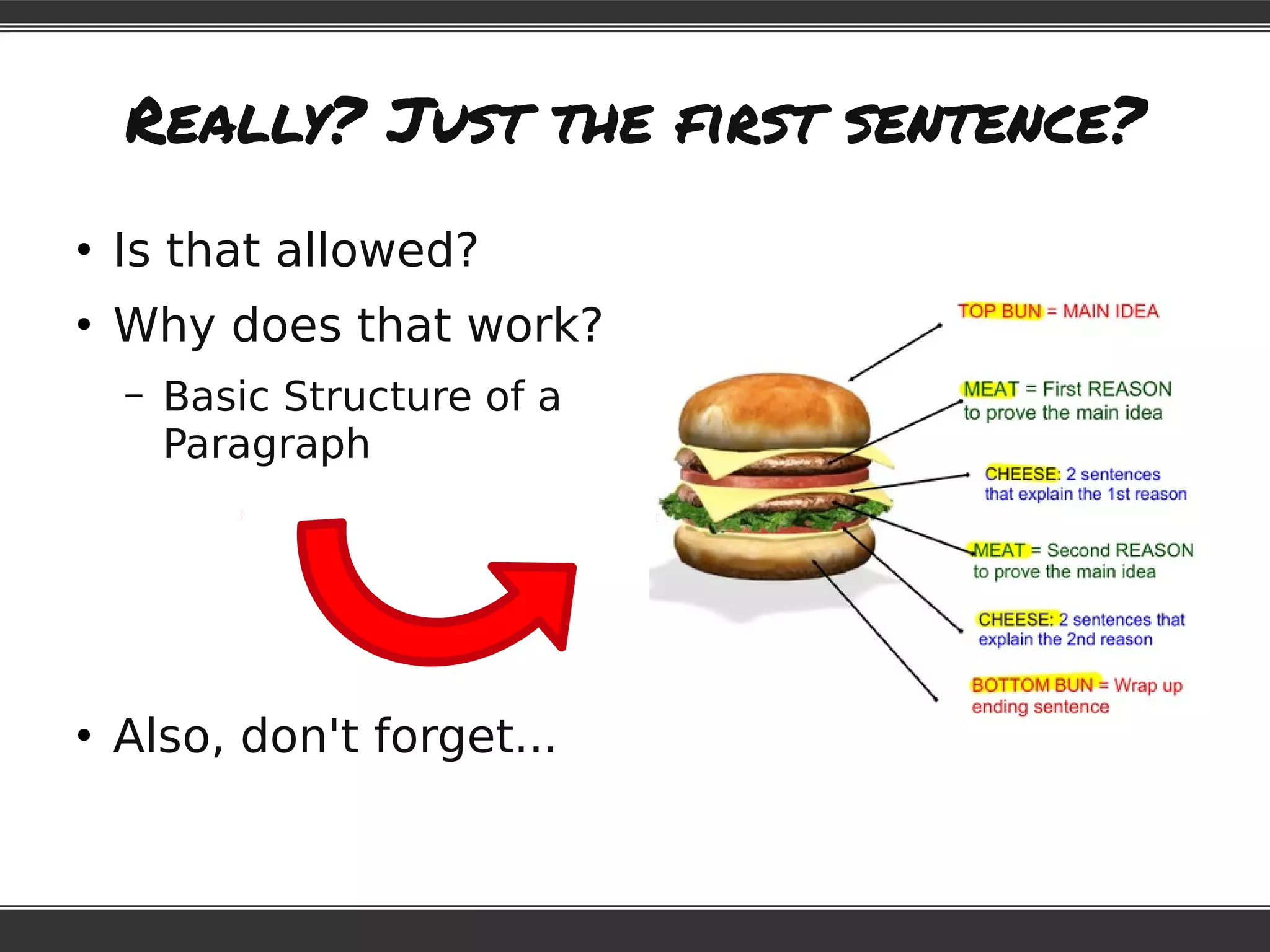
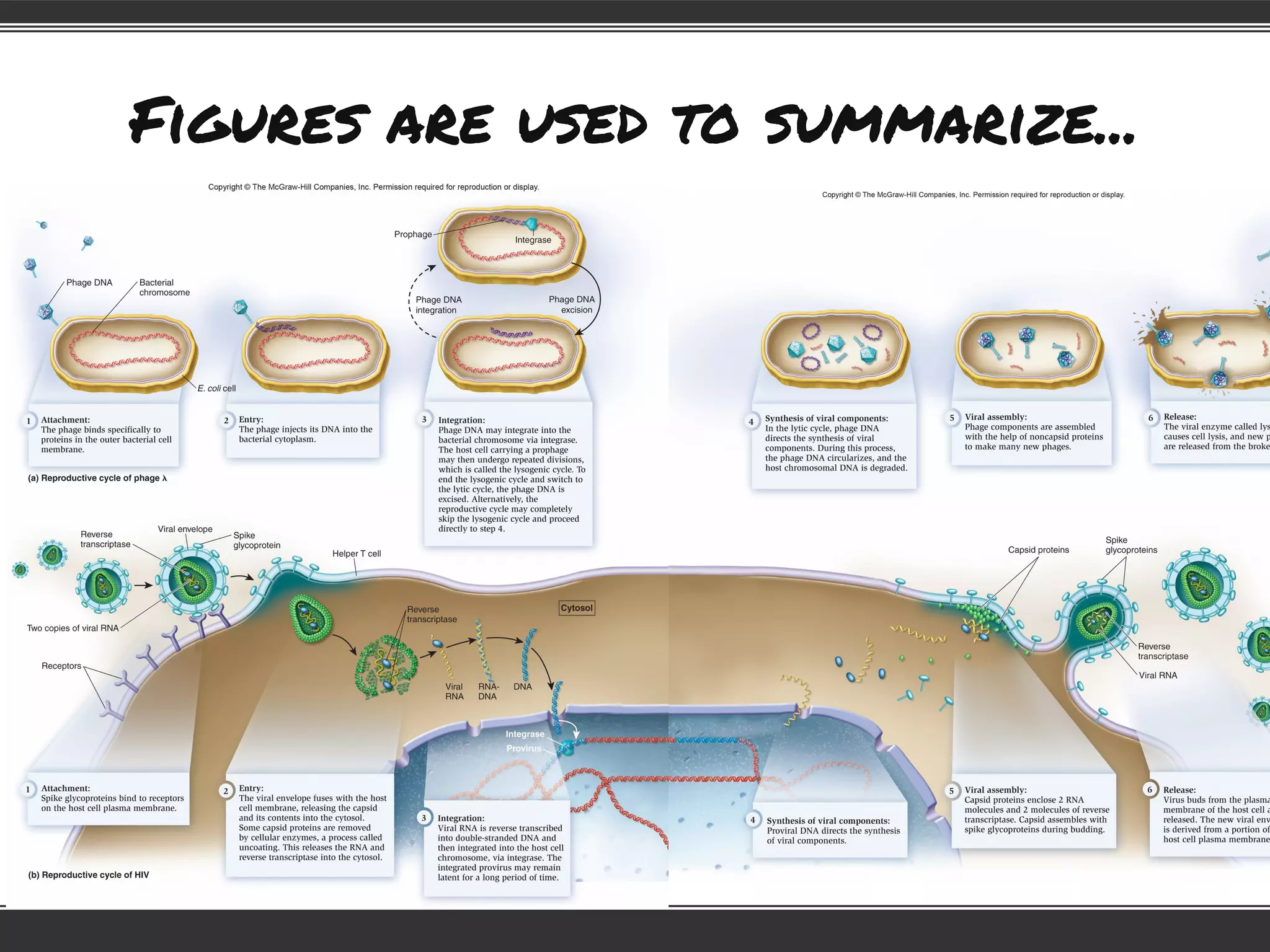
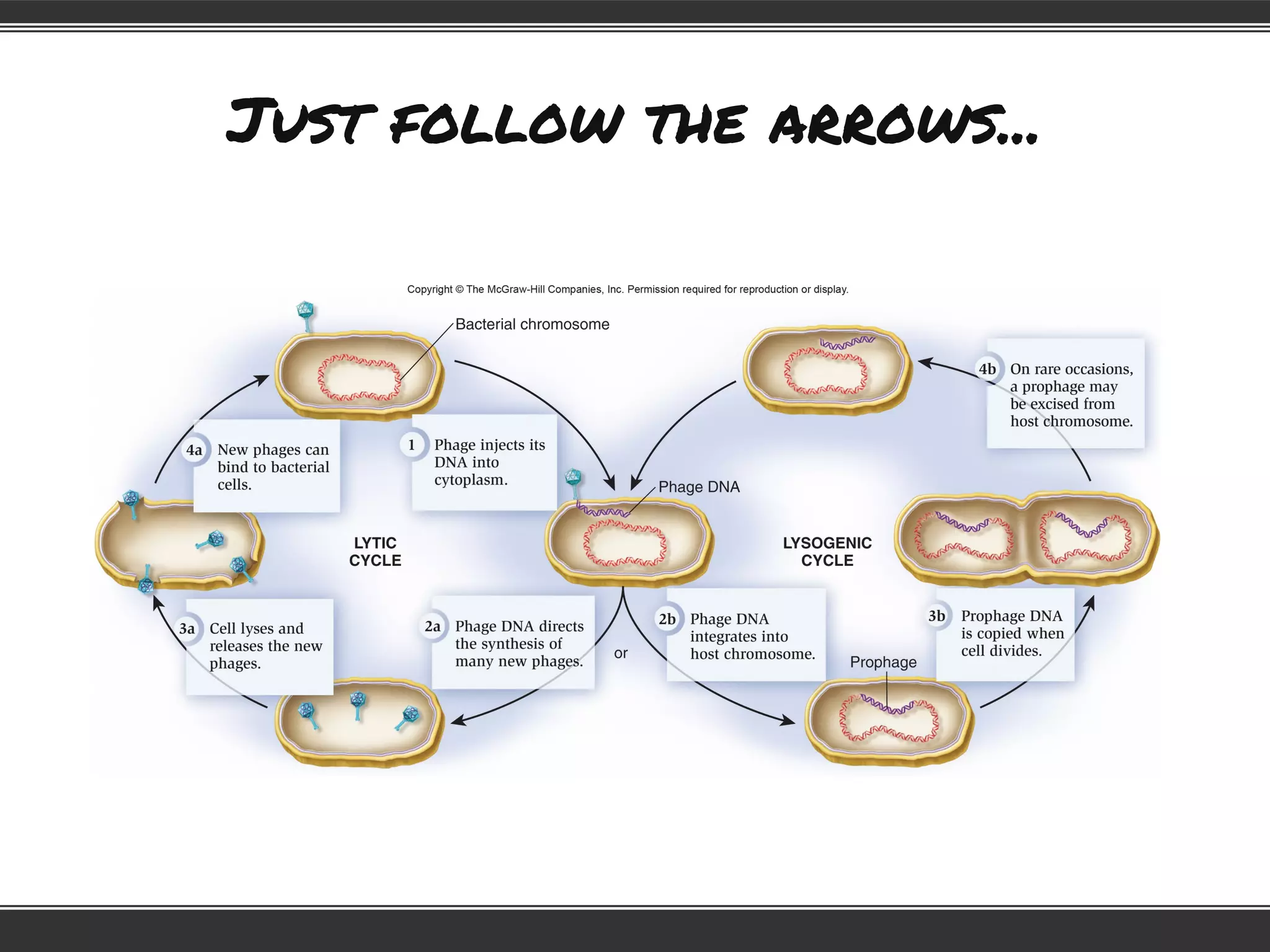
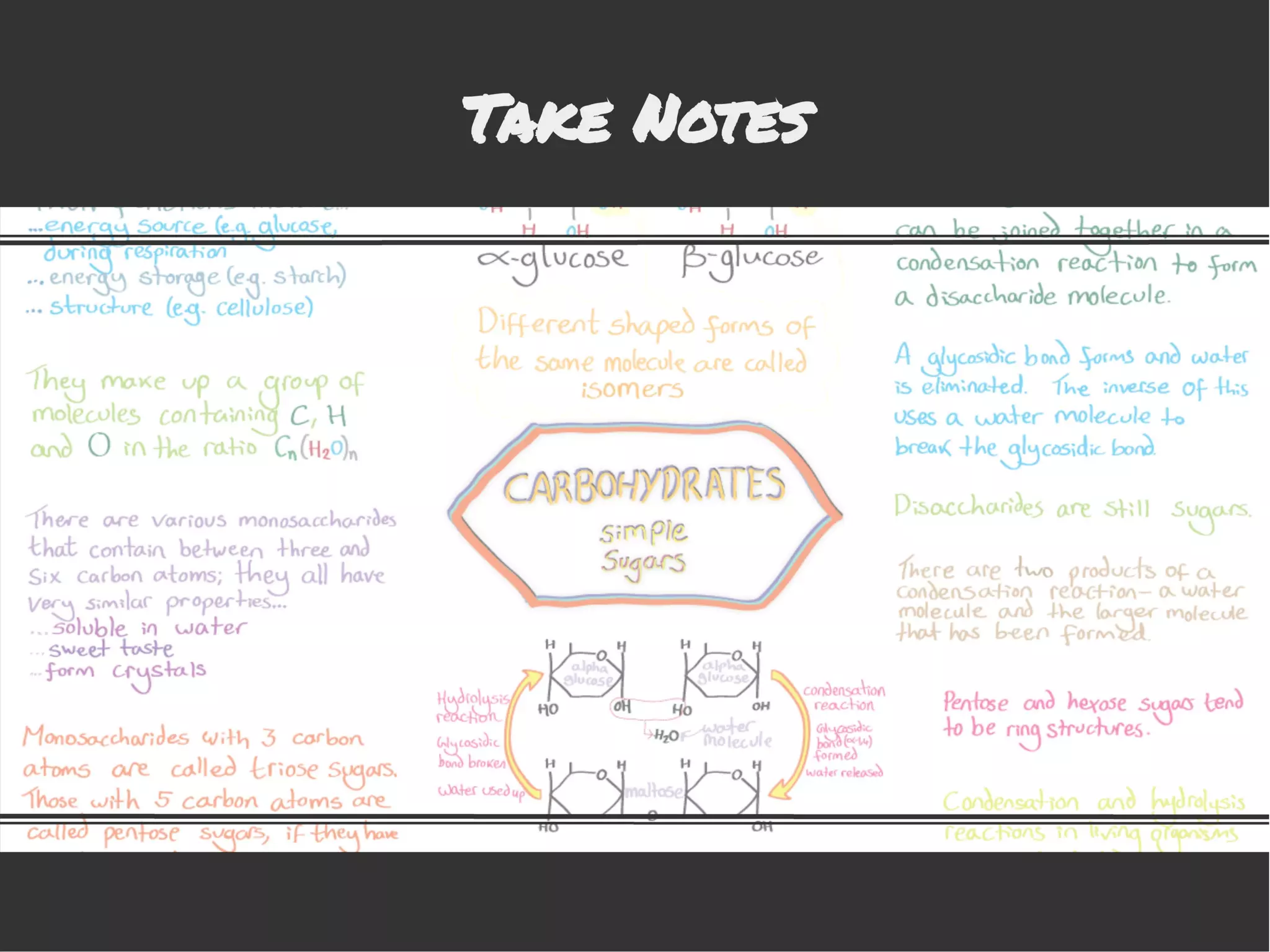
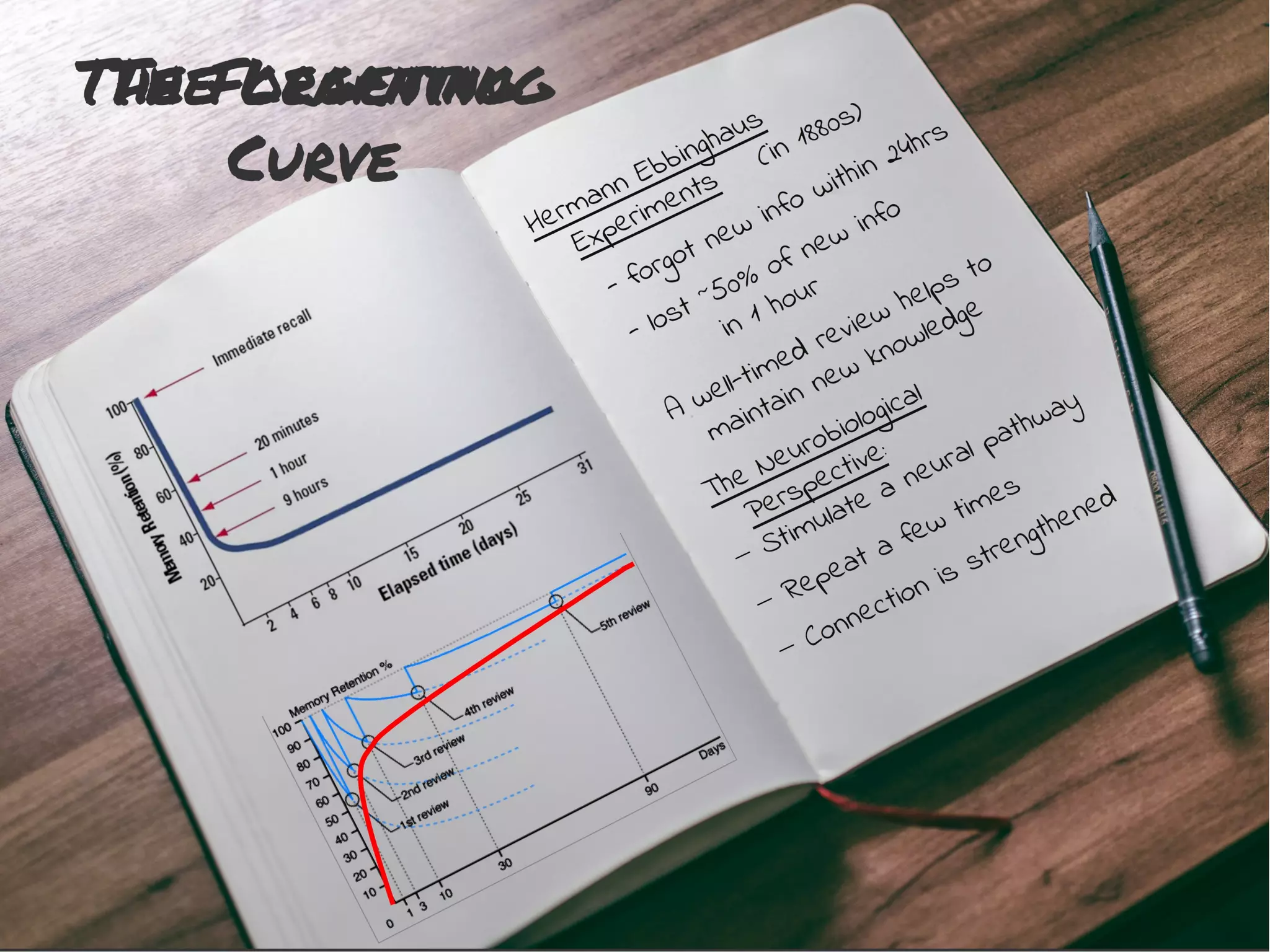
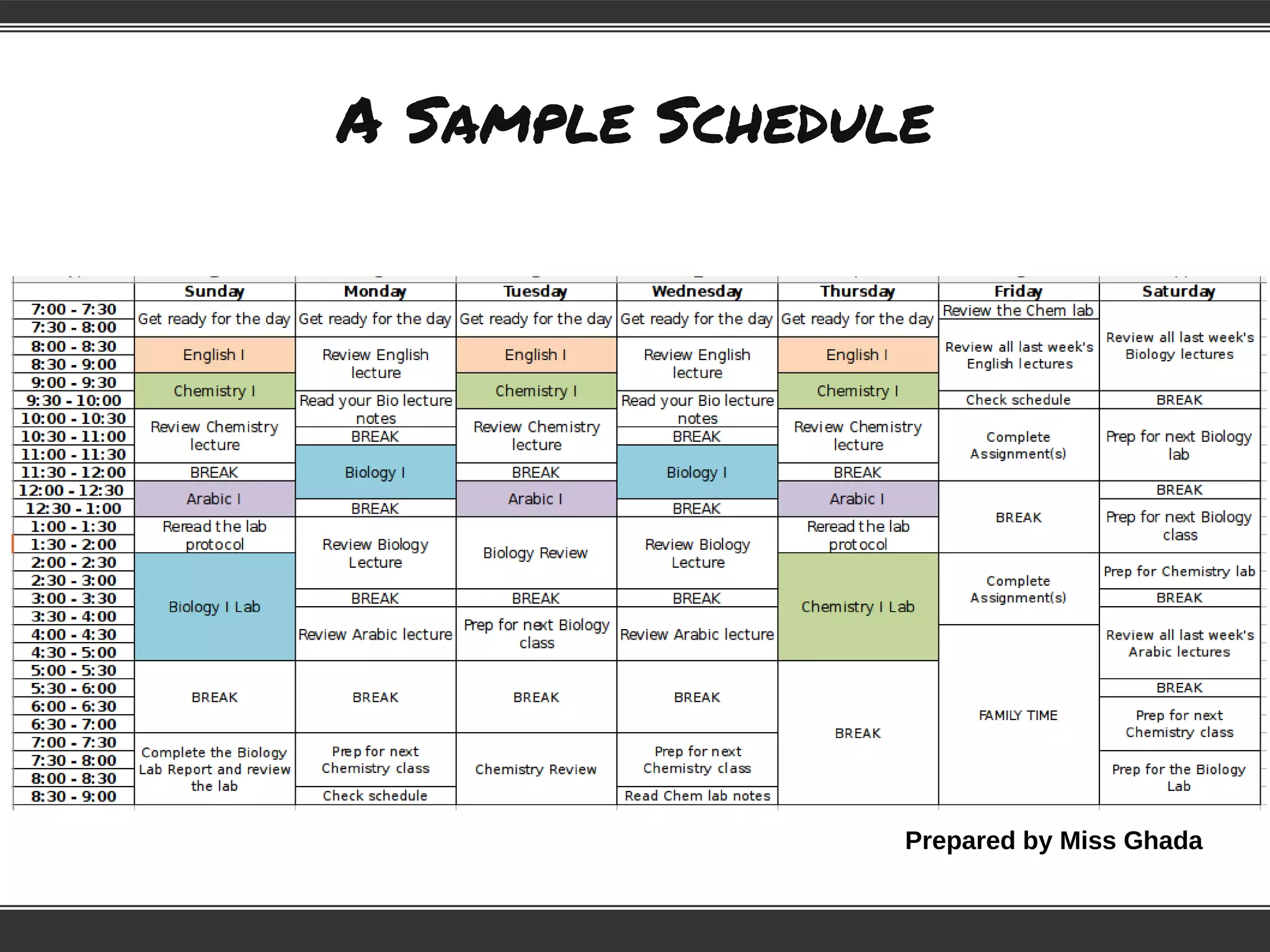
This document provides information to help students adjust to the differences between high school and university classes. It notes that high school teachers are trained to help students learn while university professors are experts in their field. It advises students that they will need to work harder to keep up in university, where lectures assume students have done necessary preparation. The document emphasizes that students need to study, and offers tips for effective studying like preparing for lectures, taking good notes, reviewing notes, and creating a study schedule.