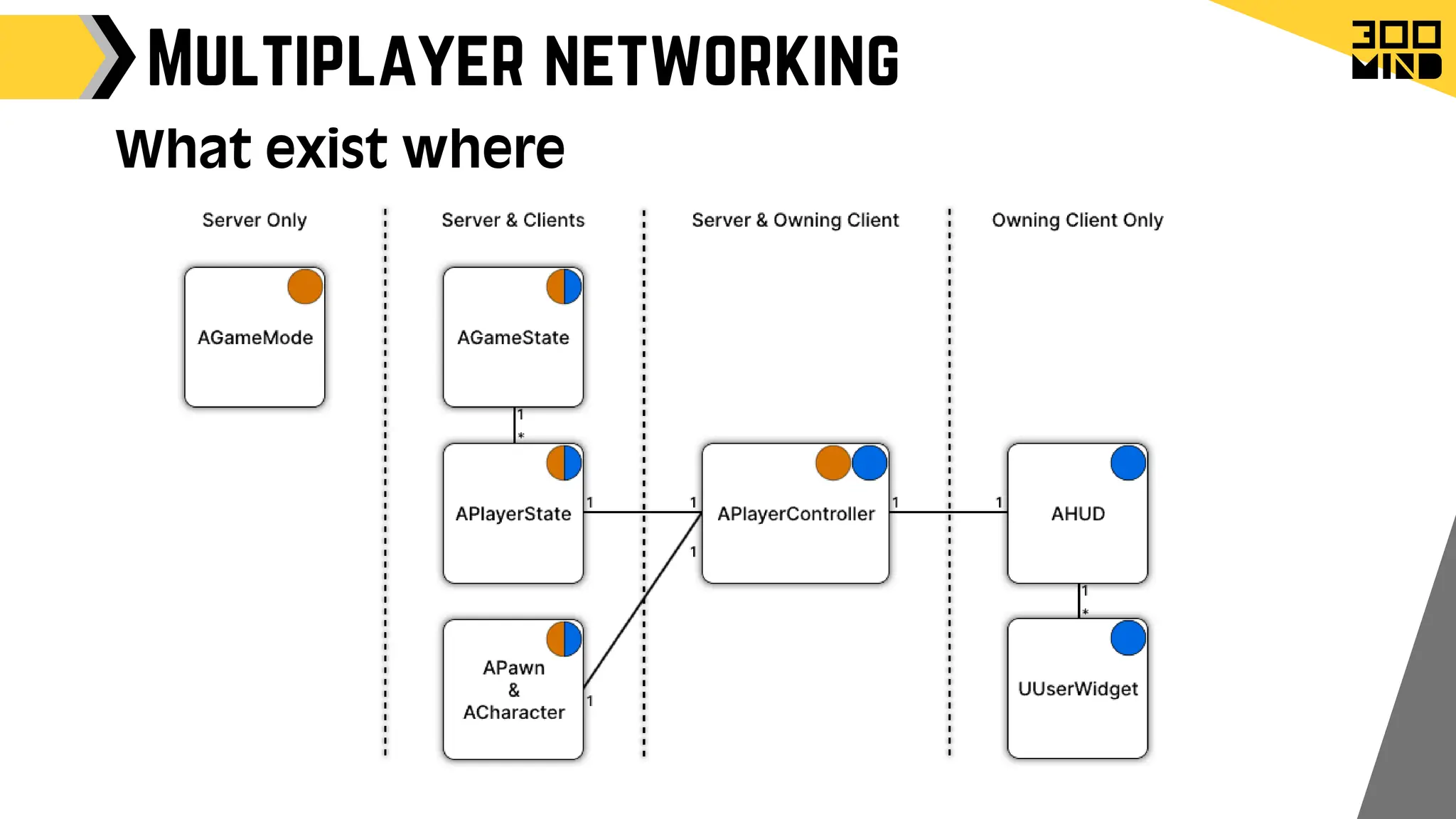
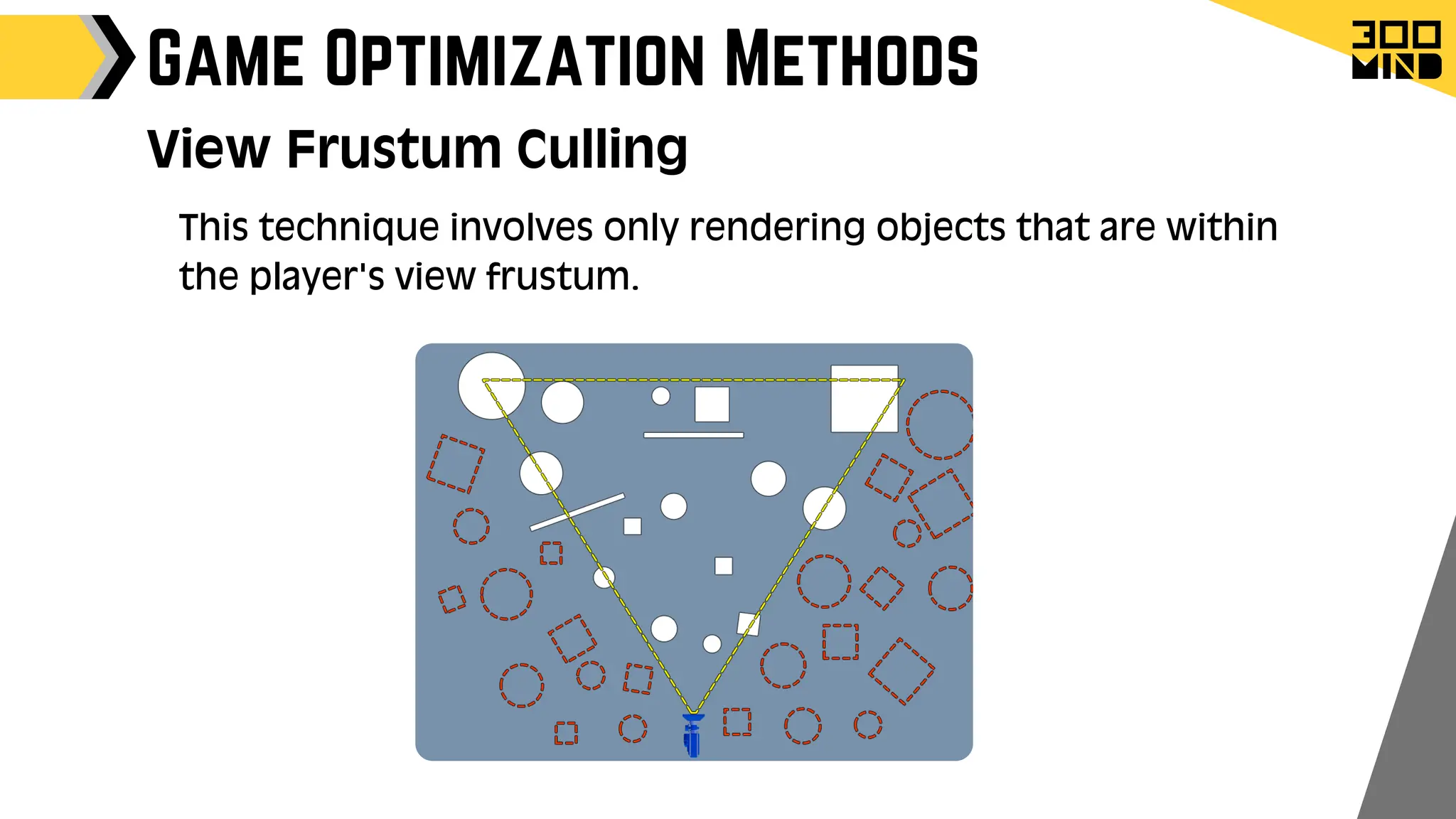
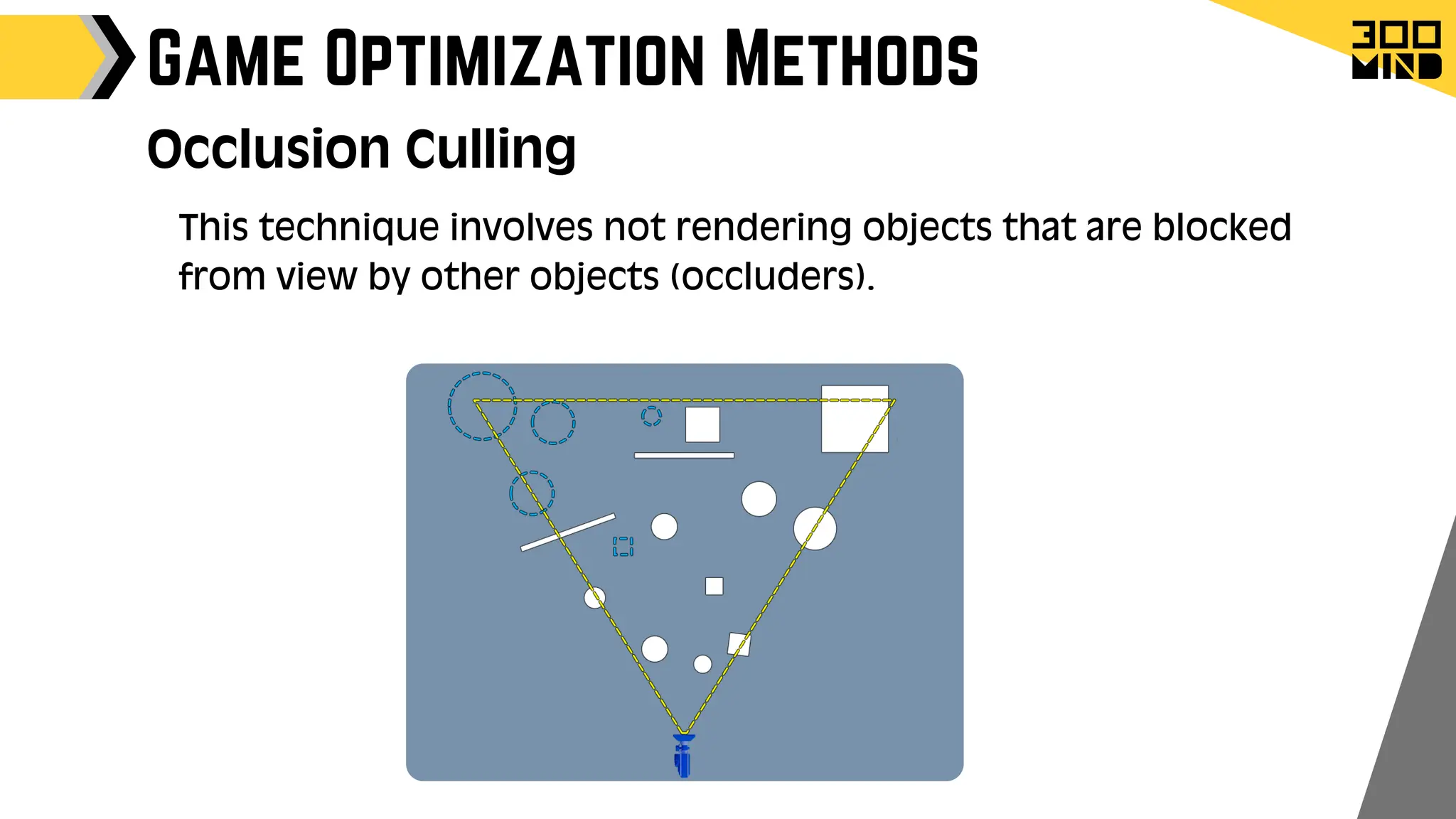
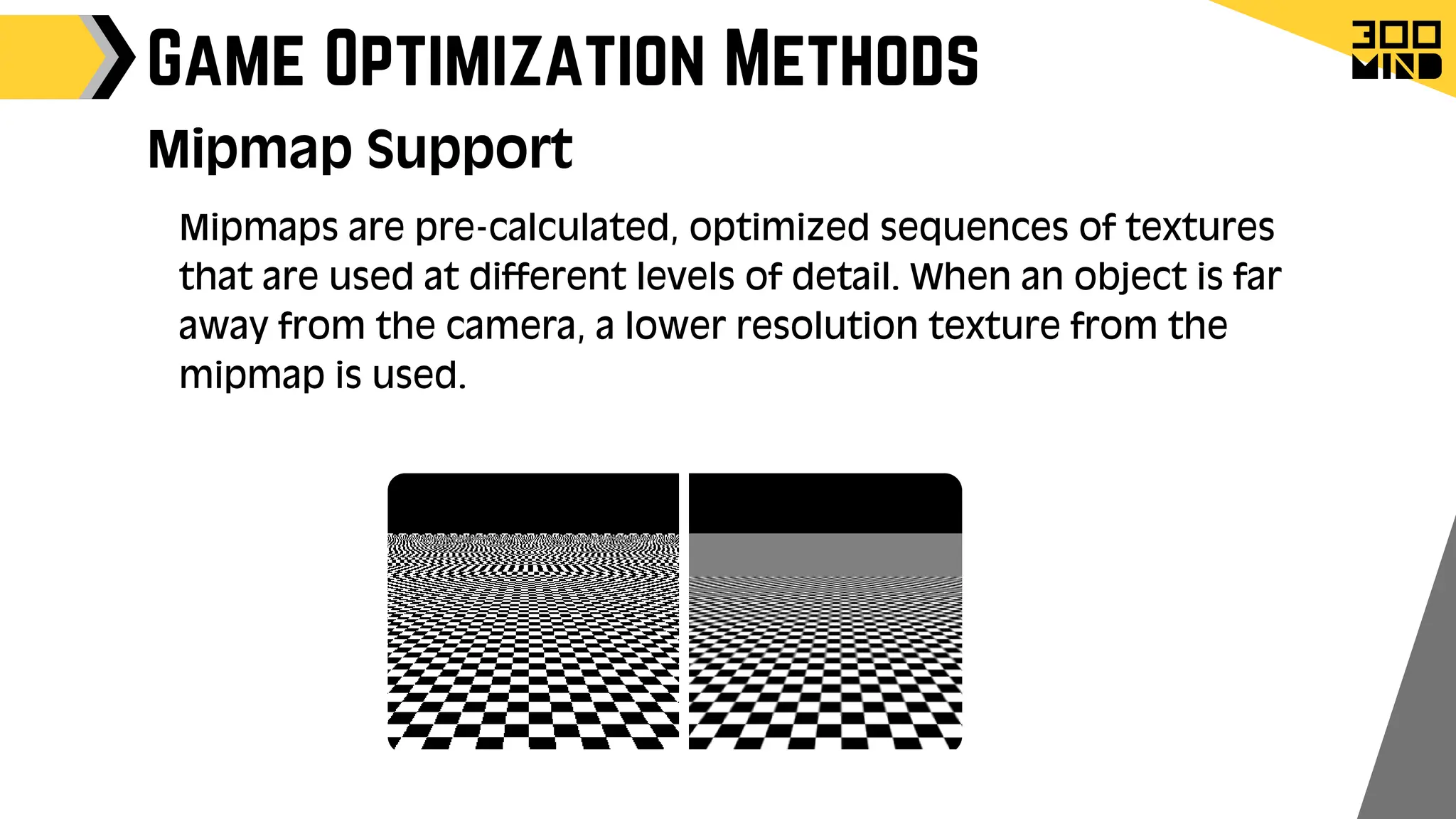
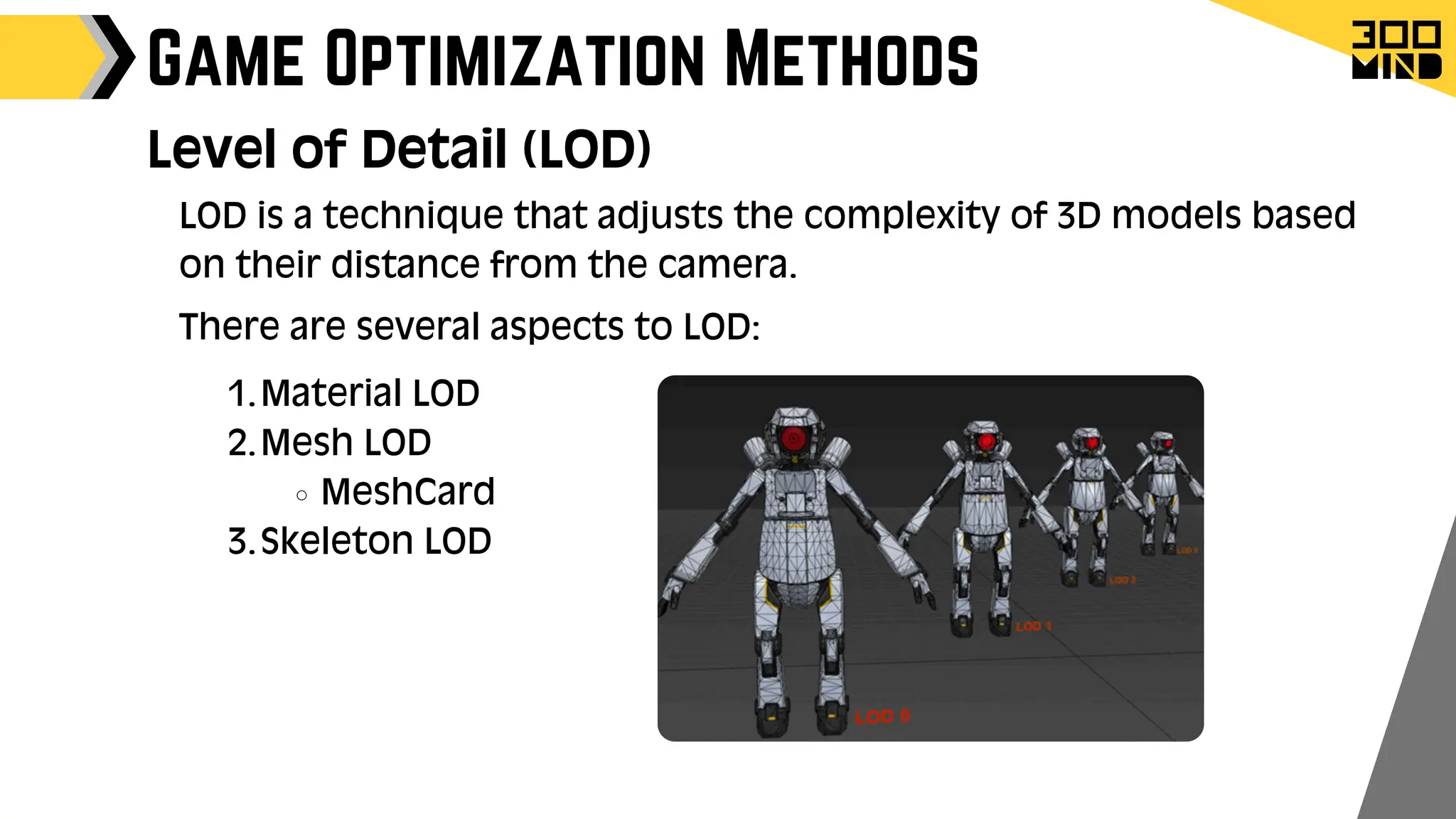
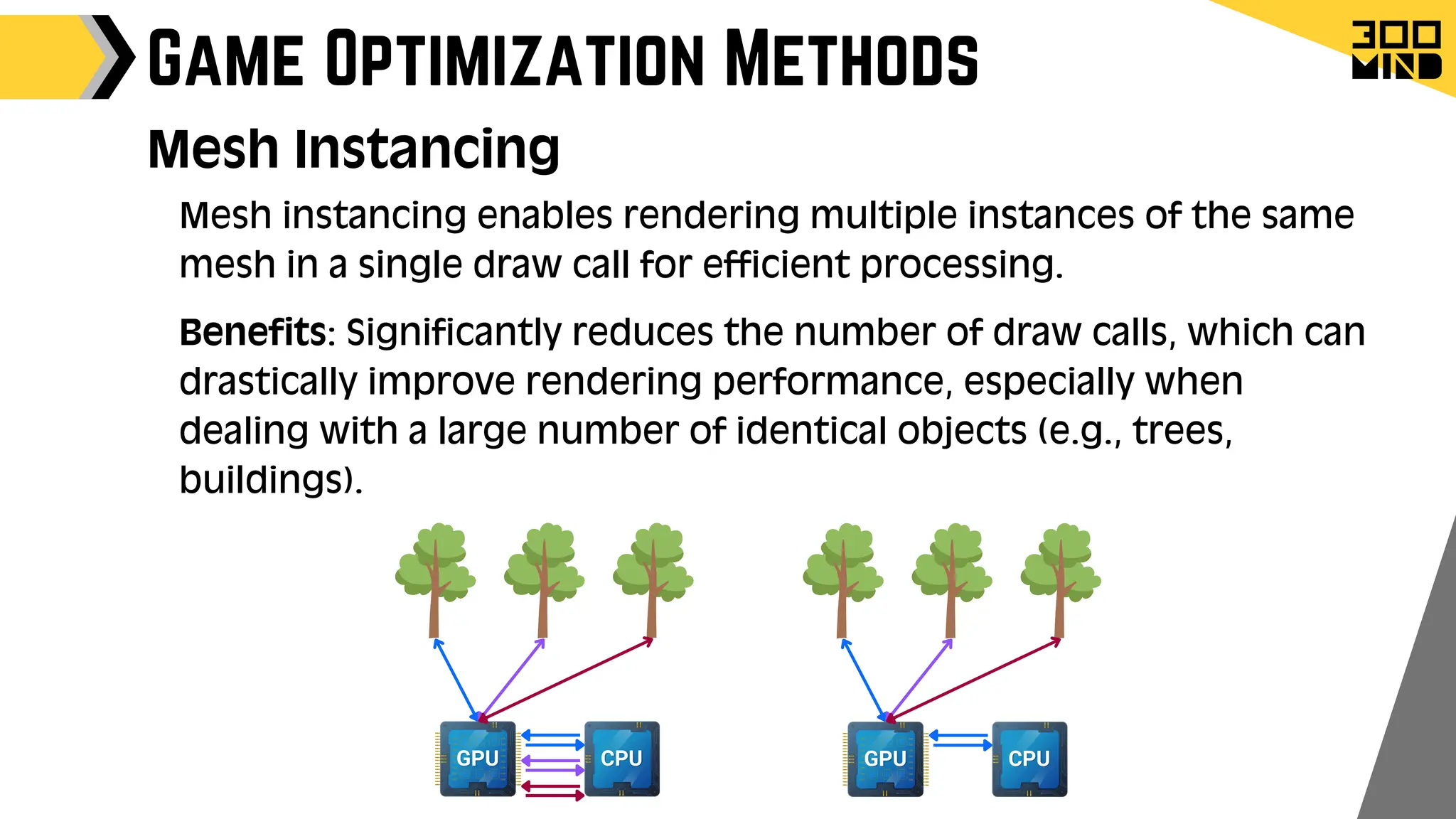
The document outlines the capabilities and features of Unreal Engine, focusing on tools such as Blueprints for visual scripting, Lumen for dynamic global illumination, and Nanite for high-detail geometry without performance constraints. It also discusses various game architecture design patterns, multiplayer networking, damage systems, and optimization techniques for enhancing game performance. Additionally, it highlights the use of synthetic data generation and advanced locomotion systems to improve game development and player experience.