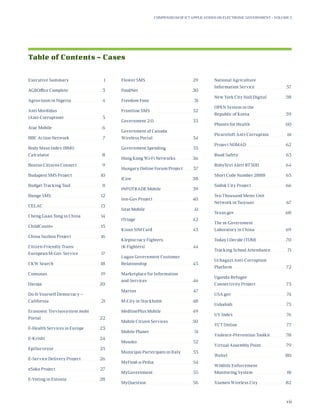
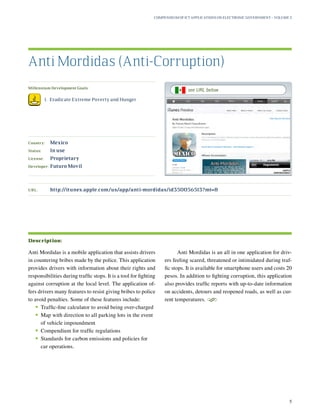
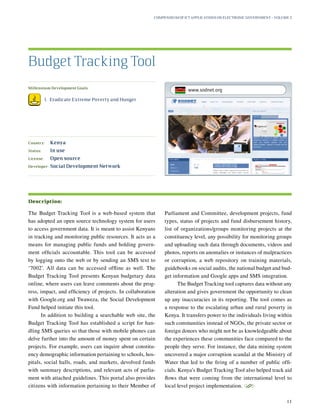
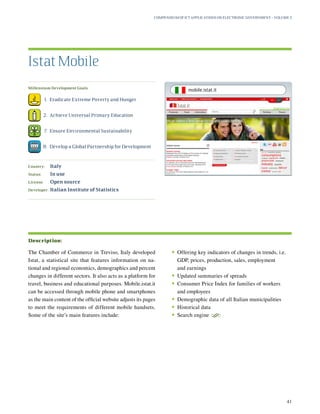
This document provides a summary of the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UNDESA) Compendium of ICT Applications on Electronic Government Volume 3: Mobile Applications on Citizen Engagement. It discusses how mobile technologies can enhance citizen engagement and support efforts towards achieving the Millennium Development Goals. The compilation surveys a broad range of current ICT applications from different world regions that demonstrate how mobile phones and other portable devices are being used for e-government services and citizen participation. The goal is to stimulate further development of tailored e-government solutions to better meet citizens' needs.