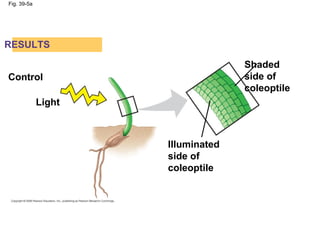
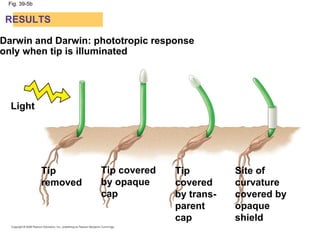
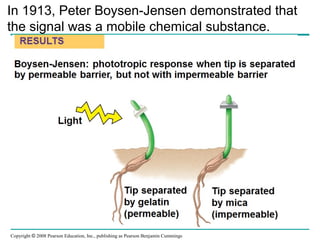
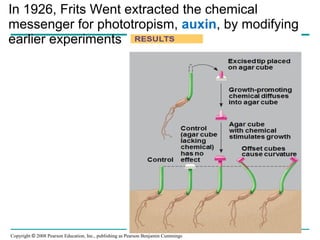
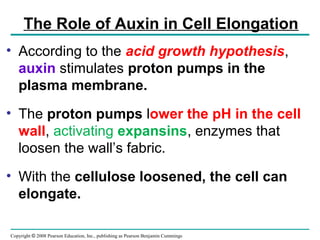
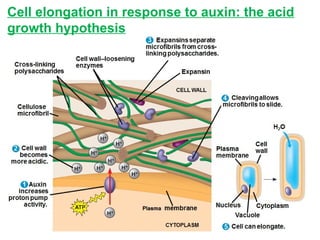
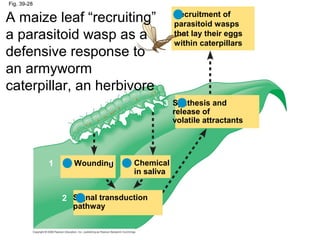
Plants respond to environmental stimuli through various morphological, physiological and developmental processes. Plants have cellular receptors that allow them to detect changes in light, gravity and the environment. Key responses include phototropism, which involves the plant hormone auxin and causes plants to bend towards light, and tropisms like gravitropism. Plants also have biological clocks and show circadian rhythms, and use photoperiodism to detect seasons and trigger processes like flowering. Plants respond to stresses through processes like closing stomata during drought and producing heat shock proteins under heat stress. They defend against herbivores and pathogens through physical defenses and chemical defenses like toxic compounds.