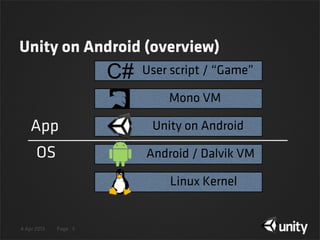
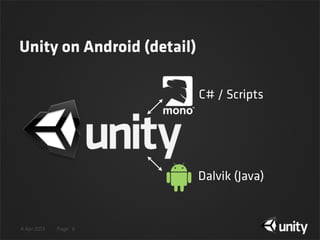
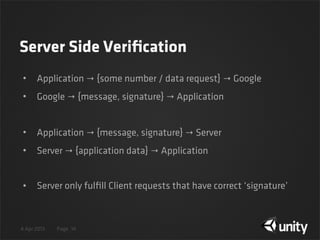
The document discusses various techniques for protecting Android content in Unity games, including authentication with Google Play Licensing, application tampering detection through signature and code checking, code obfuscation, and encryption of PlayerPrefs and other sensitive game data using encryption with a user-specific key. The agenda covers licensing, tamper detection through signature and code integrity checks, obfuscation, and encryption of game data in PlayerPrefs.















![4 Apr 2013 Page
Check the APK signature (Java)
19
// Retrieve the PackageManager and packageName (i.e. 'com.Company.Product')
Activity activity = com.unity3d.player.UnityPlayer.currentActivity;
PackageManager manager = activity.getPackageManager();
String name = activity.getPackageName();
// Fetch APK signature(s)
PackageInfo packageInfo = manager.getPackageInfo(name, PackageManager.GET_SIGNATURES);
Signature[] signatures = packageInfo.signatures;
// Process signatures (i.e. check their validity)
for (Signature signature : signatures)
{
Log.i("signature", signature.toCharsString());
Log.i("signature hash", Integer.toHexString(signature.hashCode()));
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/doneprotectingyourandroidcontenterikhemming-130522210218-phpapp01/85/UniteKorea2013-Protecting-your-Android-content-19-320.jpg)
![4 Apr 2013 Page
Check the APK signature (UnityScript)
20
// Retrieve the PackageManager and packageName (i.e. 'com.Company.Product')
var unity = new AndroidJavaClass("com.unity3d.player.UnityPlayer");
var activity = unity.GetStatic.<AndroidJavaObject>("currentActivity");
var manager = activity.Call.<AndroidJavaObject>("getPackageManager");
var name = activity.Call.<String>("getPackageName");
// Fetch APK signature(s)
var GET_SIGNATURES = 64; // PackageManager.GET_SIGNATURES
var packageInfo = manager.Call.<AndroidJavaObject>("getPackageInfo", name, GET_SIGNATURES);
var signatures = packageInfo.Get.<AndroidJavaObject[]>("signatures");
// Process signatures (i.e. check their validity)
for (var i = 0; i < signatures.length; ++i)
{
Debug.Log("signature = " + signatures[i].Call.<String>("toCharsString"));
Debug.Log("signature hash = " + signatures[i].Call.<int>("hashCode").ToString("X"));
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/doneprotectingyourandroidcontenterikhemming-130522210218-phpapp01/85/UniteKorea2013-Protecting-your-Android-content-20-320.jpg)
![4 Apr 2013 Page
Detect changes to ‘classes.dex’ (C#)
21
// Unity's WWW class supports reading 'jar:{archive-url}!/{entry}' on Android
string urlScheme = "jar:file://";
string apkPath = Application.dataPath;
string separator = "!/";
string entry = "classes.dex";
string url = urlScheme + apkPath + separator + entry;
// Read classes.dex inside package.apk
WWW www = new WWW(url);
yield return www;
// Calculate the MD5 sum of classes.dex contents
MD5 md5 = new MD5CryptoServiceProvider();
byte[] hash = md5.ComputeHash(www.bytes);
// Print MD5 sum
System.Text.StringBuilder sb = new System.Text.StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < hash.Length; i++)
sb.Append(hash[i].ToString("x2"));
Debug.Log("md5sum(classes.dex) = " + sb.ToString());](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/doneprotectingyourandroidcontenterikhemming-130522210218-phpapp01/85/UniteKorea2013-Protecting-your-Android-content-21-320.jpg)
![4 Apr 2013 Page
Native libs check (UnityScript)
22
// Retrieve main Activity
var unity = new AndroidJavaClass("com.unity3d.player.UnityPlayer");
var activity = unity.GetStatic.<AndroidJavaObject>("currentActivity");
// Retrieve ApplicationInfo and nativeLibraryDir (N.B. API-9 or newer only!)
var info = activity.Call.<AndroidJavaObject>("getApplicationInfo");
var nativeLibraryDir = info.Get.<String>("nativeLibraryDir");
var unityPath = Path.Combine(nativeLibraryDir, "libunity.so");
var file = new FileStream(unityPath, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read);
var sha1 = new SHA1CryptoServiceProvider();
var hash = sha1.ComputeHash(file);
file.Close();
// Print SHA1 sum
var sb = new System.Text.StringBuilder();
for (var i = 0; i < hash.Length; i++)
sb.Append(hash[i].ToString("x2"));
Debug.Log("sha1sum(libunity.so) = " + sb.ToString());](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/doneprotectingyourandroidcontenterikhemming-130522210218-phpapp01/85/UniteKorea2013-Protecting-your-Android-content-22-320.jpg)


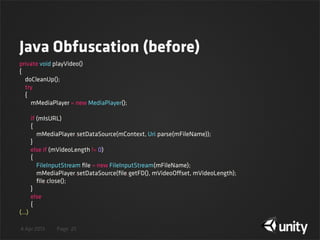
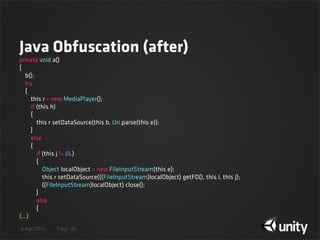


![4 Apr 2013 Page
SetString(key, value, secret)
29
// Hide 'key' string
string key_string = MD5(key);
// Convert 'value' into a byte array
byte[] bytes = UTF8Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(value);
// Encrypt 'value' with 3DES('secret')
TripleDES des = new TripleDESCryptoServiceProvider();
des.Key = secret;
des.Mode = CipherMode.ECB;
ICryptoTransform xform = des.CreateEncryptor();
byte[] encrypted = xform.TransformFinalBlock(bytes, 0, bytes.Length);
// Convert encrypted array into a "readable" string
string encrypted_string = Convert.ToBase64String(encrypted, 0, encrypted.Length);
// Set the { key, encrypted value } pair in regular PlayerPrefs
PlayerPrefs.SetString(key_string, encrypted_string);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/doneprotectingyourandroidcontenterikhemming-130522210218-phpapp01/85/UniteKorea2013-Protecting-your-Android-content-29-320.jpg)
![4 Apr 2013 Page
value GetString(key, secret)
30
// Hide 'key' string
string key_string = MD5(key);
// Retrieve encrypted 'value' and Base64 decode it
string value = PlayerPrefs.GetString(key_string);
byte[] bytes = Convert.FromBase64String(value);
// Decrypt 'value' with 3DES('secret')
TripleDES des = new TripleDESCryptoServiceProvider();
des.Key = secret;
des.Mode = CipherMode.ECB;
ICryptoTransform xform = des.CreateDecryptor();
byte[] decrypted = xform.TransformFinalBlock(bytes, 0, bytes.Length);
// Return decrypted value as a proper string
return UTF8Encoding.UTF8.GetString(decrypted);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/doneprotectingyourandroidcontenterikhemming-130522210218-phpapp01/85/UniteKorea2013-Protecting-your-Android-content-30-320.jpg)
![4 Apr 2013 Page
Encrypted SetString() / GetString()
31
// Generate a secret based on 'username'
string username = "Turrican II";
MD5 md5 = new MD5CryptoServiceProvider();
byte[] secret = md5.ComputeHash(UTF8Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(username));
// Game progress { key, value } pair
string key = "unlocked levels";
string value = "the desert rocks,traps,secret dungeons,the wall,the final challenge,the final fight";
// Insert { key, value } pair
SetString(key, value, secret);
// Retrieve { key, value }
string ret = GetString(key, secret);
// Output to the logcat
Debug.Log("secret = " + username);
Debug.Log(key + " = " + ret);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/doneprotectingyourandroidcontenterikhemming-130522210218-phpapp01/85/UniteKorea2013-Protecting-your-Android-content-31-320.jpg)

![4 Apr 2013 Page
Encryption of Scripts
• How?
• Compile scripts outside Unity
• Run a symmetric / asymmetric encryption on the Script.dll
• Choose a delivery mechanism
• Embed in the application, or
• Download it from a trusted server
• Decrypt the Script.dll in memory
• Load it through Assembly.Load(byte[])
33](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/doneprotectingyourandroidcontenterikhemming-130522210218-phpapp01/85/UniteKorea2013-Protecting-your-Android-content-33-320.jpg)


![4 Apr 2013 Page
Plugin.cs
36
using UnityEngine;
public class SomeImportantGameClass
{
static SomeImportantGameClass()
{
const int GET_SIGNATURES = 64;
AndroidJavaObject activity = new AndroidJavaClass("com.unity3d.player.UnityPlayer")
.GetStatic<AndroidJavaObject>("currentActivity");
AndroidJavaObject manager = activity.Call<AndroidJavaObject>("getPackageManager");
string packageName = activity.Call<string>("getPackageName");
AndroidJavaObject packageInfo =
manager.Call<AndroidJavaObject>("getPackageInfo", packageName, GET_SIGNATURES);
AndroidJavaObject[] signatures = packageInfo.Get<AndroidJavaObject[]>("signatures");
foreach (AndroidJavaObject signature in signatures)
{
Debug.Log("signature hash = " + signature.Call<int>("hashCode").ToString("X"));
}
}
(...)
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/doneprotectingyourandroidcontenterikhemming-130522210218-phpapp01/85/UniteKorea2013-Protecting-your-Android-content-36-320.jpg)
![4 Apr 2013 Page
Decrypt and run assembly
37
public TextAsset assembly;
void Start () {
// Load encrypted data and decryption keys
byte[] bytes = Convert.FromBase64String(assembly.text);
byte[] key = new byte[] { <key from encryption step> };
byte[] iv = new byte[] { <iv from encryption step> };
// Decrypt assembly
RC2 rc2 = new RC2CryptoServiceProvider();
rc2.Mode = CipherMode.CBC;
ICryptoTransform xform = rc2.CreateDecryptor(key, iv);
byte[] decrypted = xform.TransformFinalBlock(bytes, 0, bytes.Length);
// Load assembly and instantiate 'SomeImportantGameClass' to trigger static constructor
Assembly asm = Assembly.Load(decrypted);
Type SomeClass = asm.GetType("SomeImportantGameClass");
SomeClass.GetConstructor(Type.EmptyTypes).Invoke(null);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/doneprotectingyourandroidcontenterikhemming-130522210218-phpapp01/85/UniteKorea2013-Protecting-your-Android-content-37-320.jpg)

![4 Apr 2013 Page
Encryption of Assets
• How?
• Create an AssetBundle from the “secret” assets.
• Run a symmetric / asymmetric encryption on the AssetBundle.unity3d
• Choose a delivery mechanism
• Embed in the application, or
• Download it from a trusted server
• Decrypt the AssetBundle.unity3d in memory
• Load it through AssetBundle.CreateFromMemory(Byte[])
39](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/doneprotectingyourandroidcontenterikhemming-130522210218-phpapp01/85/UniteKorea2013-Protecting-your-Android-content-39-320.jpg)