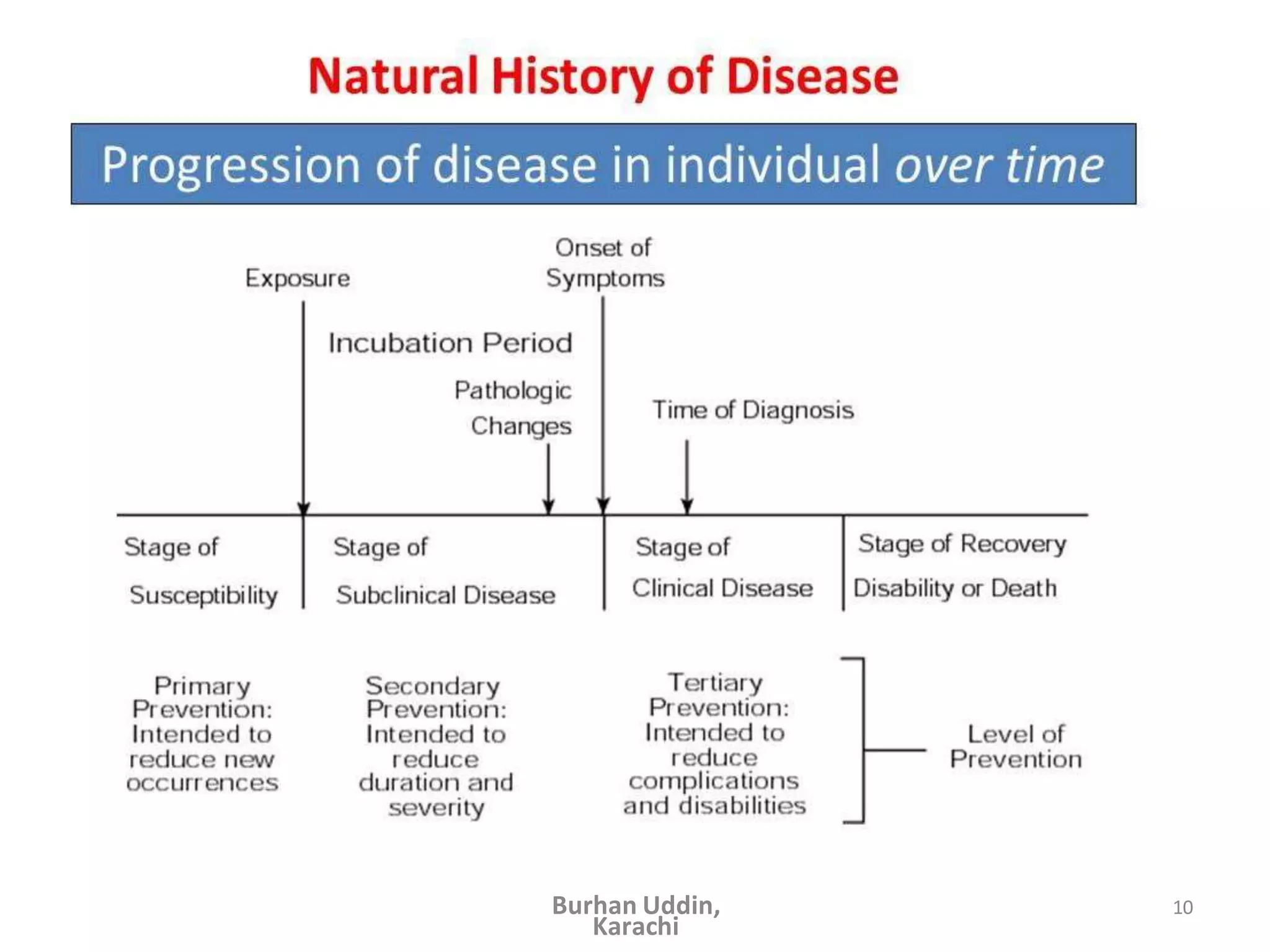
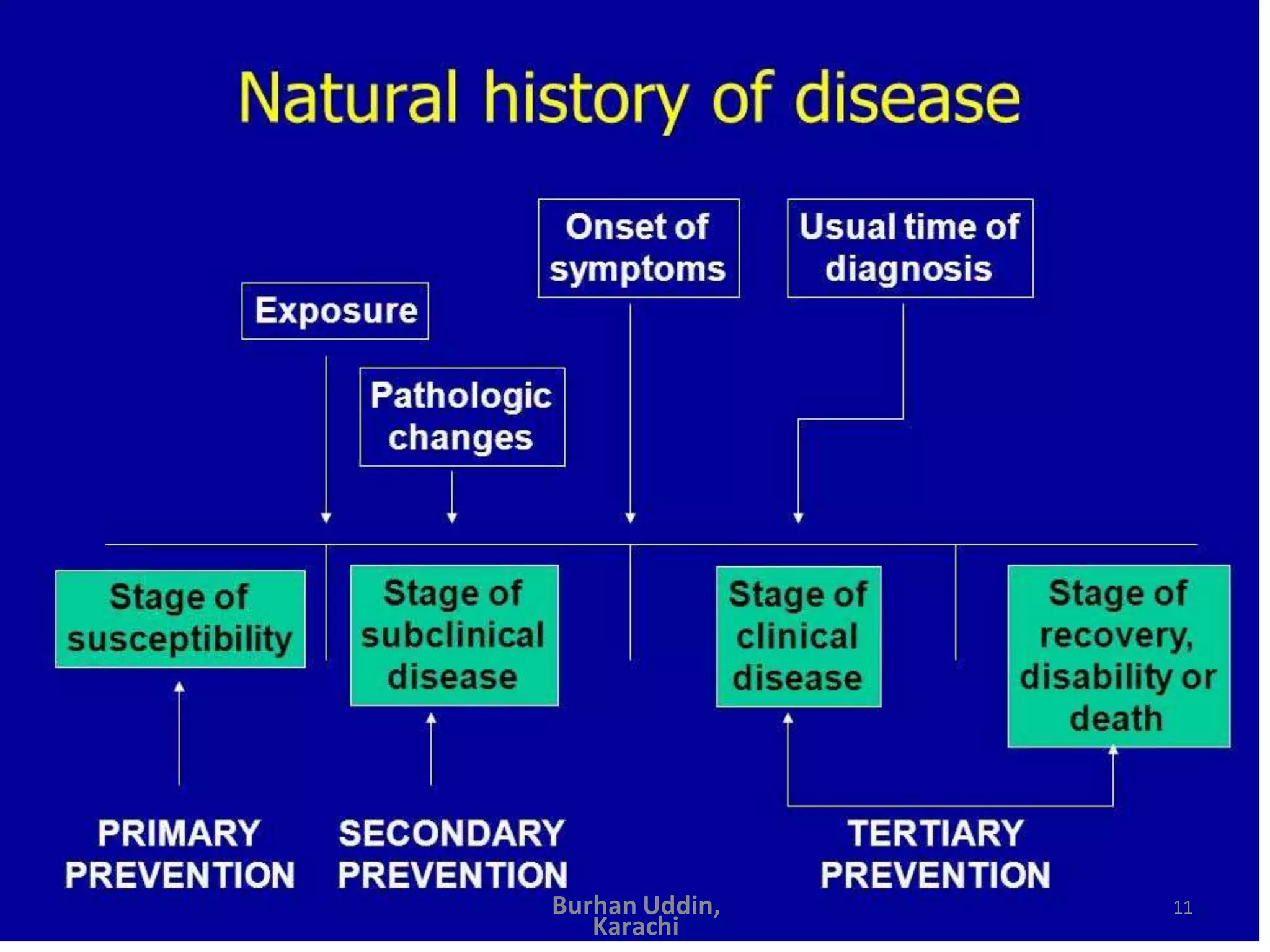
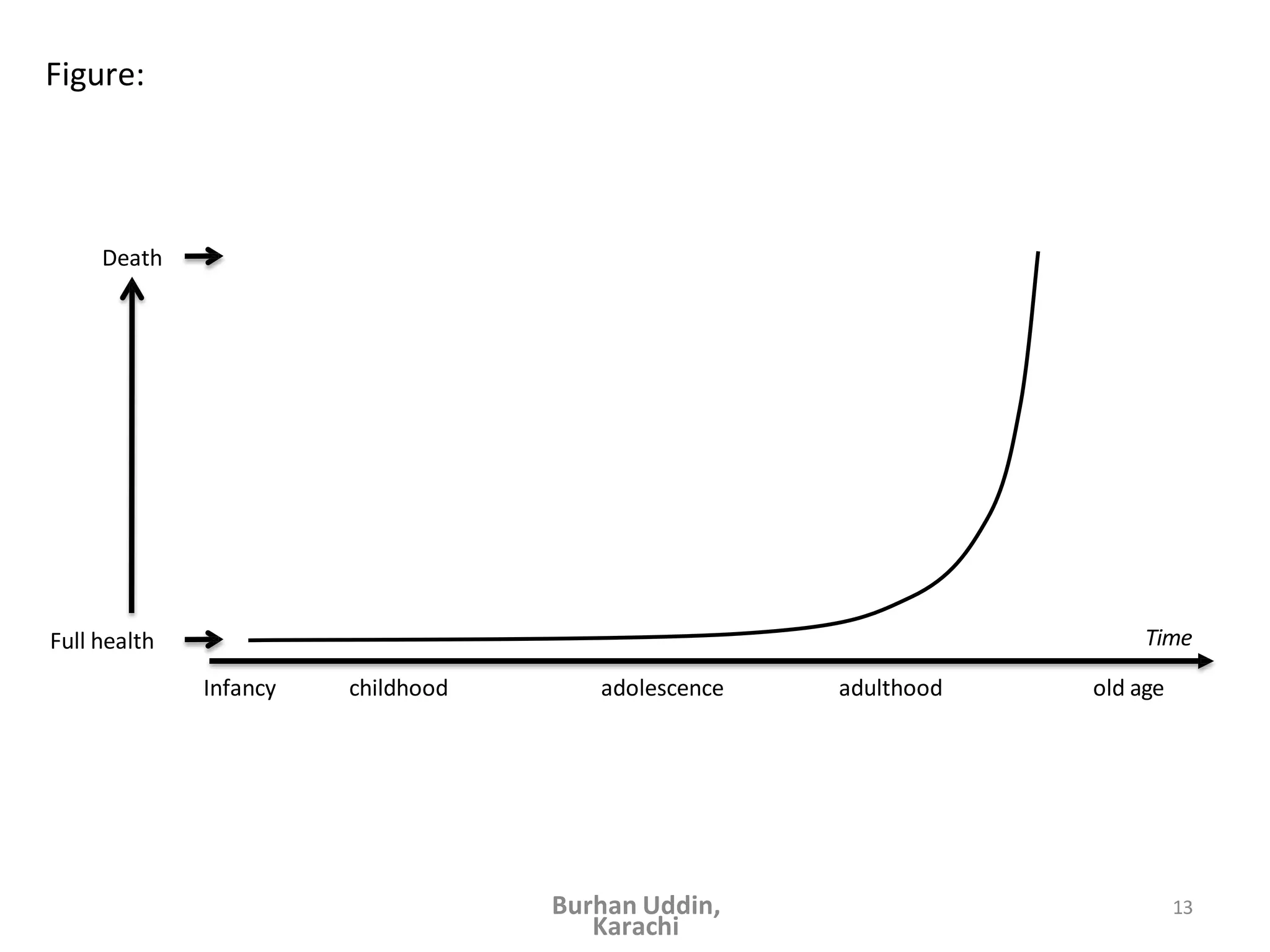
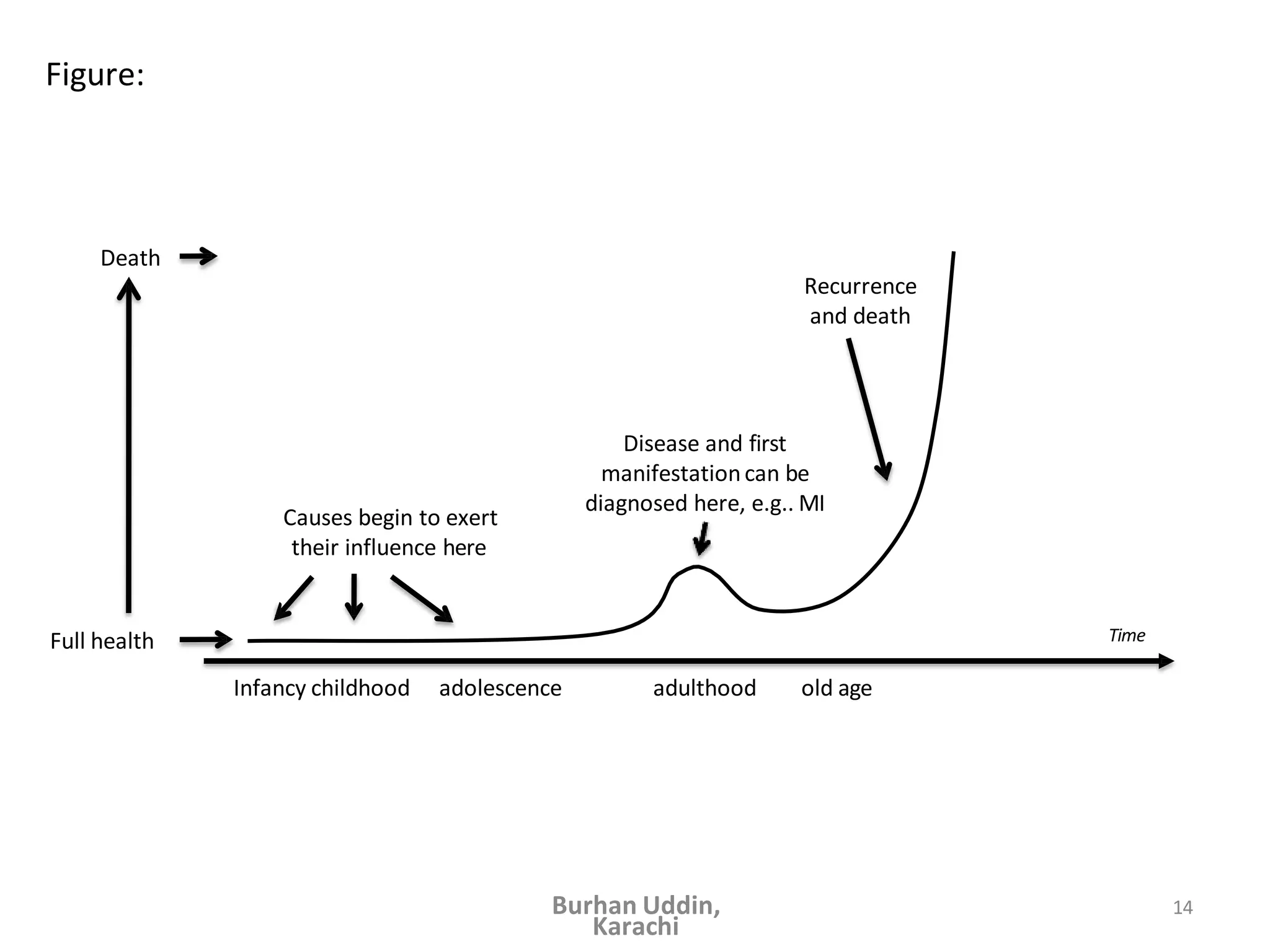
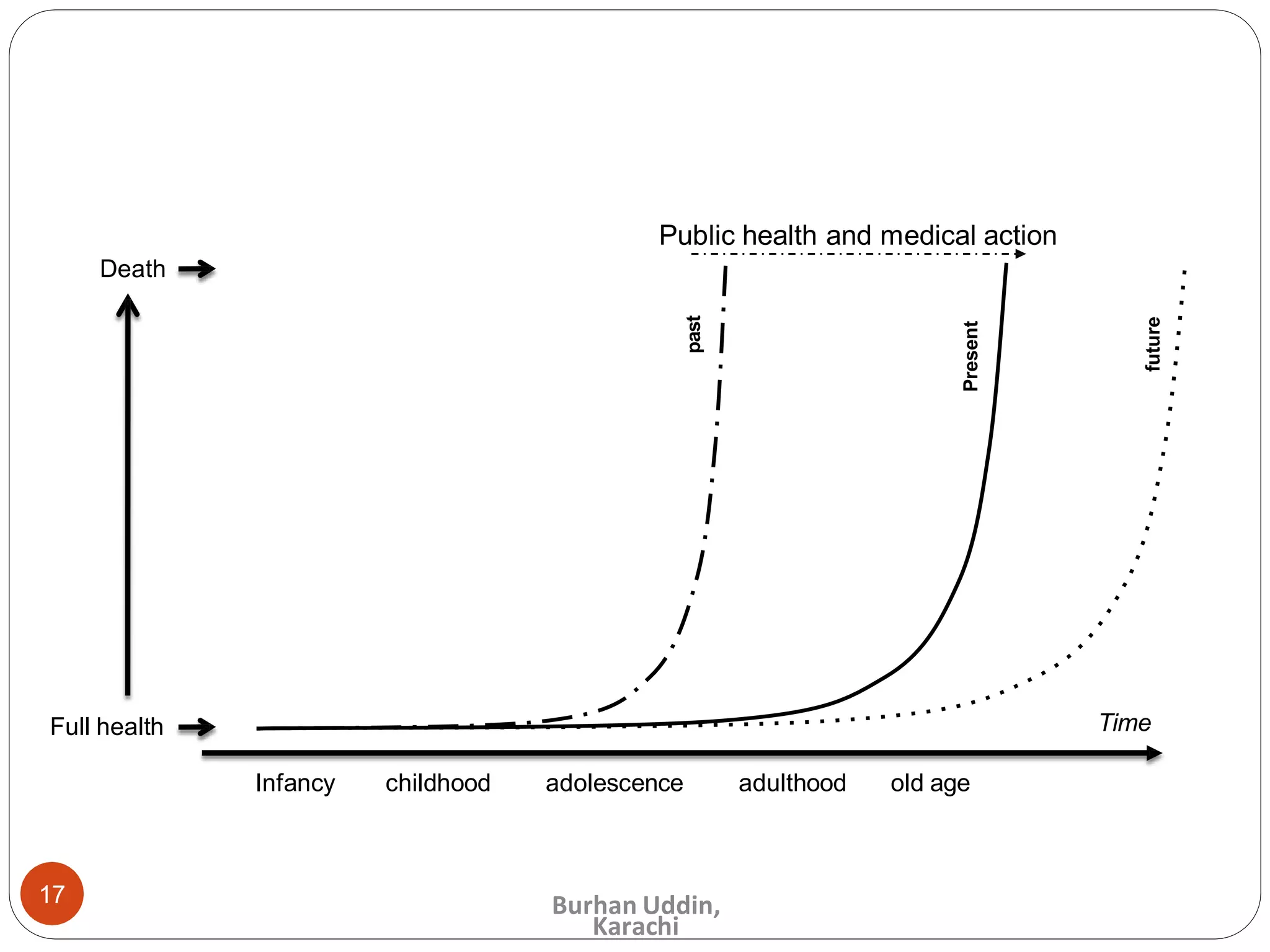
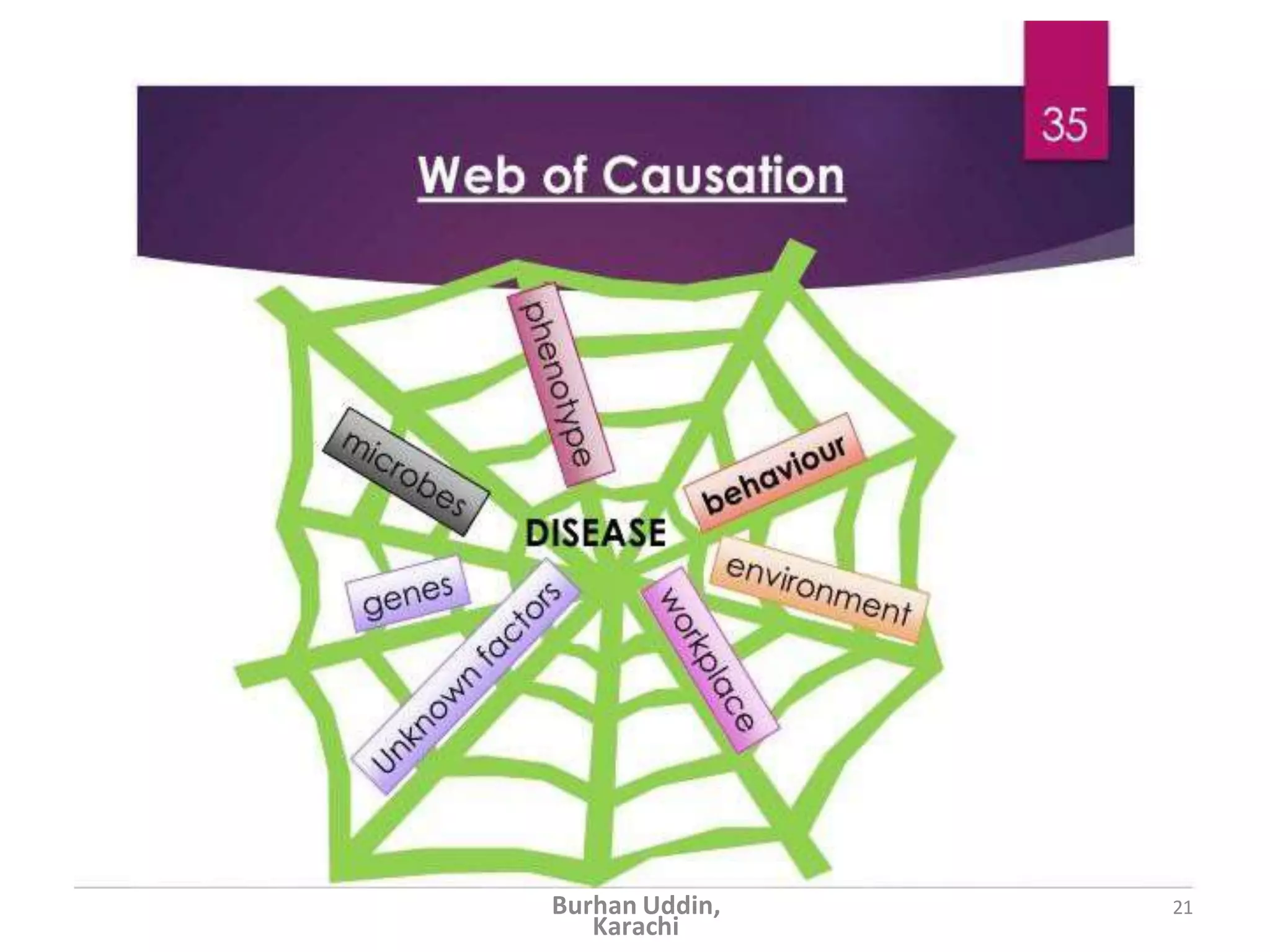
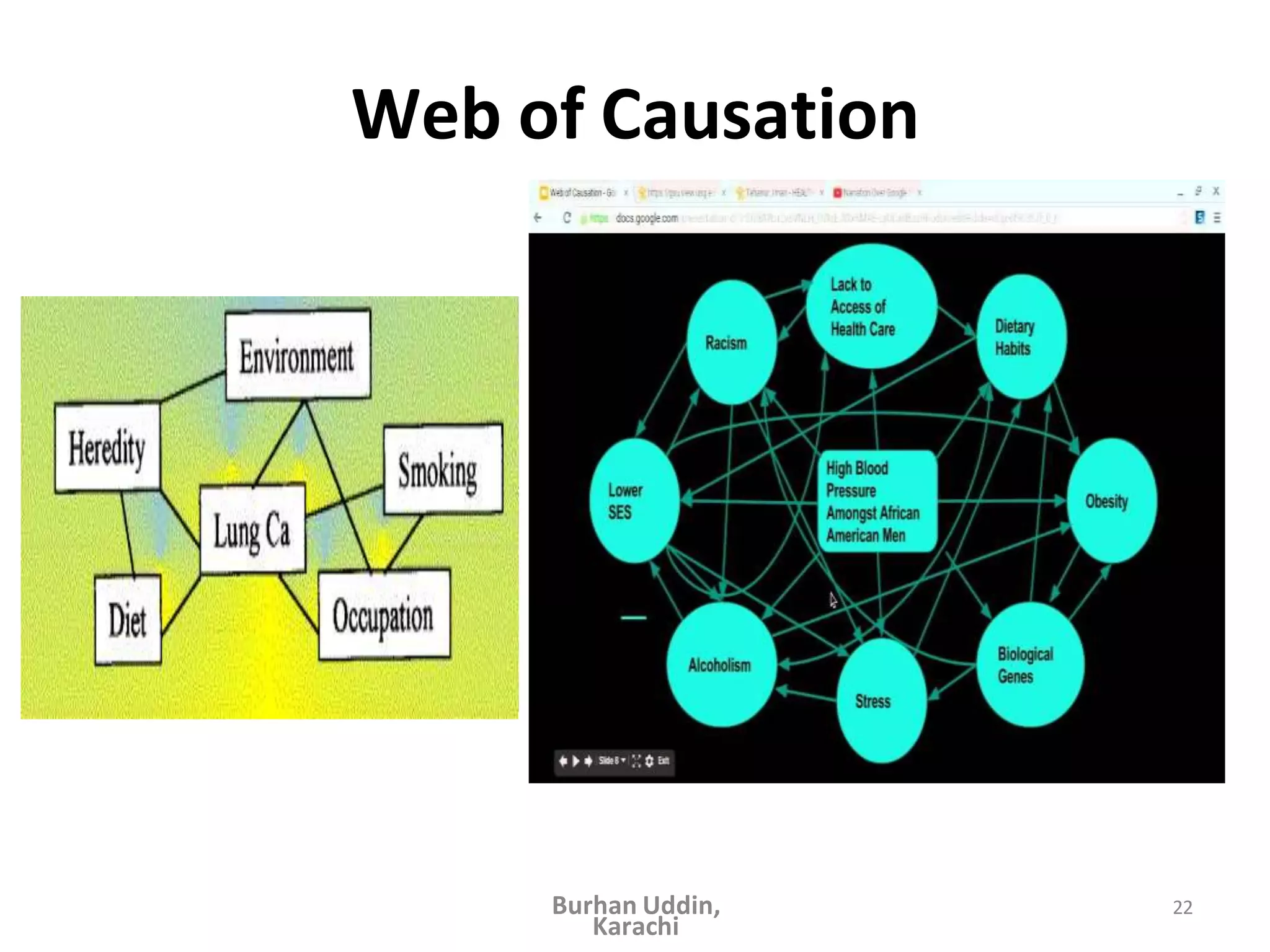
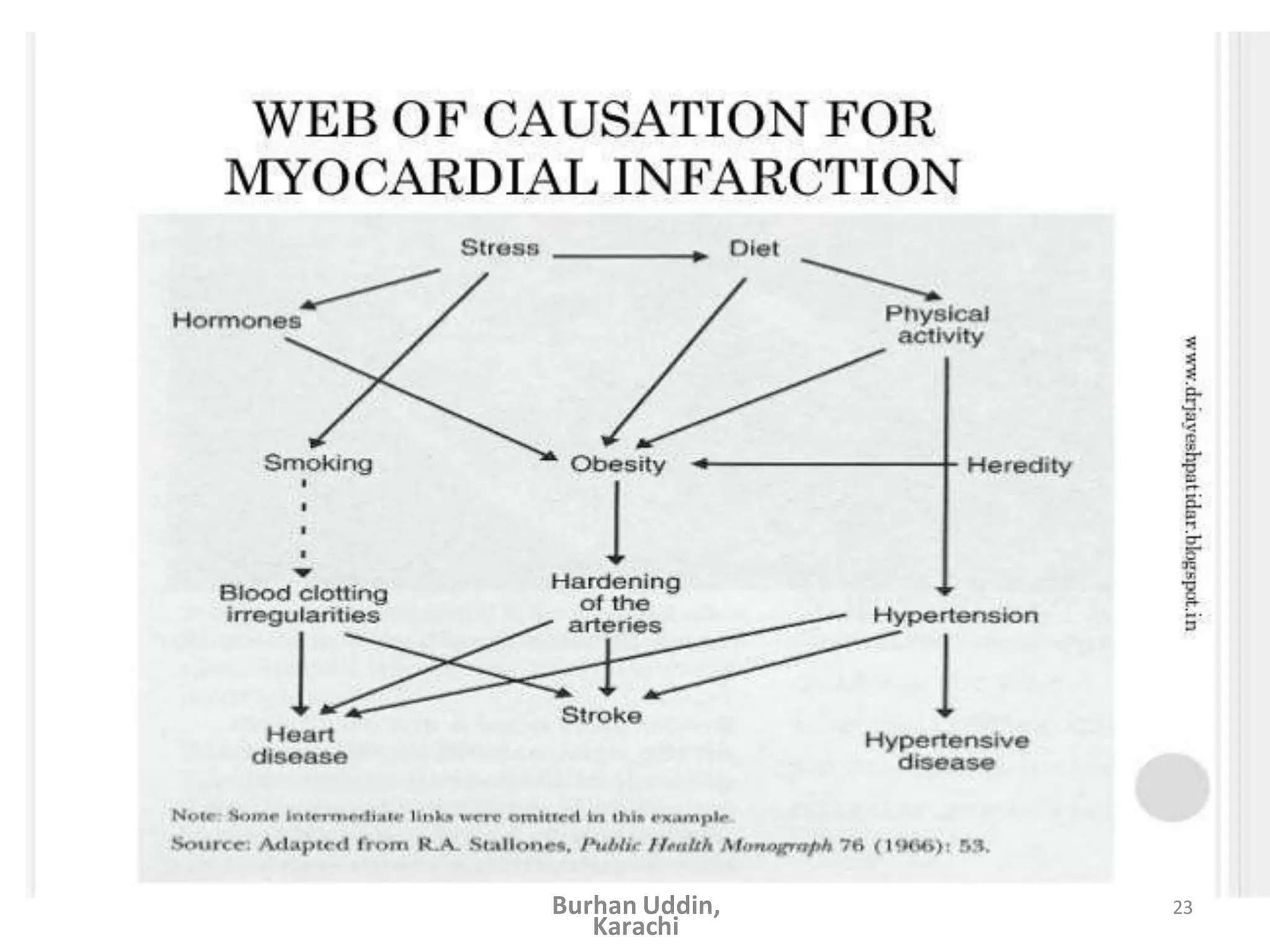
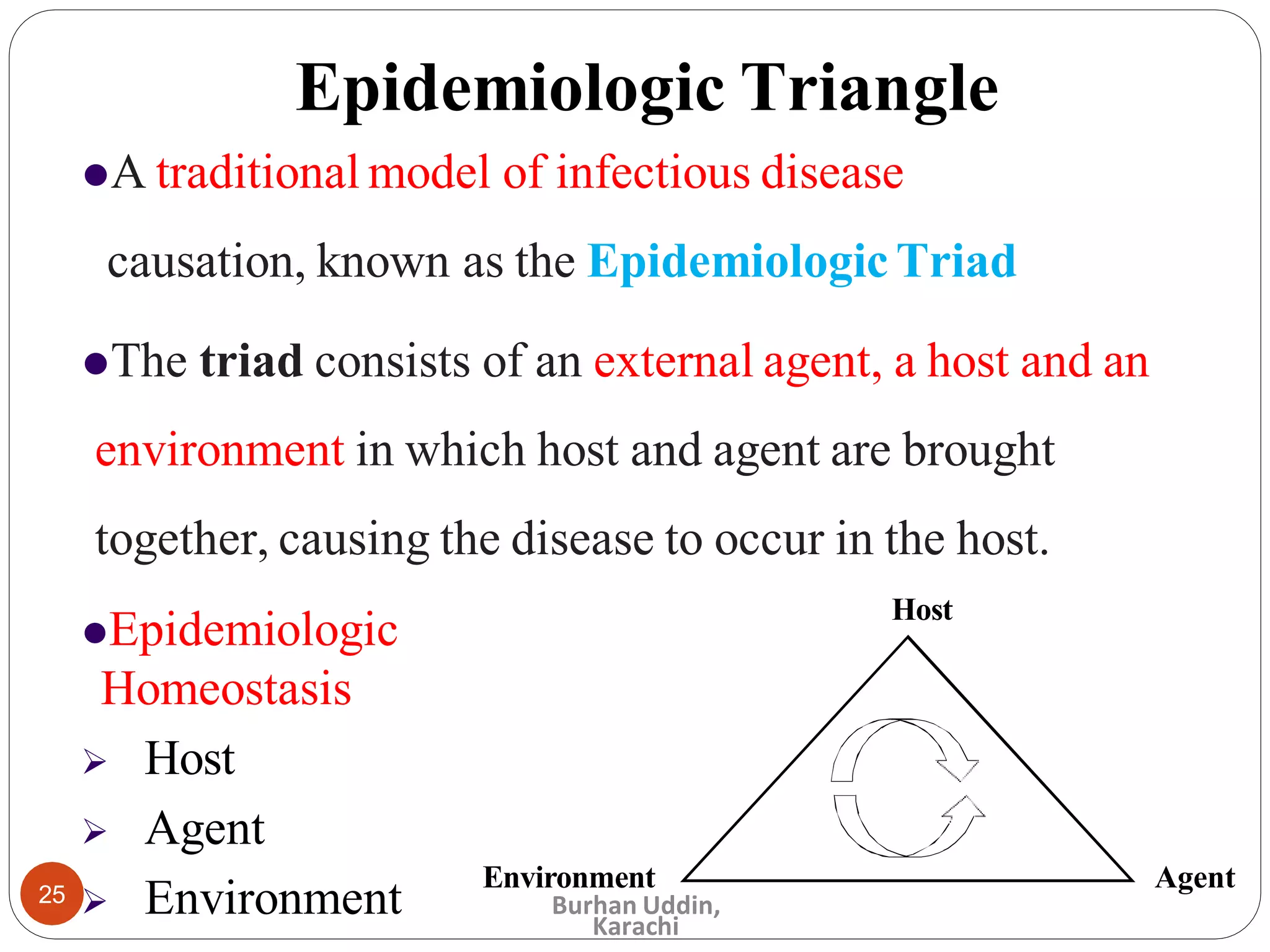
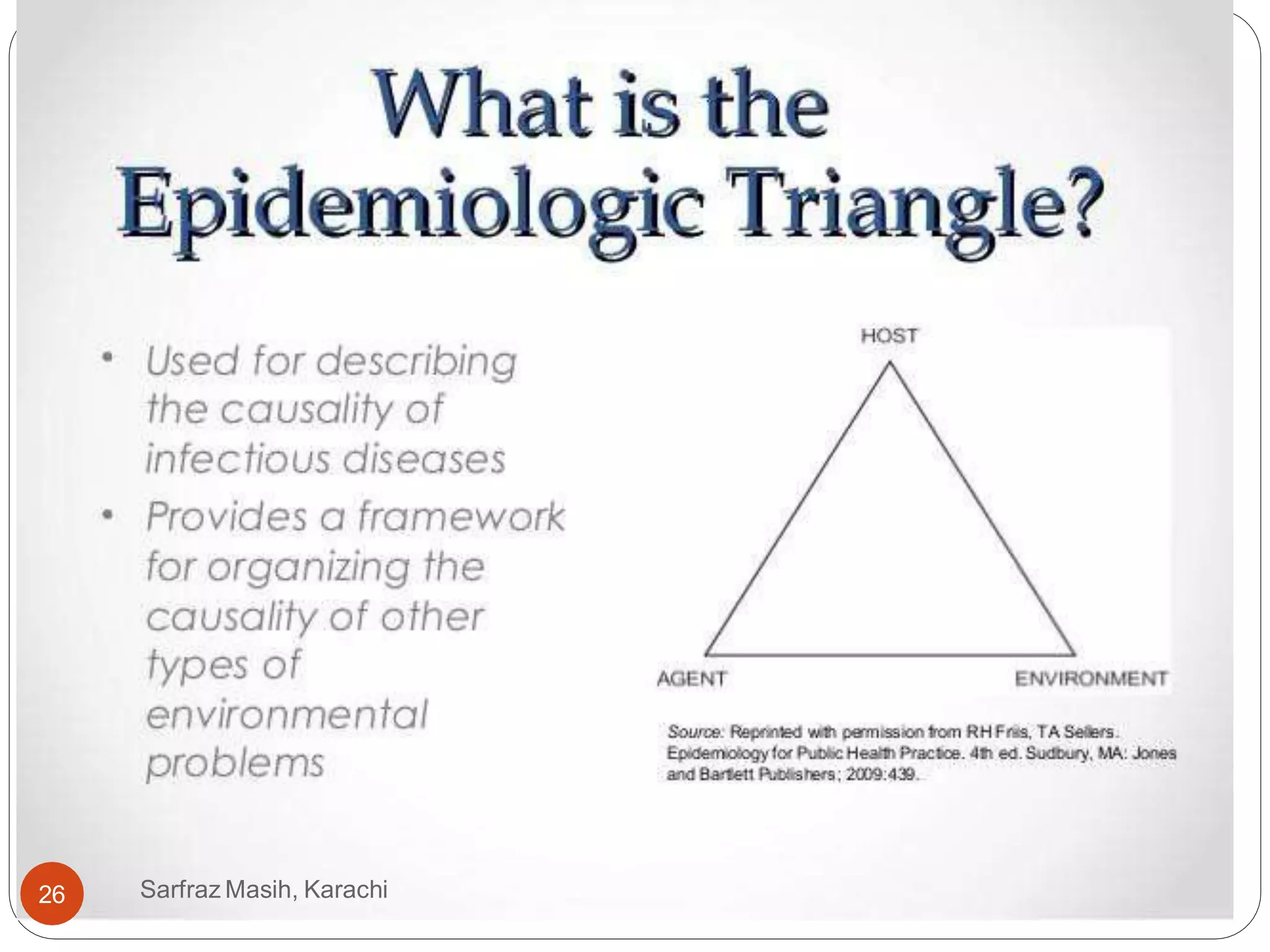
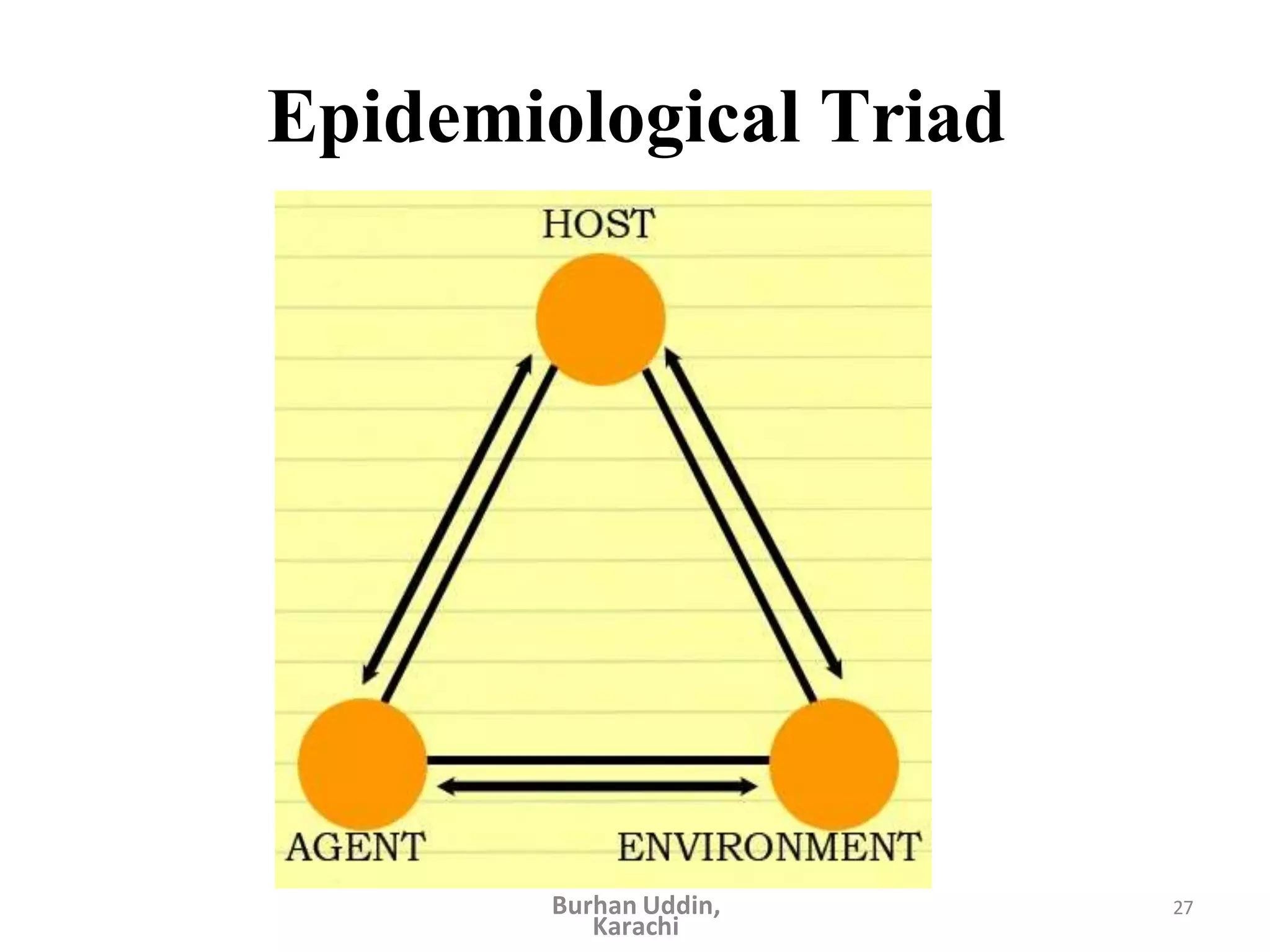
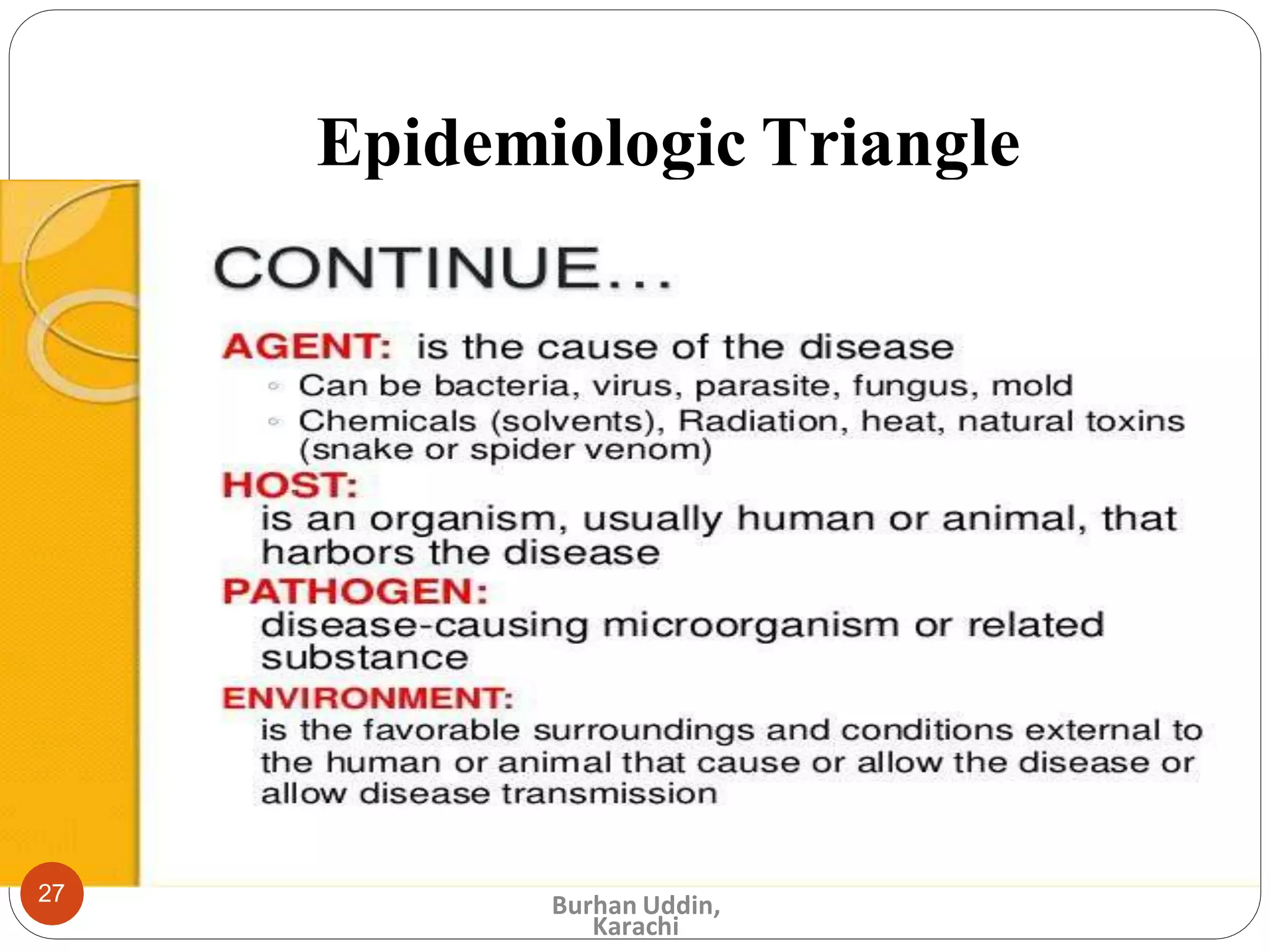
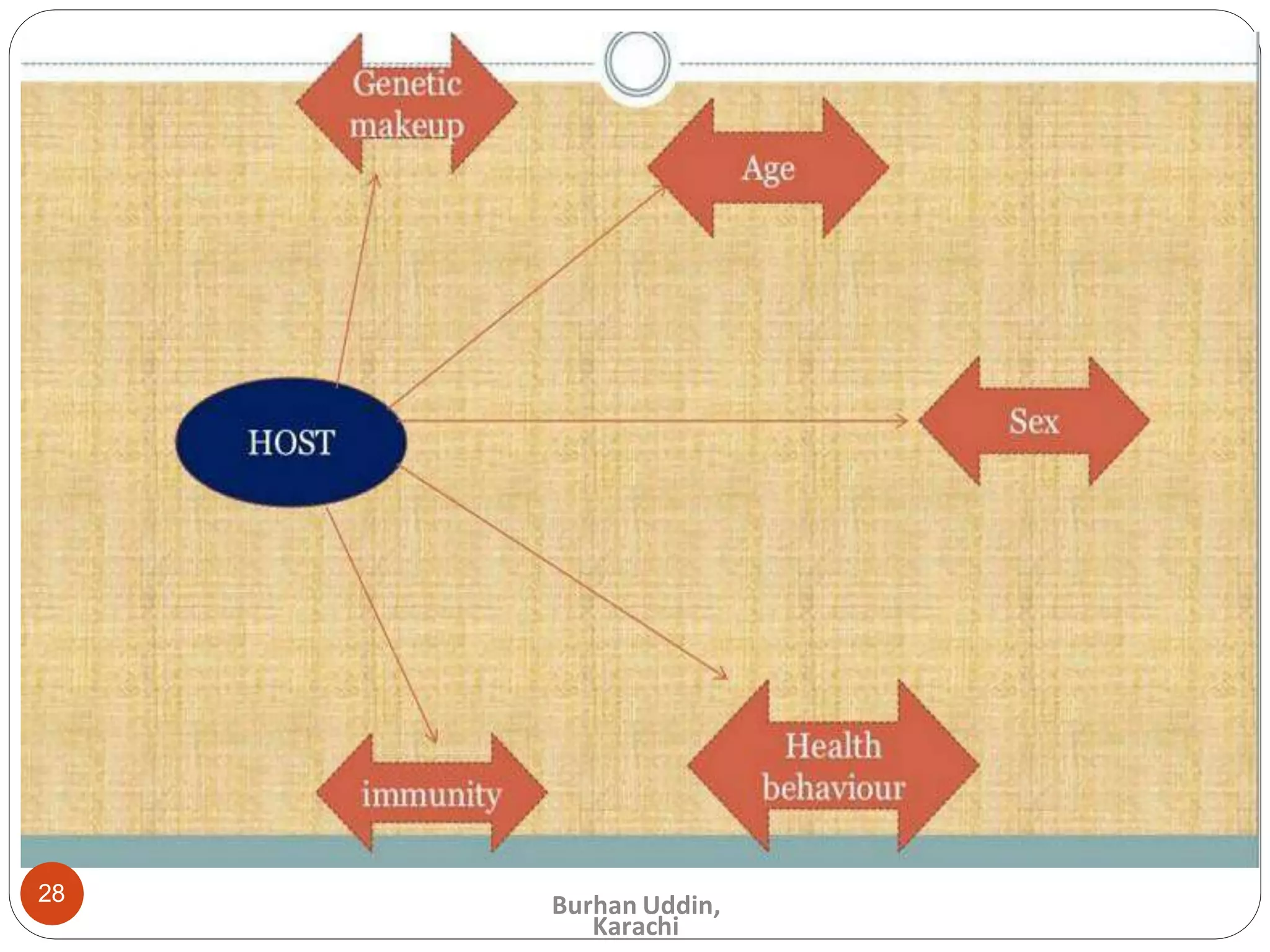
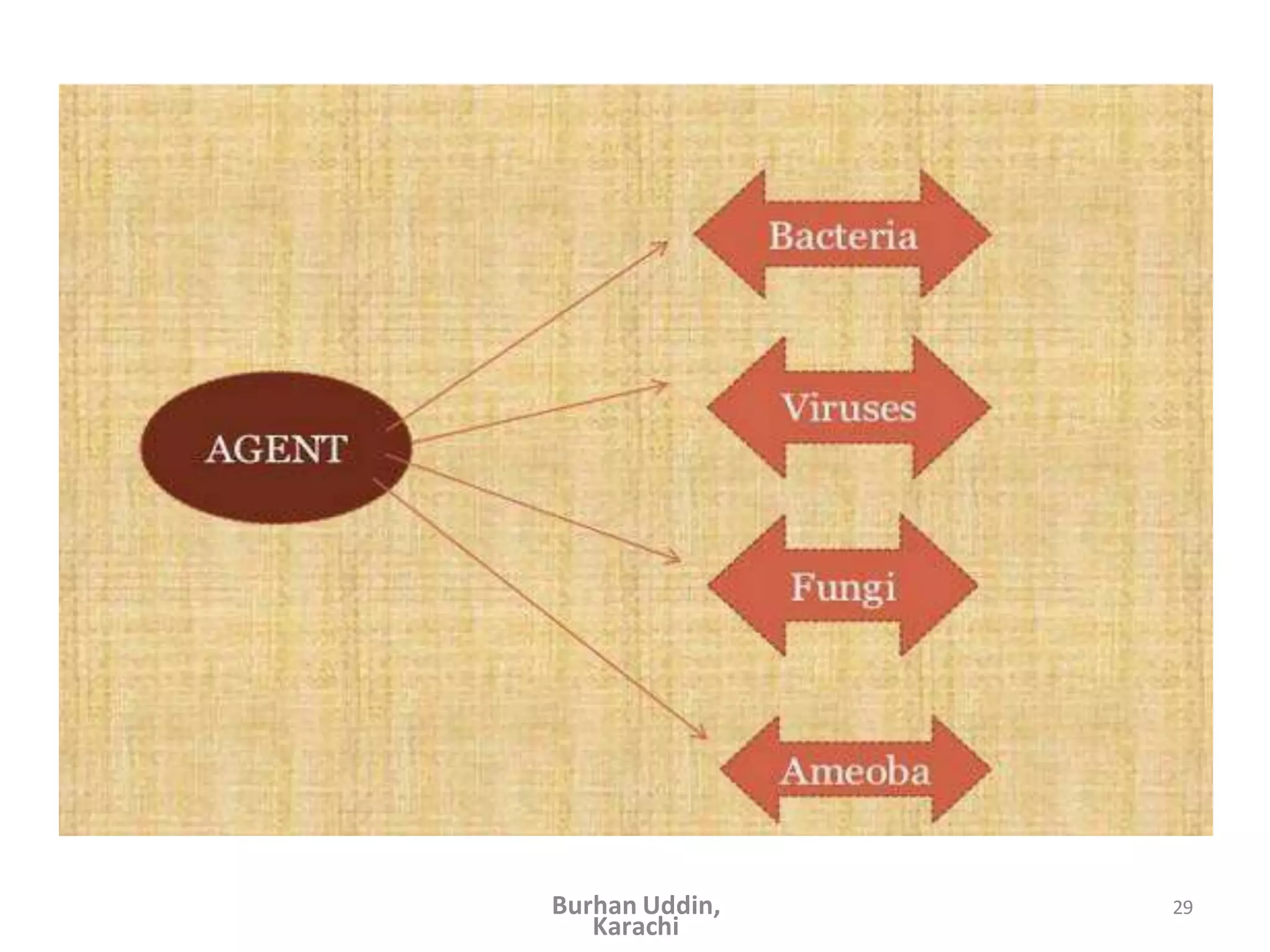
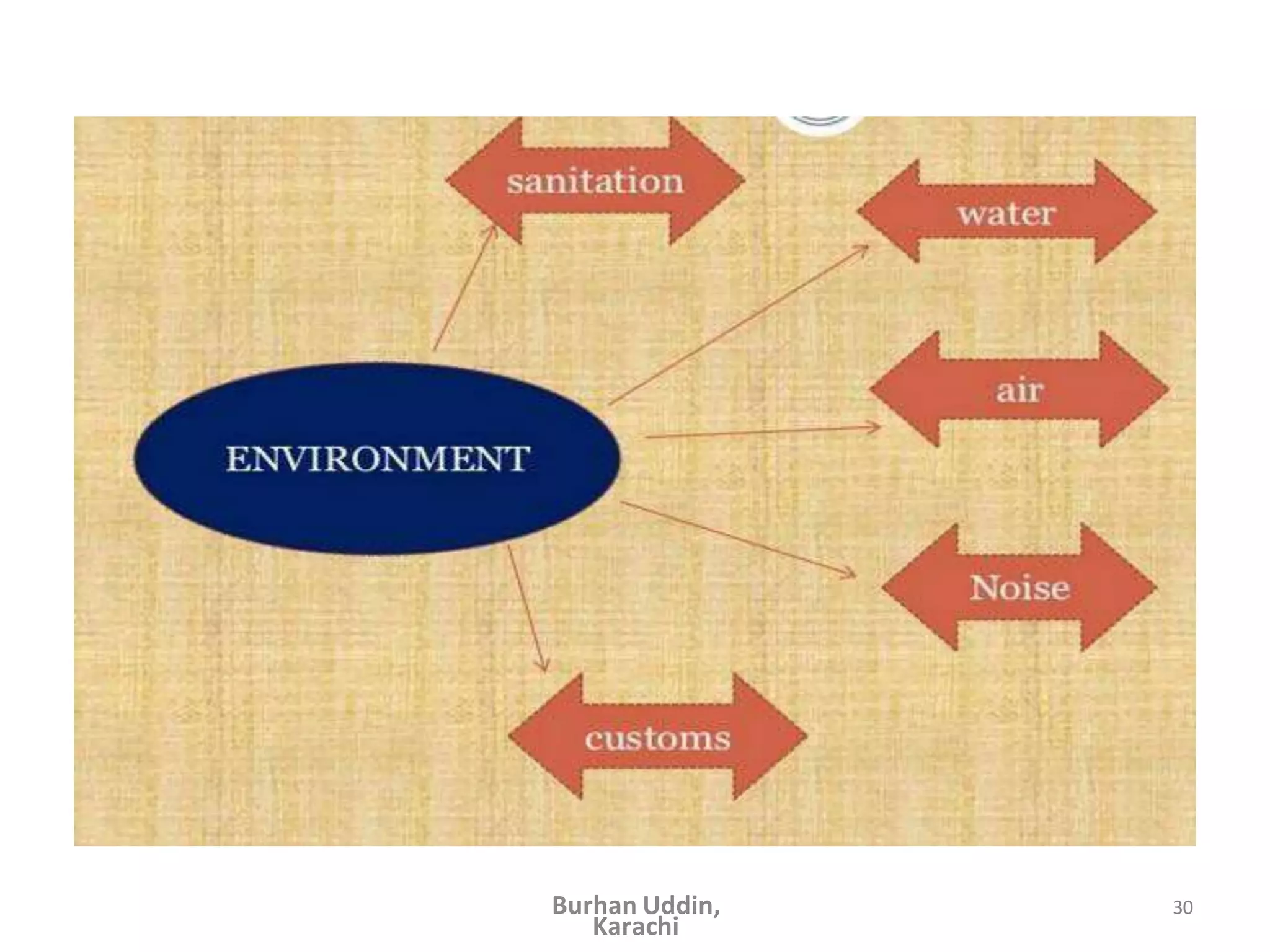
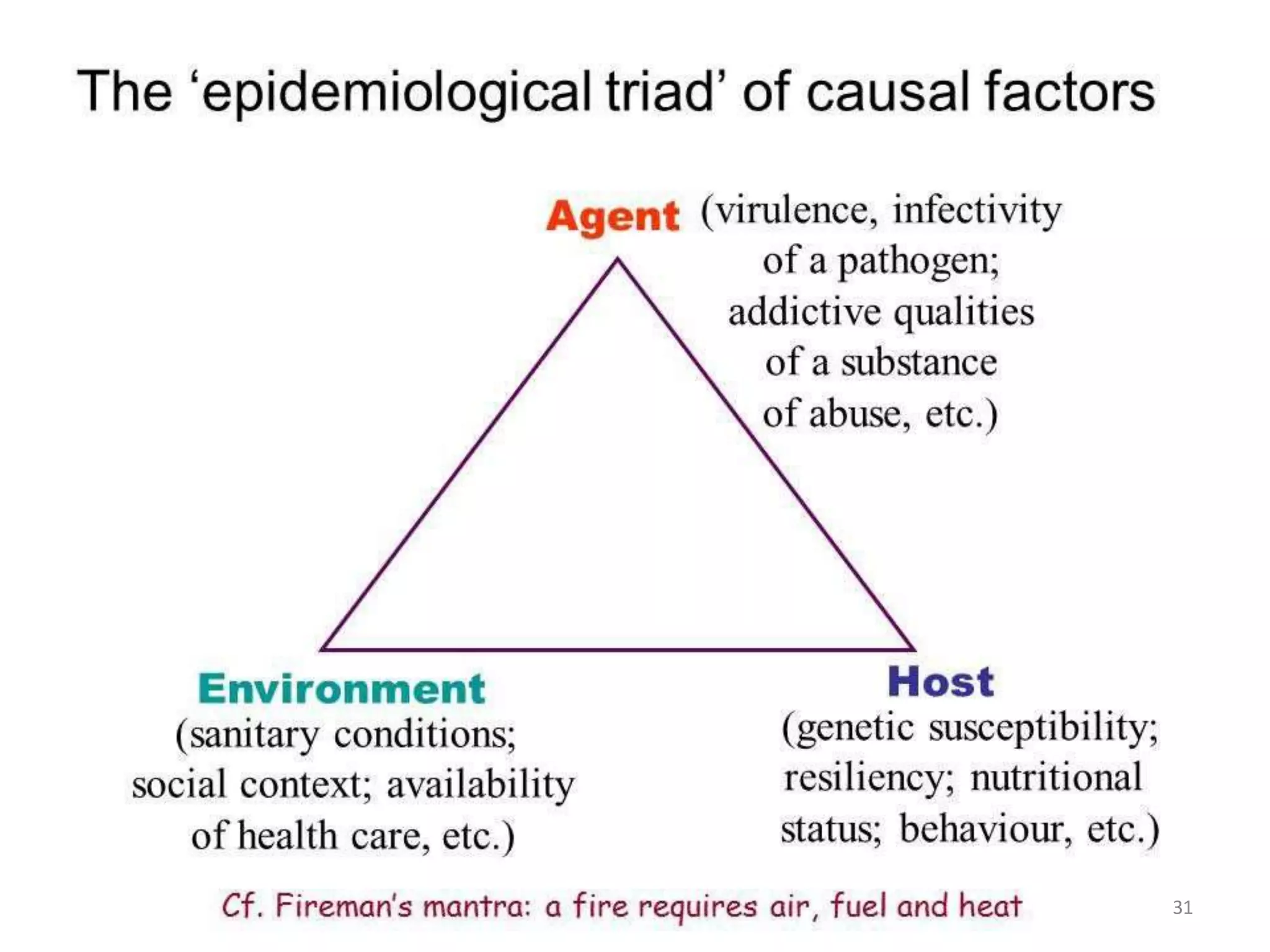
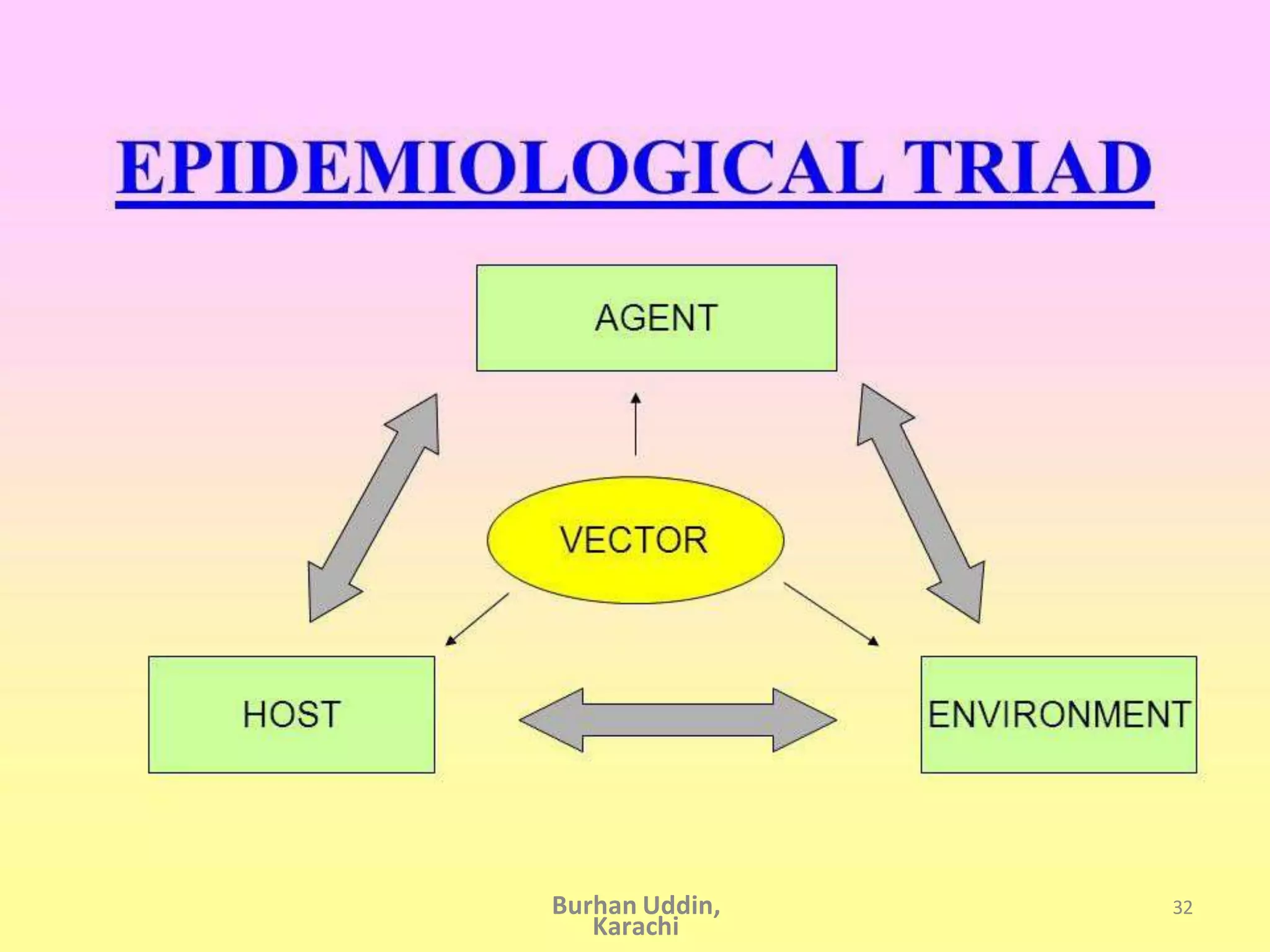
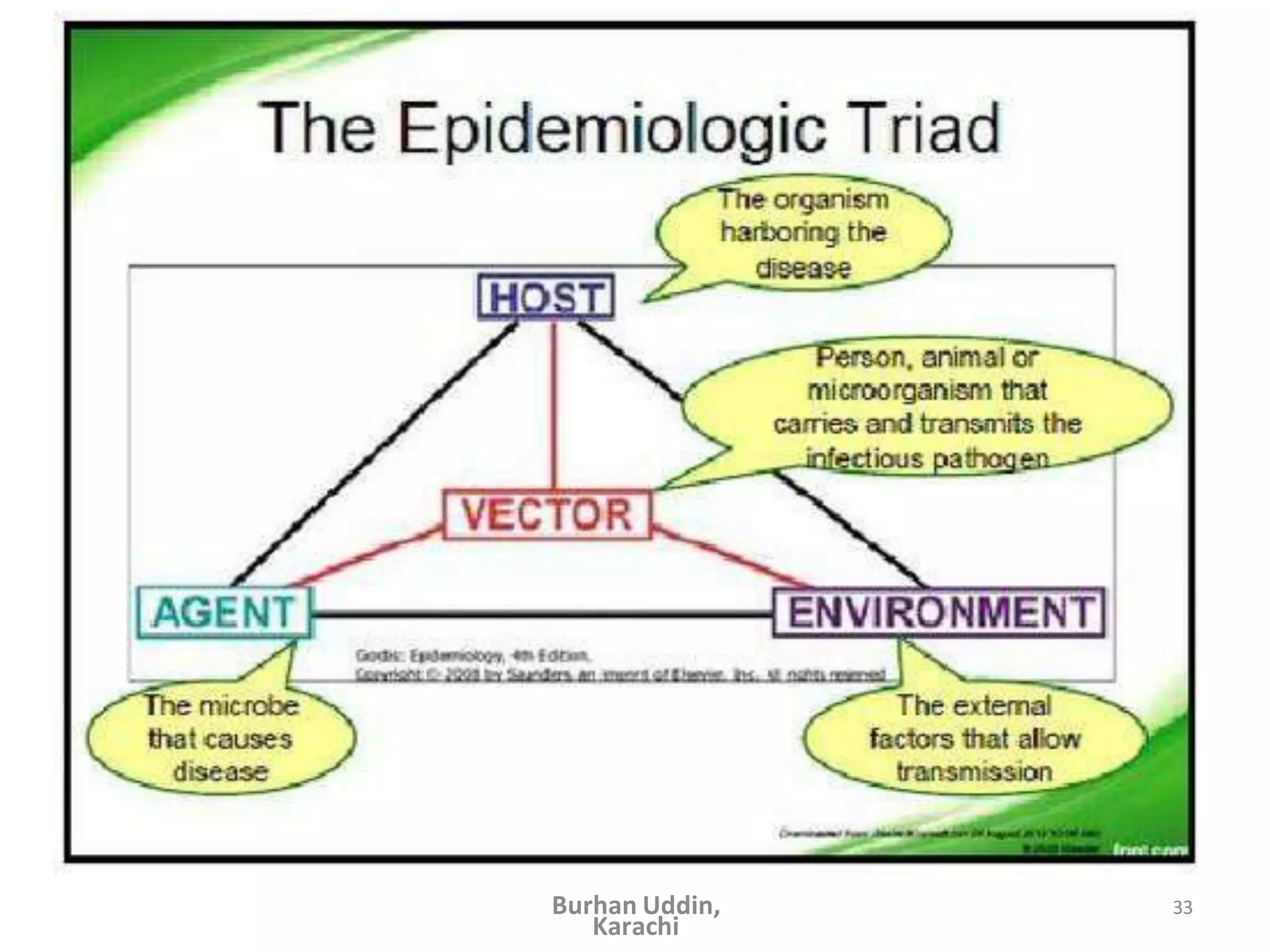
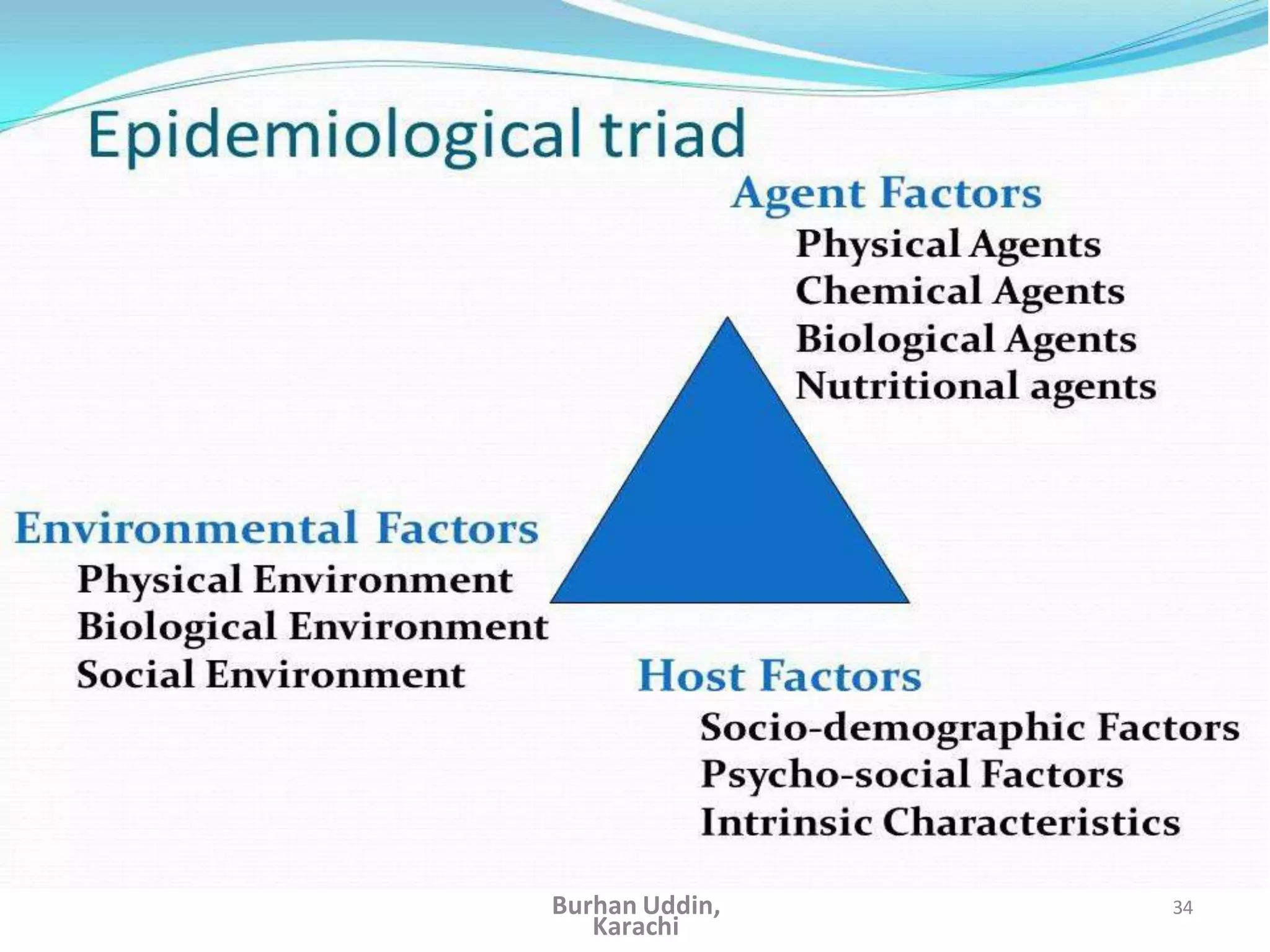
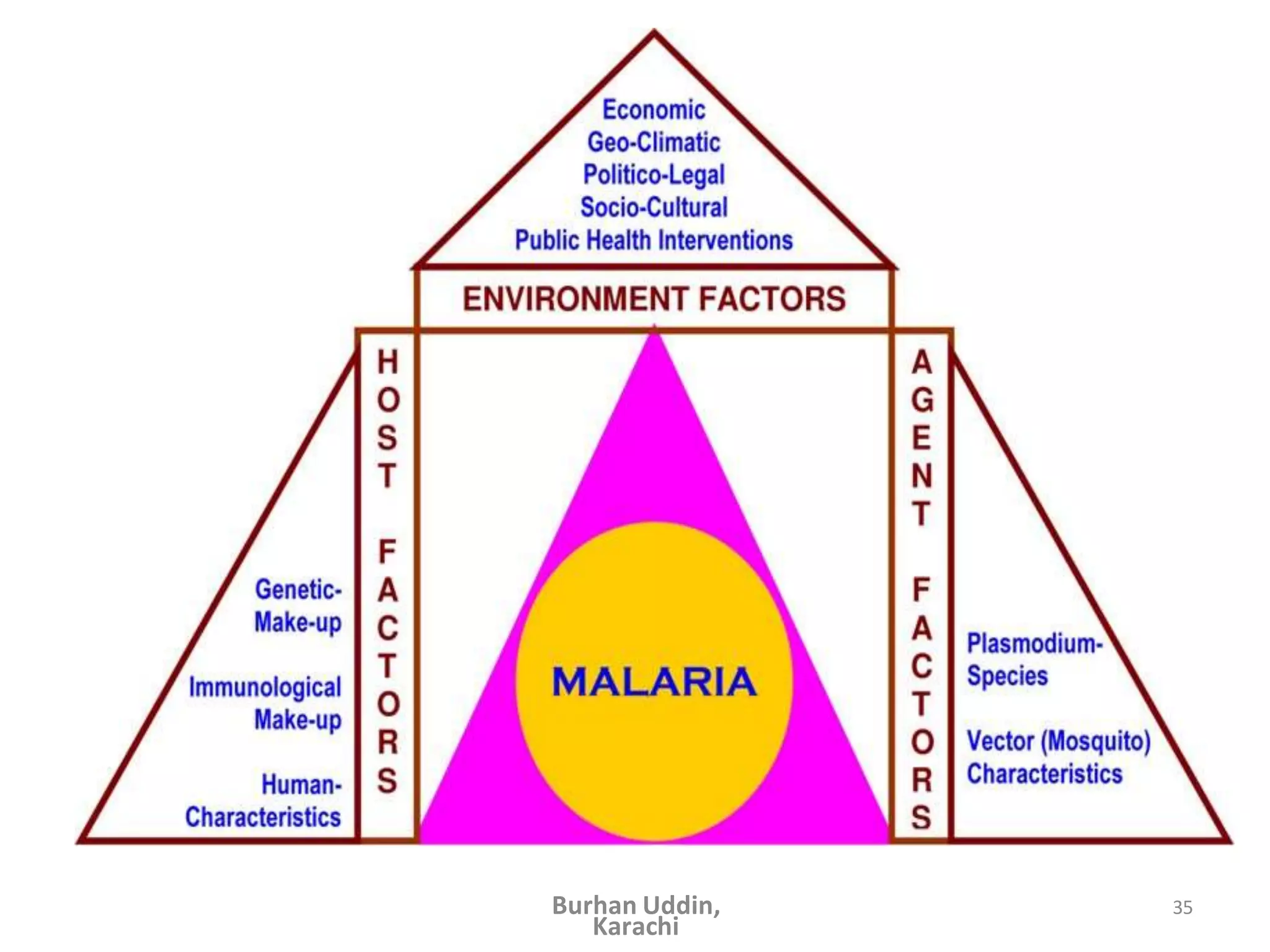
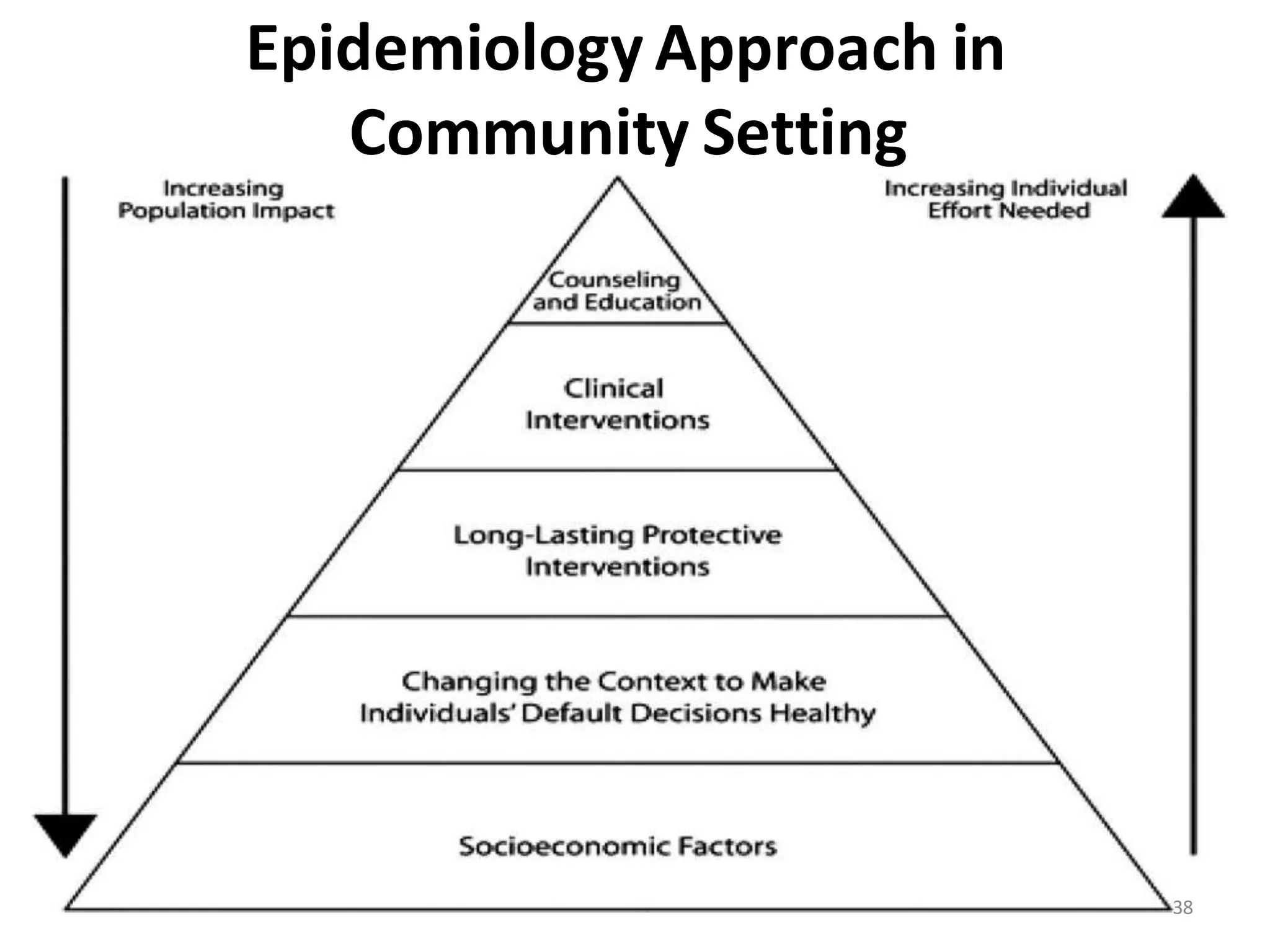
The document discusses the natural history of disease and the epidemiological triad. It defines the natural history of disease as the progression of a disease from exposure to an agent until resolution via recovery or death without intervention. There are typically stages of susceptibility, subclinical disease, clinical disease, and finally recovery, disability, or death. The epidemiological triad model describes the interaction between an external agent, host, and environment that results in disease. When these factors are not in balance, epidemics can arise. The document also notes that epidemiology examines disease patterns and causation at the community level.