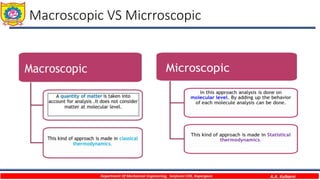
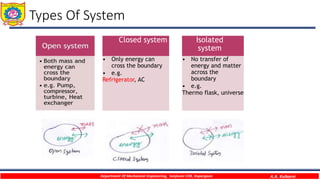
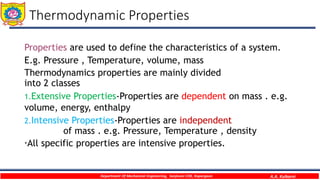
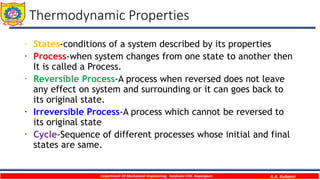
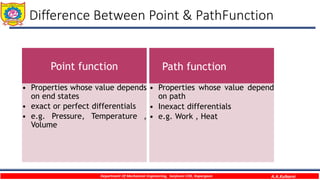
This document provides an overview of basic thermodynamic concepts and definitions for mechanical engineering students. It defines thermodynamics as the branch of science dealing with heat and energy interactions. It discusses microscopic and macroscopic views, types of systems (open, closed, isolated), thermodynamic properties (extensive, intensive, point functions, path functions), processes (reversible, irreversible, cycles), and conditions for thermodynamic equilibrium. The document is intended to introduce students to fundamental thermodynamic concepts.