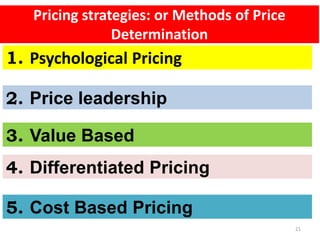
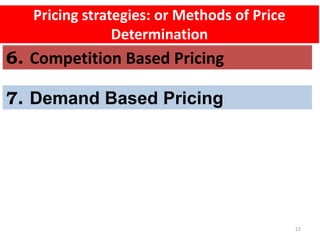
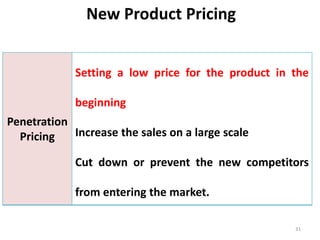
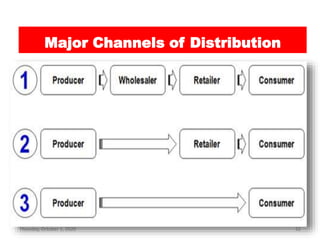
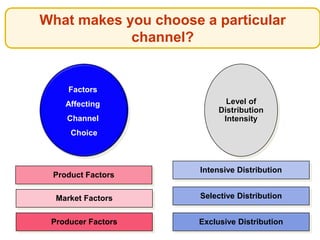
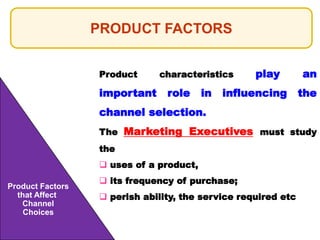
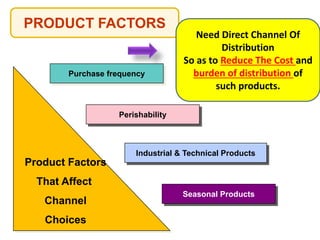
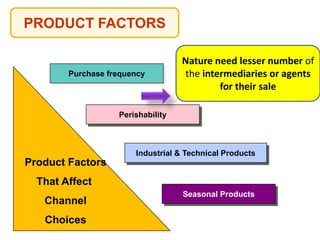
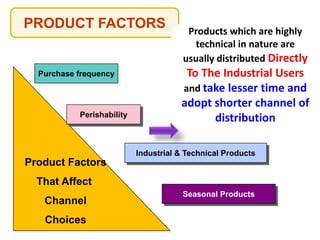
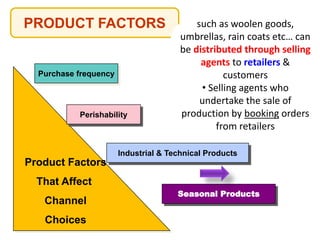
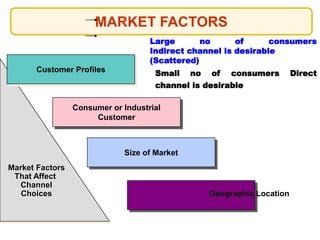
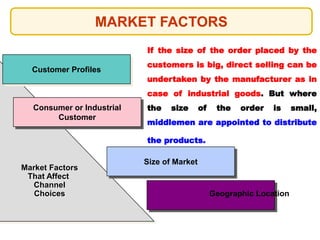
This document outlines the topics that will be covered in a marketing management course. The course will cover 6 units: Marketing Concepts, Product Decision, Price Decision, Physical Distribution Decision, Promotion Decision, and Consumer Behavior. Each unit will explore key concepts and factors related to that area of marketing. For example, the Pricing Decision unit will discuss concepts of price, factors affecting price determination, pricing policies and types of price. The document also provides an overview of some lecture topics within each unit, such as new product development, branding, pricing strategies, and distribution channels.