The document discusses structures in C programming. Some key points covered include: defining a structure with member variables of different data types; declaring structure variables; accessing structure members using the dot operator; arrays of structures; passing structures to functions; and nested structures. Examples are provided for each concept.

![CSC COMPUTER EDUCATION,
M.K.B.NAGAR
Structure are collection of different datatype
grouped together under a single variable name for
convienient handling. 'struct' is a keyword, struct type
is a name which identifies the structure.
syntax : struct <structure name or tagname>
{
datatype member1;
datatype member2;
};
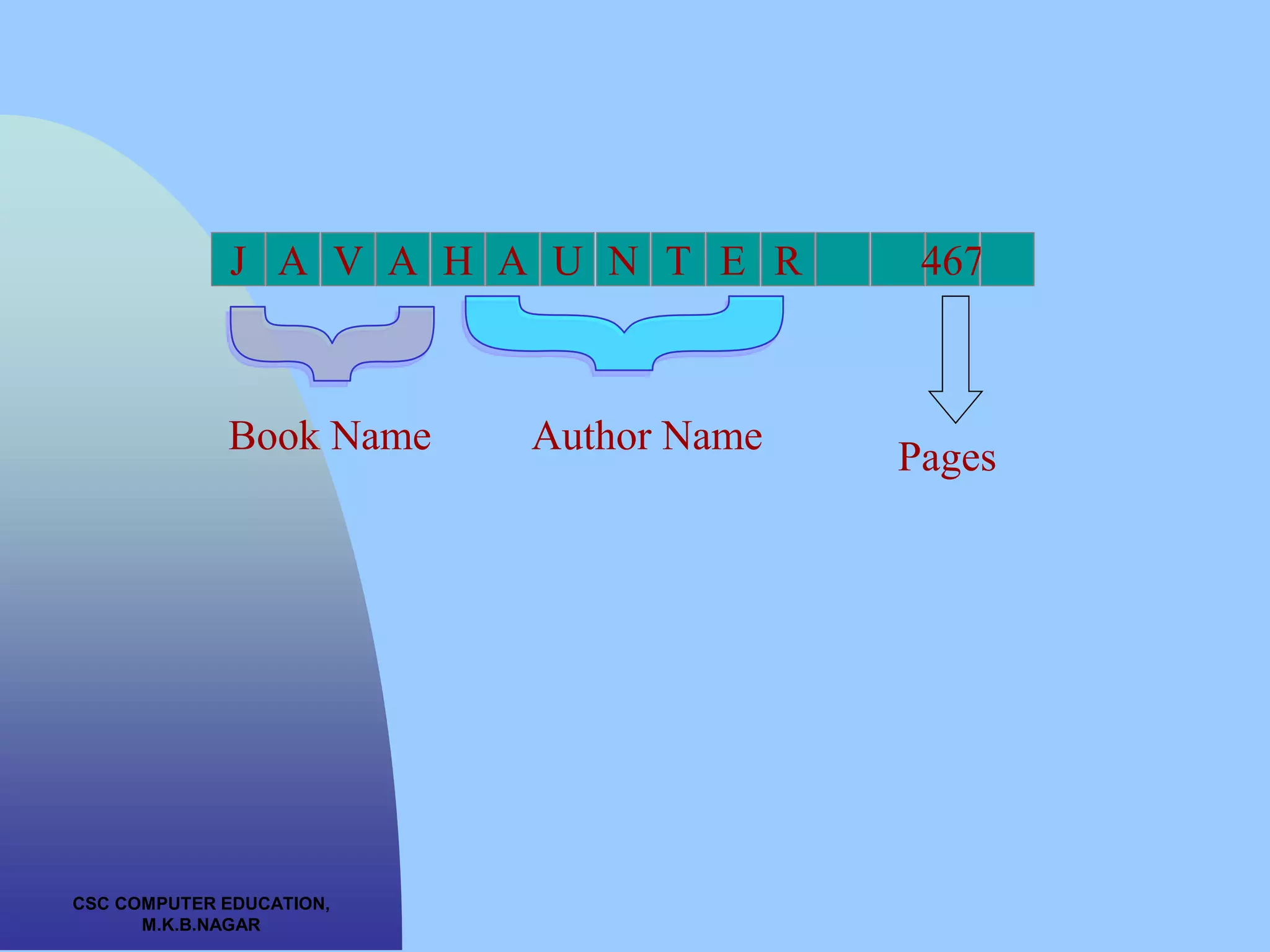
struct book
{
int pages;
char bookname[10];
char author[20];
float price;
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structure-230721044715-a3fb58c5/75/structure-ppt-3-2048.jpg)
![Write a Program the create the Account Details using Structure?
#include<stdio.h>
struct amount
{
int ac_no;
char name[10];
int balance;
};
void main()
{
struct amount v;
printf("nEnter the account Details");
scanf("%d%s%d",&v.ac_no,&v.name, &v.balance);
printf("The values are %d%s%d",v.ac_no,
v.name, v.balance);
printf("%d",sizeof(struct amount));
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structure-230721044715-a3fb58c5/75/structure-ppt-6-2048.jpg)
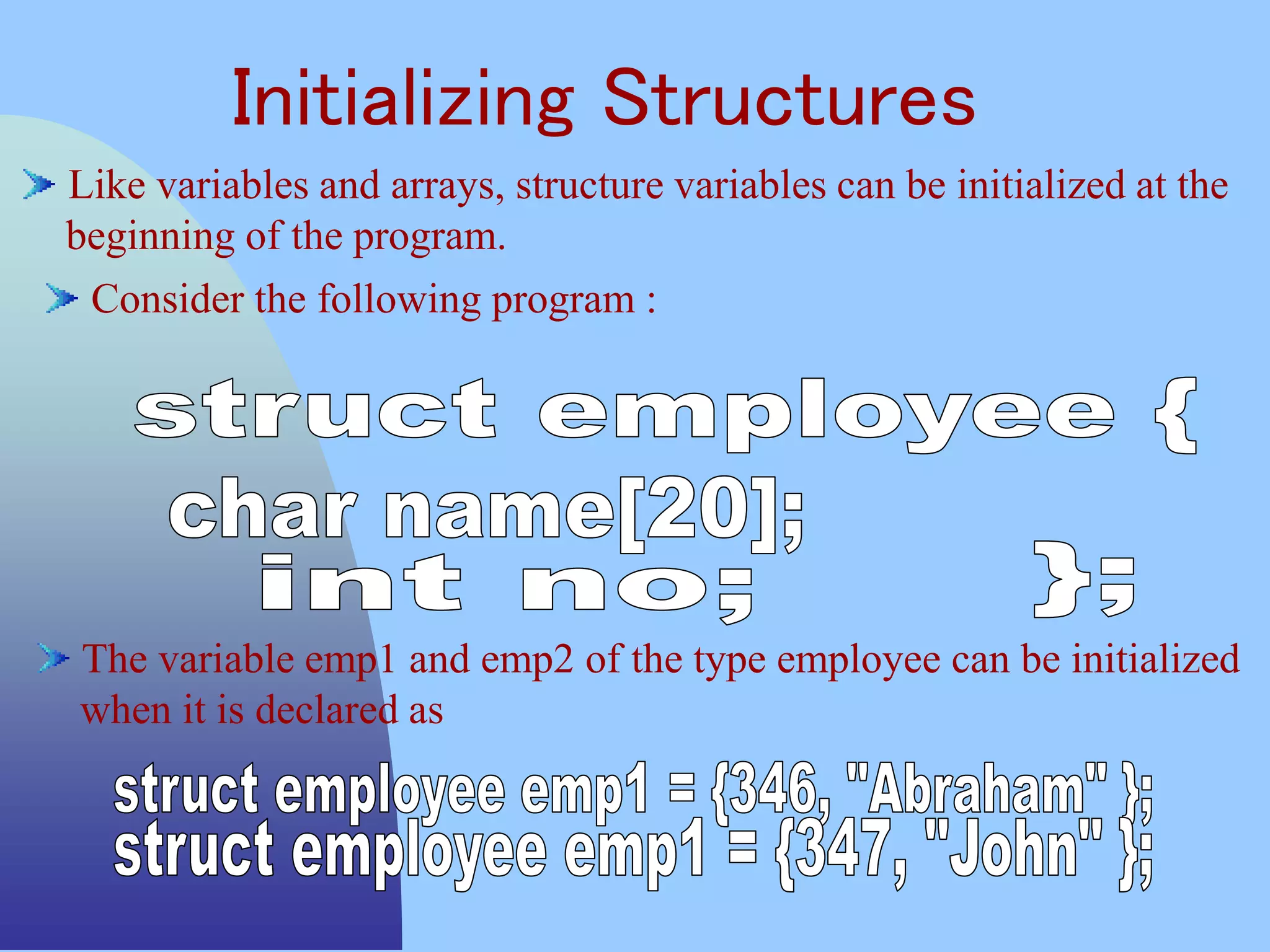
![CSC COMPUTER EDUCATION,
M.K.B.NAGAR
Write a program to create student structure
#include<stdio.h>
struct stud
{
int id;
char name[20];
int mark1,mark2,mark3;
int total;
int avg;
}b;
void main()
{
printf("nEnter the student details");
scanf("%d %s %d %d %d",&b.id,&b.name,
&b.mark1,&b.mark2,&b.mark3);
b.total=b.mark1+b.mark2+b.mark3;
b.avg=b.total/3;
printf("%d %s %d %d %d",b.id,b.name, b.mark1, b.mark2,
b.mark3);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structure-230721044715-a3fb58c5/75/structure-ppt-7-2048.jpg)
![Array of structures are defined as a group of data of
different data types stored in a consecutive memory location with a
common variable name.
For Example,
struct employee
{
int empno;
char empname[20];
char deptname[10];
float salary;
}emp[5];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structure-230721044715-a3fb58c5/75/structure-ppt-9-2048.jpg)


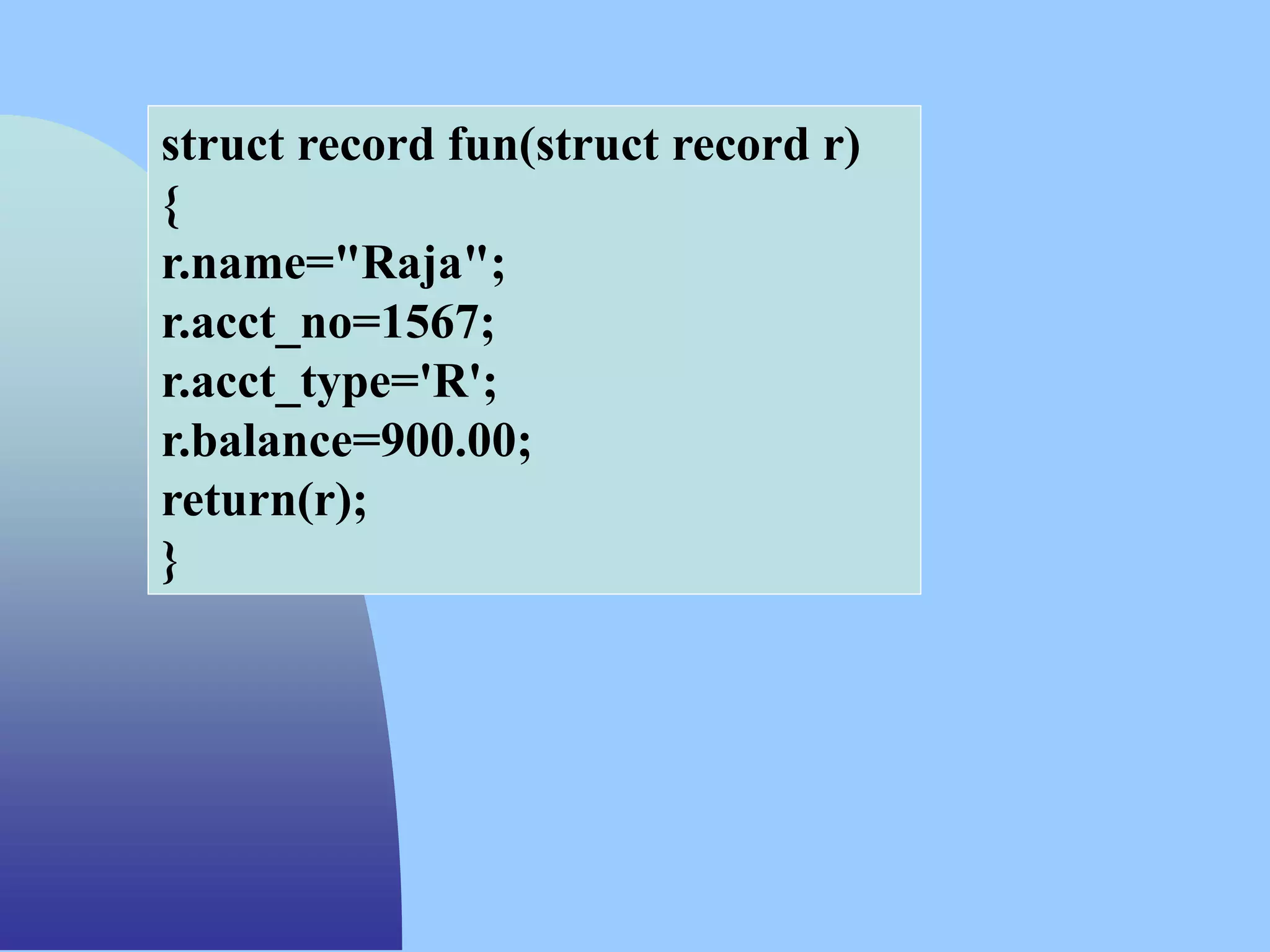
![Passing the structure member as a
parameter to the function
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef struct stud
{
int roll_no;
char name[20];
float marks;
}student;
student st;
void print_rec(int,char [],float);
void main()
{
char ans;
clrscr();
do
{
printf("n t Enter the record");
printf("n Enter the Roll Number");
scanf("%d",&st.roll_no);
printf("n Enter the Name");
scanf("%s",st.name);
printf("n Enter the Marks");
scanf("%f",&st.marks);
print_rec(st.roll_no,st.name,st.marks);
printf("n Do U Want to store the More
record ");
ans=getche();
}while(ans=='y');
}
void print_rec(int r,char n[],float m)
{
printf("n You have Entered Following
record");
printf("n %d %s %f",r,n,m);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structure-230721044715-a3fb58c5/75/structure-ppt-13-2048.jpg)
![Nested Structure
A structure within another structure is called Nesting of
structures.The declaration of the embedded structure must appear before
the declaration of the outer structure.
Example
Struct date
{
int month;
int day;
int year;
};
struct account
{
int acc_no;
char name[40];
char acc_type;
float balance;
struct date dob;
} customer;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structure-230721044715-a3fb58c5/75/structure-ppt-14-2048.jpg)
![/* NESTED STRUCTURES
A structure within another
structure */
#include<stdio.h>
struct dob {
int date;
int month;
int year; };
struct stud{
int sno;
char sname[10];
struct dob sdob;
char sex; };
void main()
{
struct stud s;
clrscr();
printf("enter the snon");
scanf("%d",&s.sno);
printf("enter the snamen");
scanf("%s",s.sname);
printf("enter the dobn");
scanf("%d%d%d %c",&s.sdob.date,
&s.sdob.month,&s.sdob.year,&s.sex);
printf("%dt %st %d %d %d t
%c", s.sno, s.sname, s.sdob.date,
s.sdob.month, s.sdob.year, s.sex);
getch();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structure-230721044715-a3fb58c5/75/structure-ppt-15-2048.jpg)

