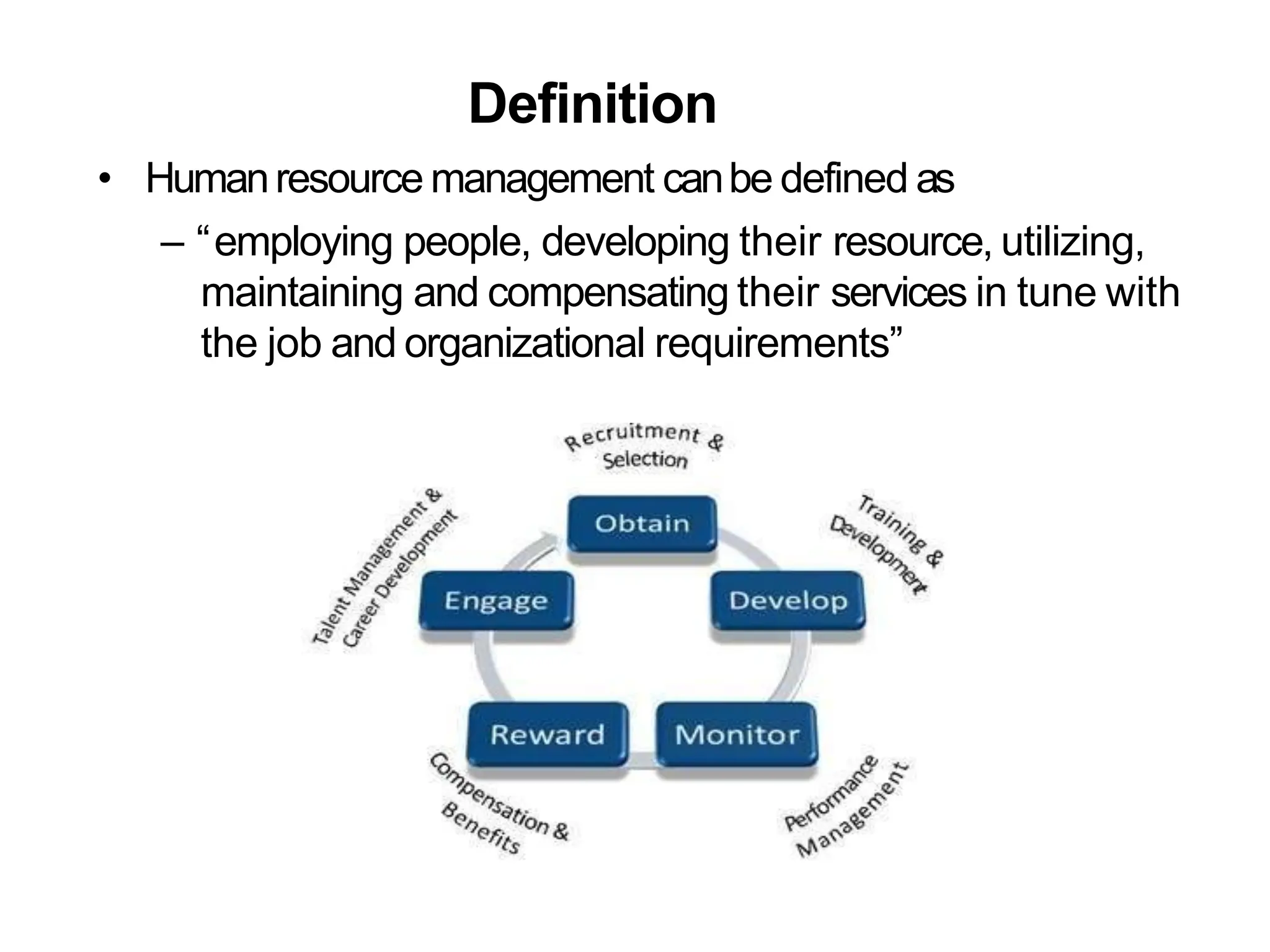
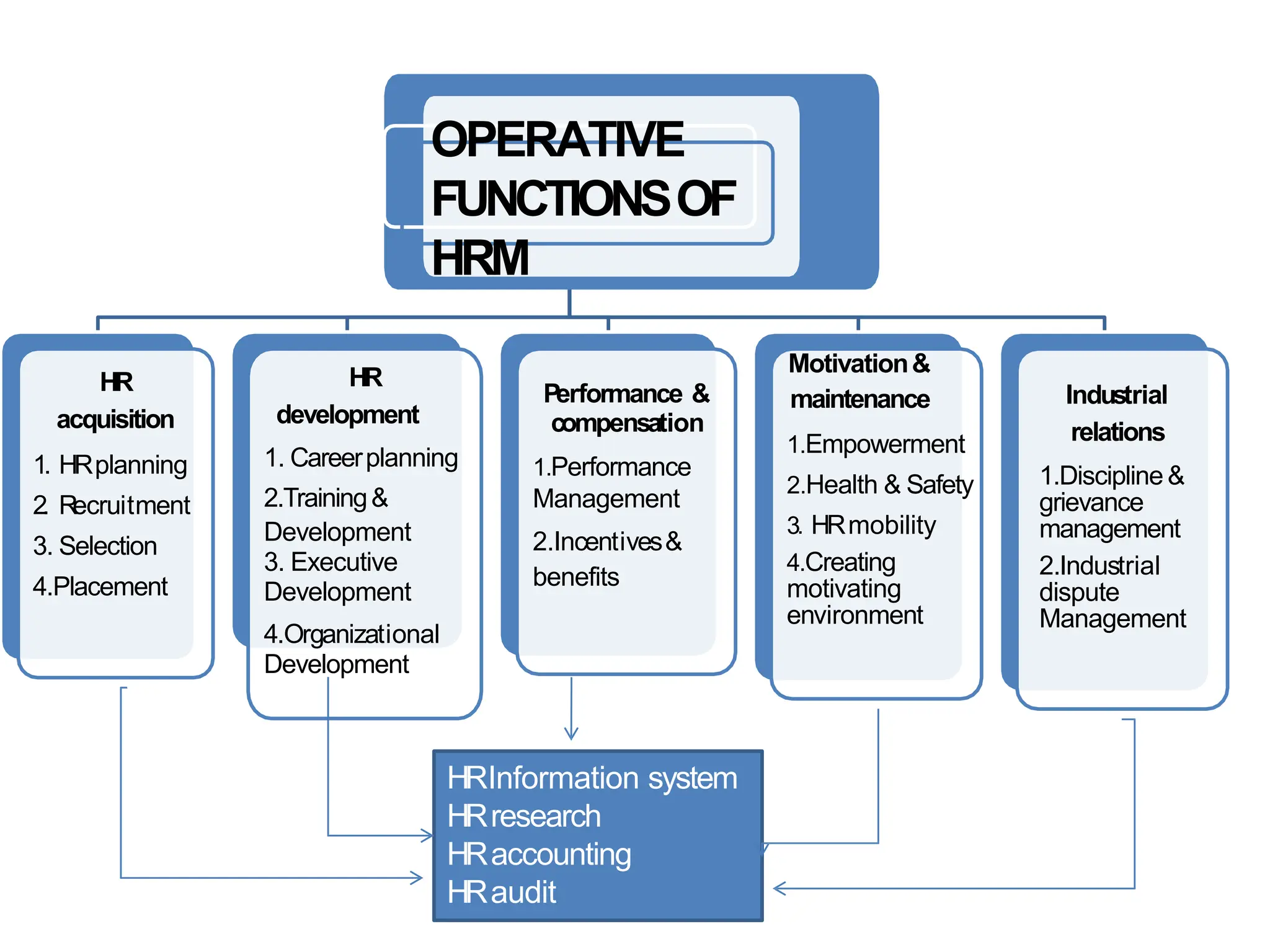
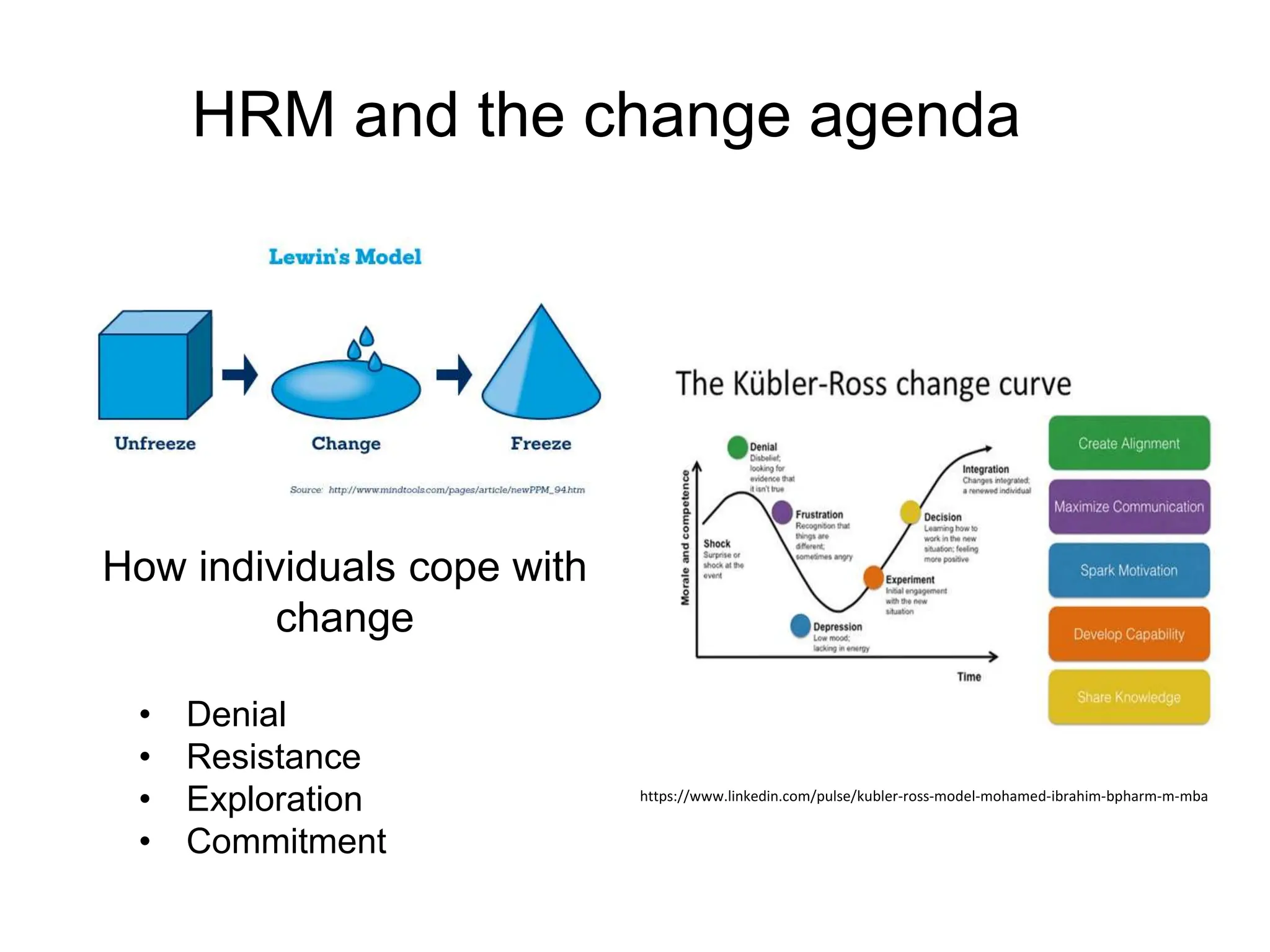
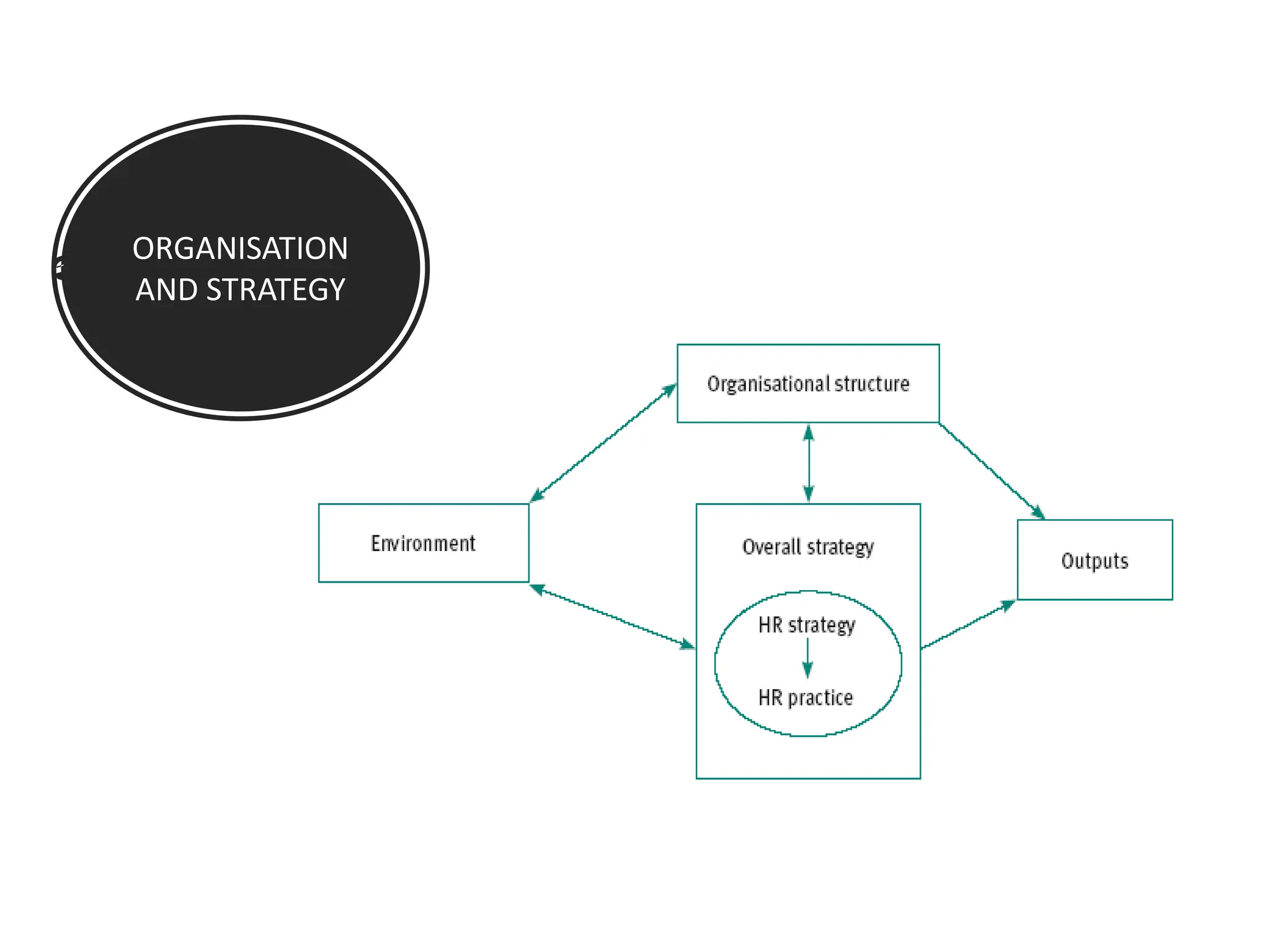
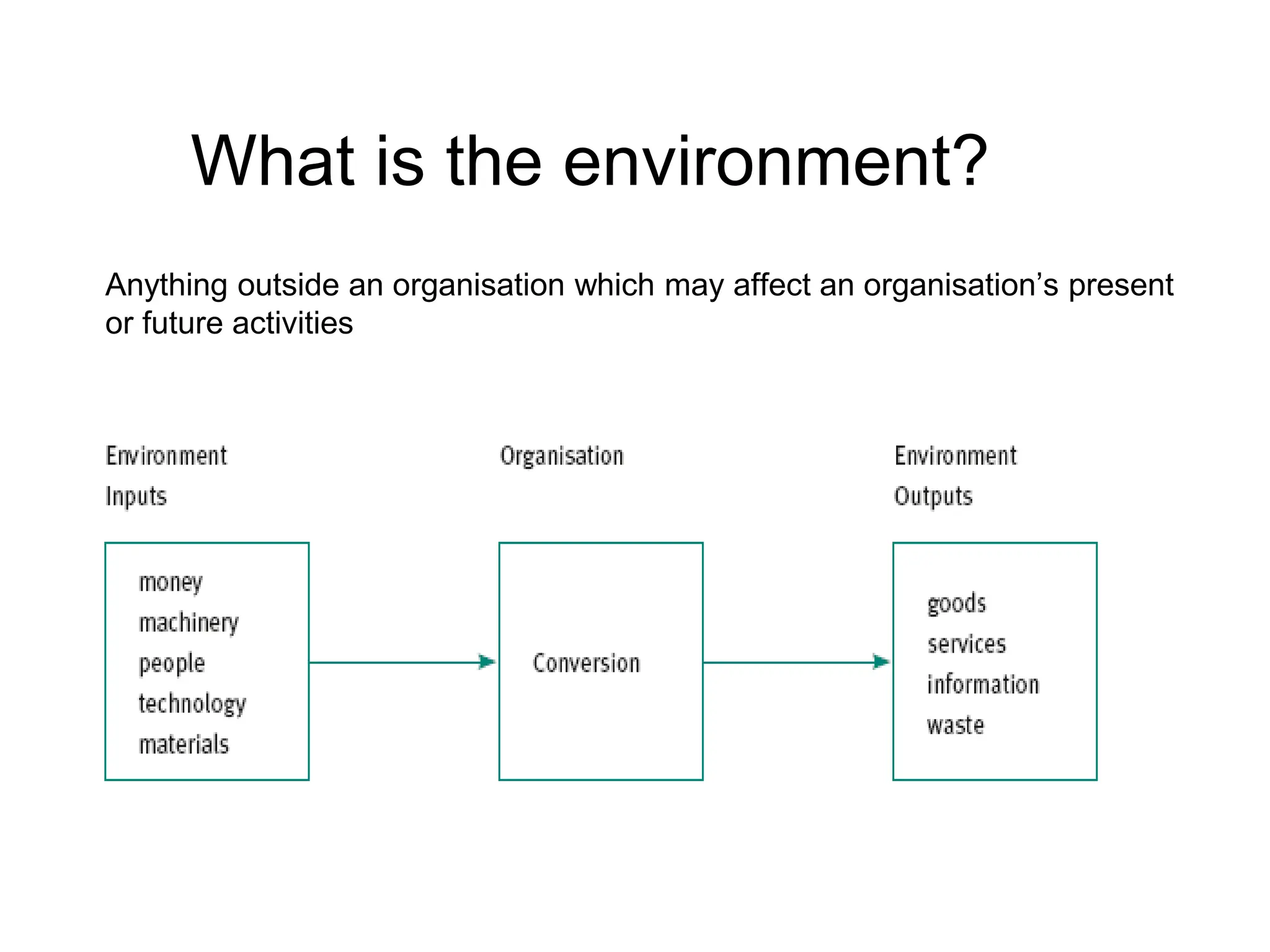
The document provides an overview of Human Resource Management (HRM), defining it as the systematic management of employment relationships and the effective utilization of human resources to meet organizational objectives. It contrasts HRM with traditional personnel management, emphasizing a strategic, employee-focused approach to acquiring, developing, and retaining talent. Additionally, it outlines the core functions, objectives, and emerging challenges faced by HR professionals in a changing work environment.