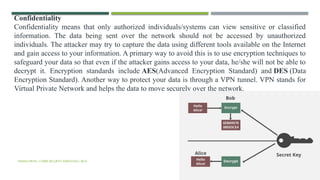
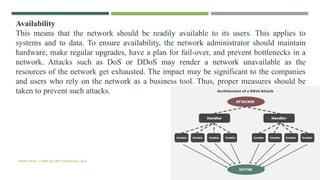
The document provides an overview of cyber security, discussing its importance in protecting computer systems and data from various cyber threats like cybercrime and terrorism. It emphasizes the need for comprehensive security measures, including both technical safeguards and individual responsibilities, as well as outlining key concepts such as the CIA triad (Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability). Additionally, it explores the complexities of internet governance and the challenges associated with establishing global security standards and regulations.