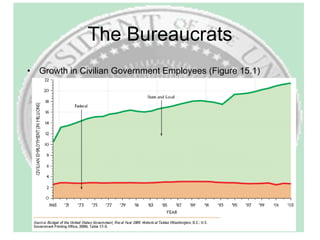
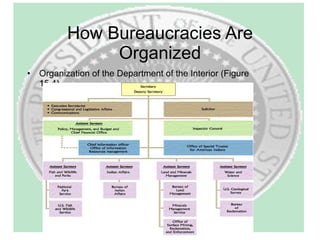
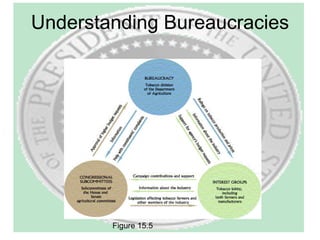
The document provides an overview of the executive branch of the US government according to Article II of the Constitution. It discusses the basic structure and roles of the presidency, vice presidency, cabinet, White House staff, civil service, and major agencies. Key points covered include the qualifications for president, duties like chief of government and commander-in-chief, and how early presidents like Washington, Adams, and Jefferson shaped the office. It also summarizes trends in perceptions of presidential power over time.