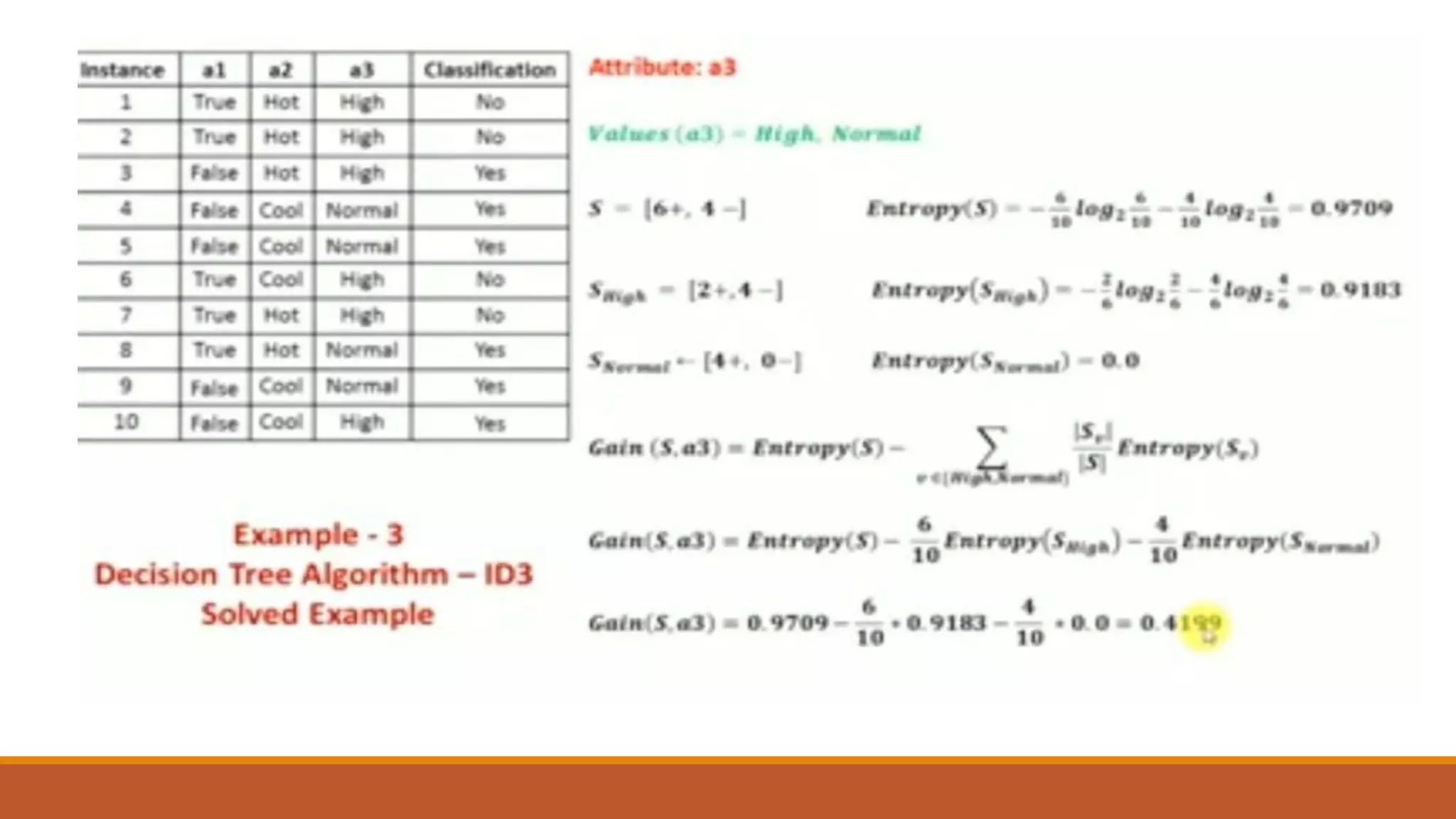
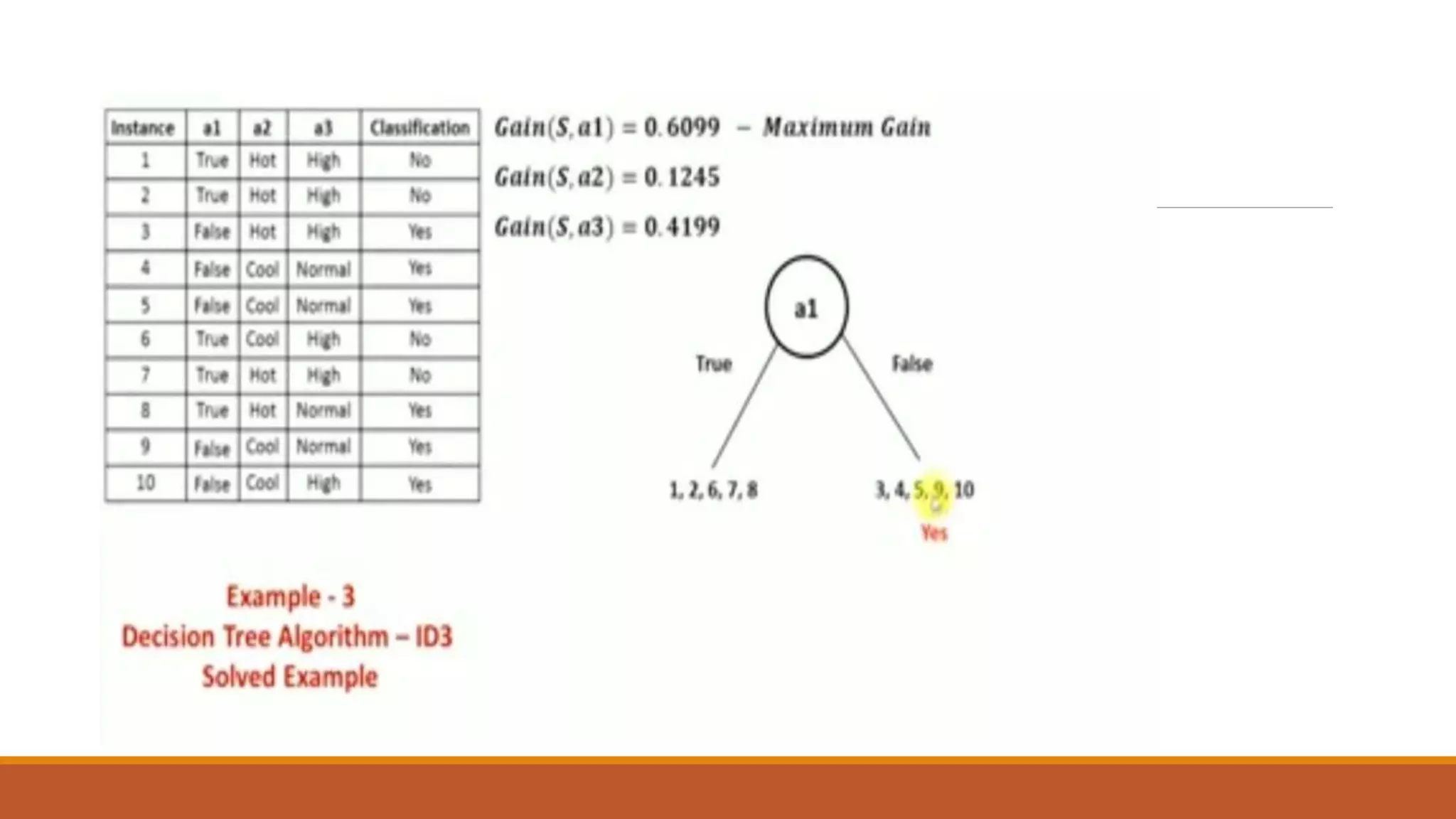
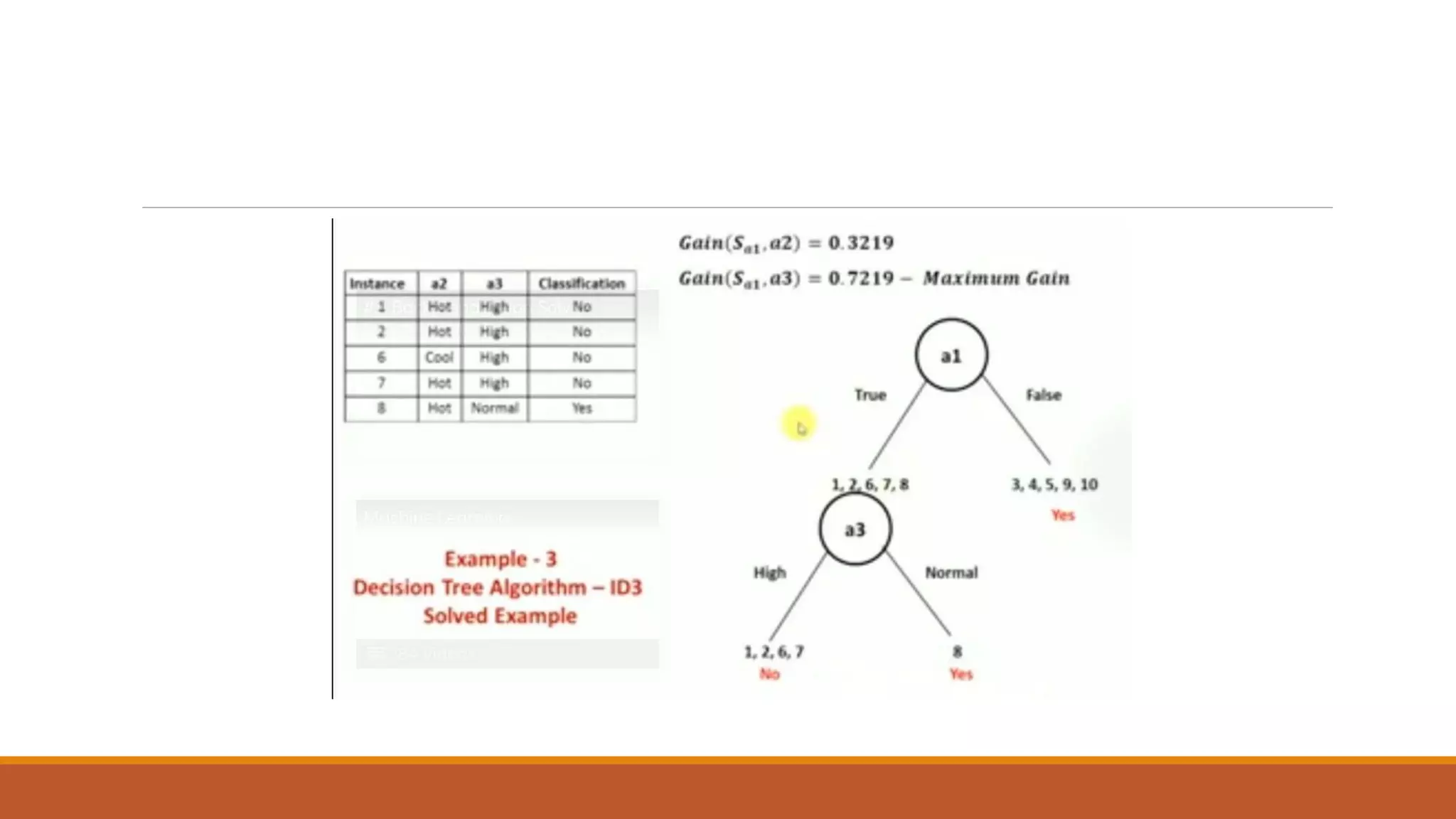
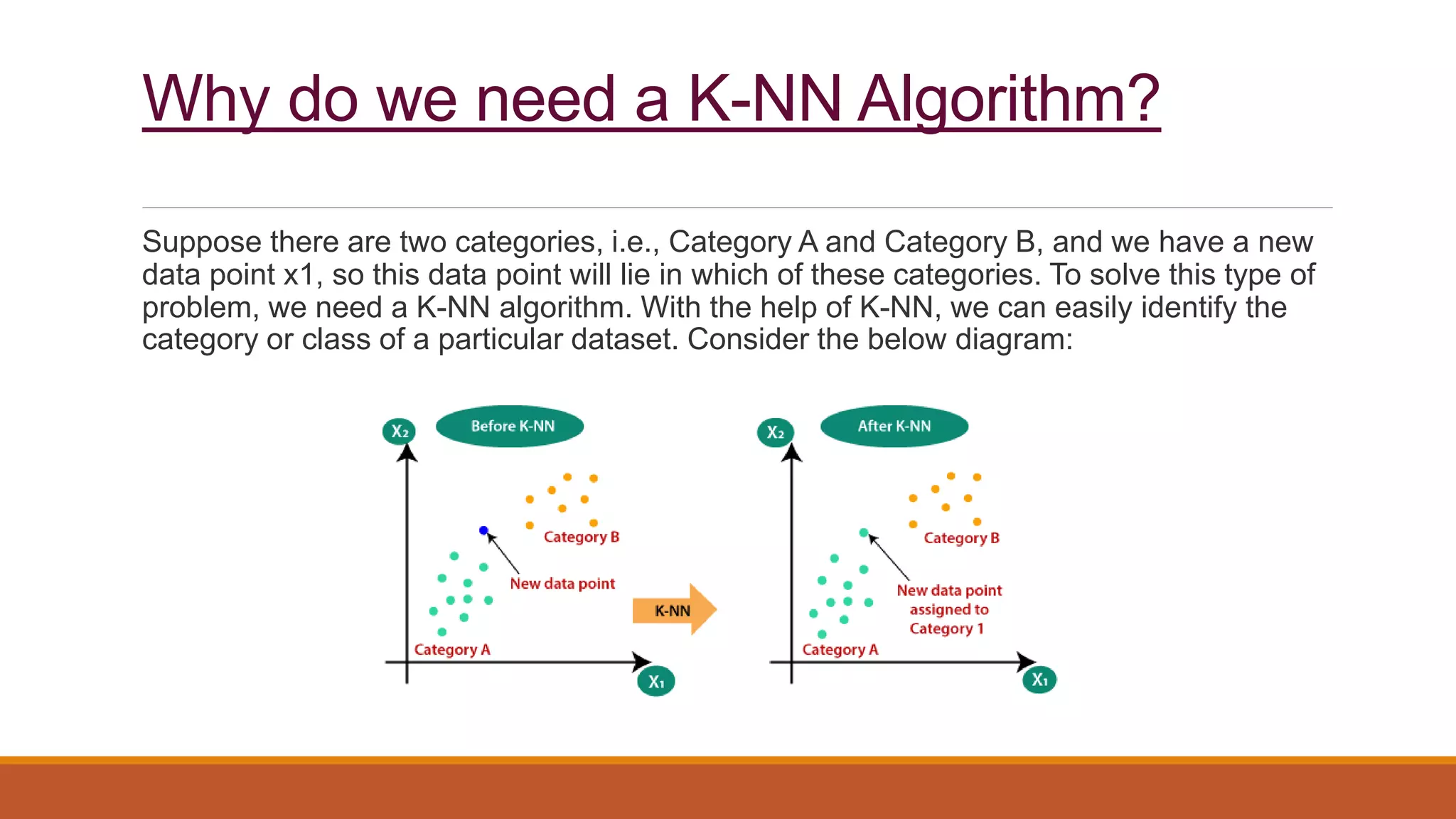
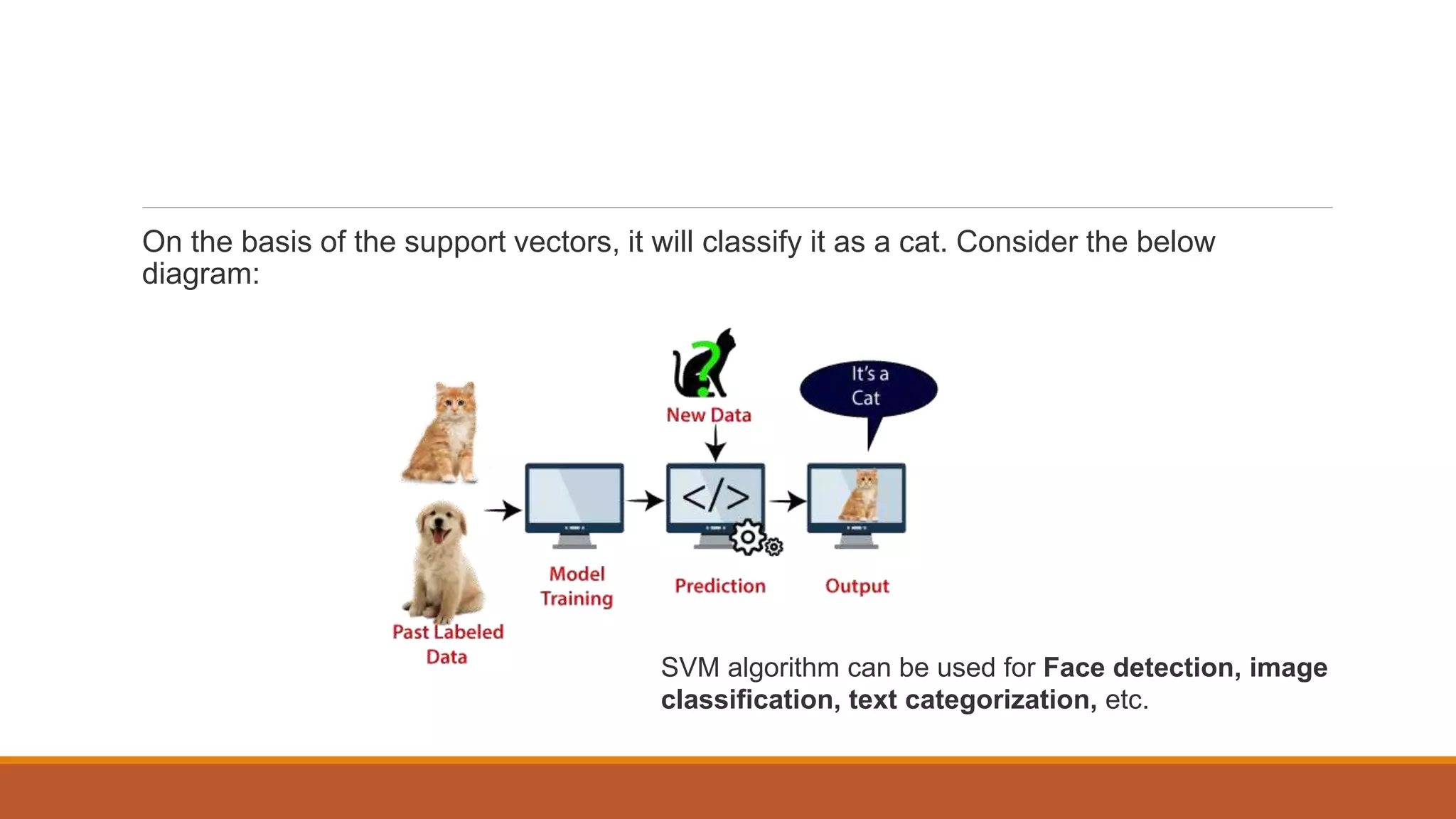
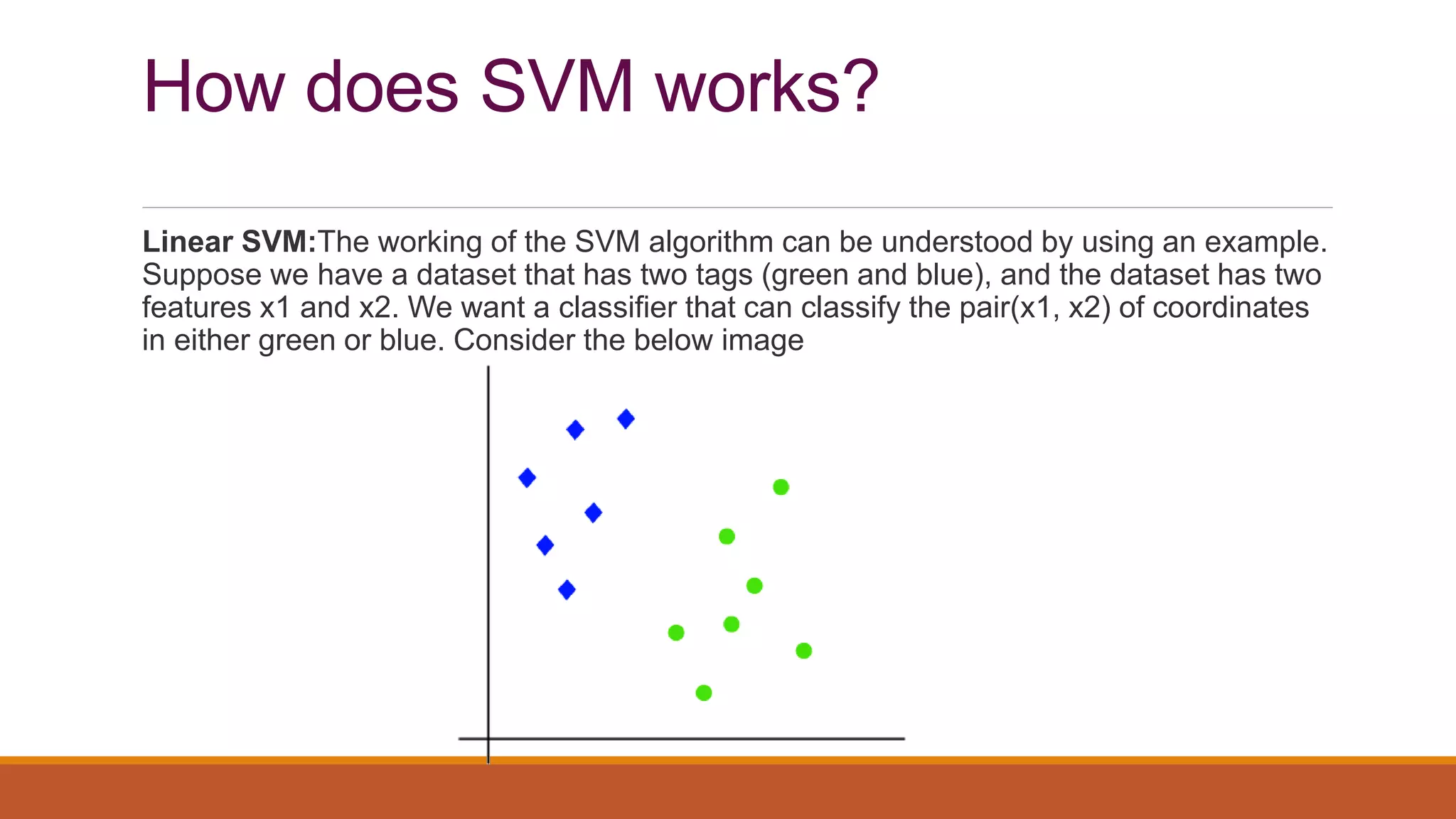
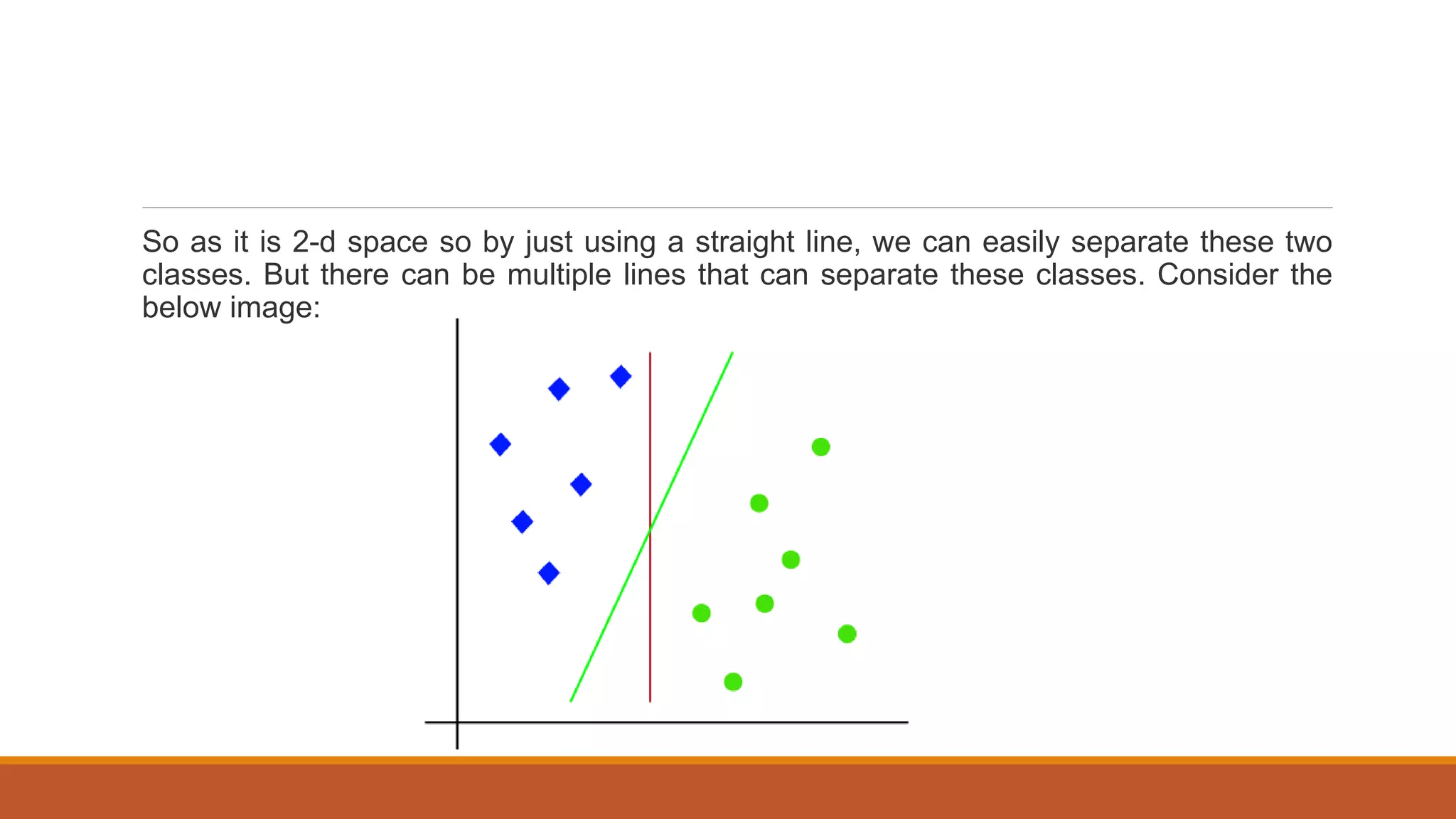
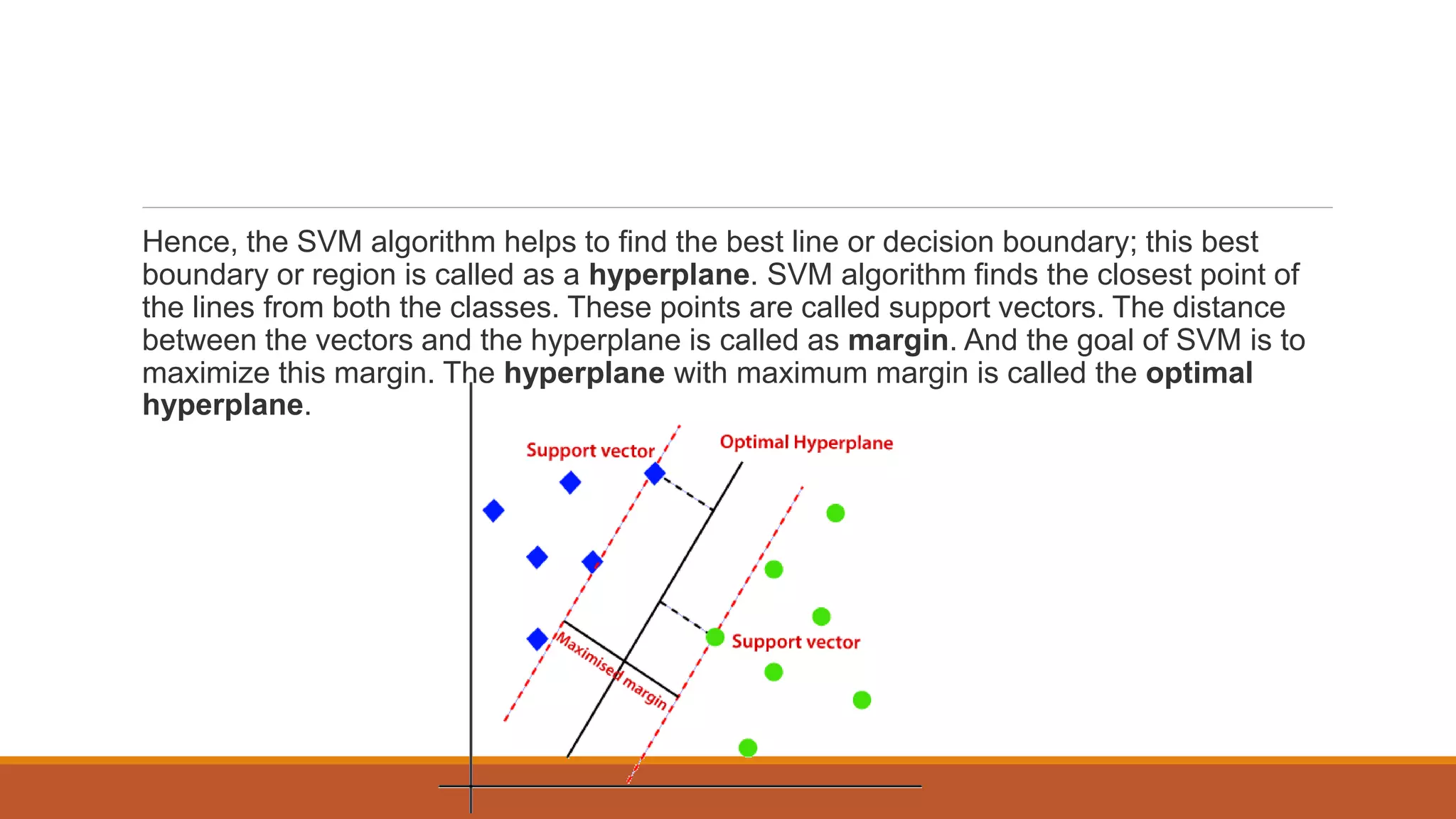
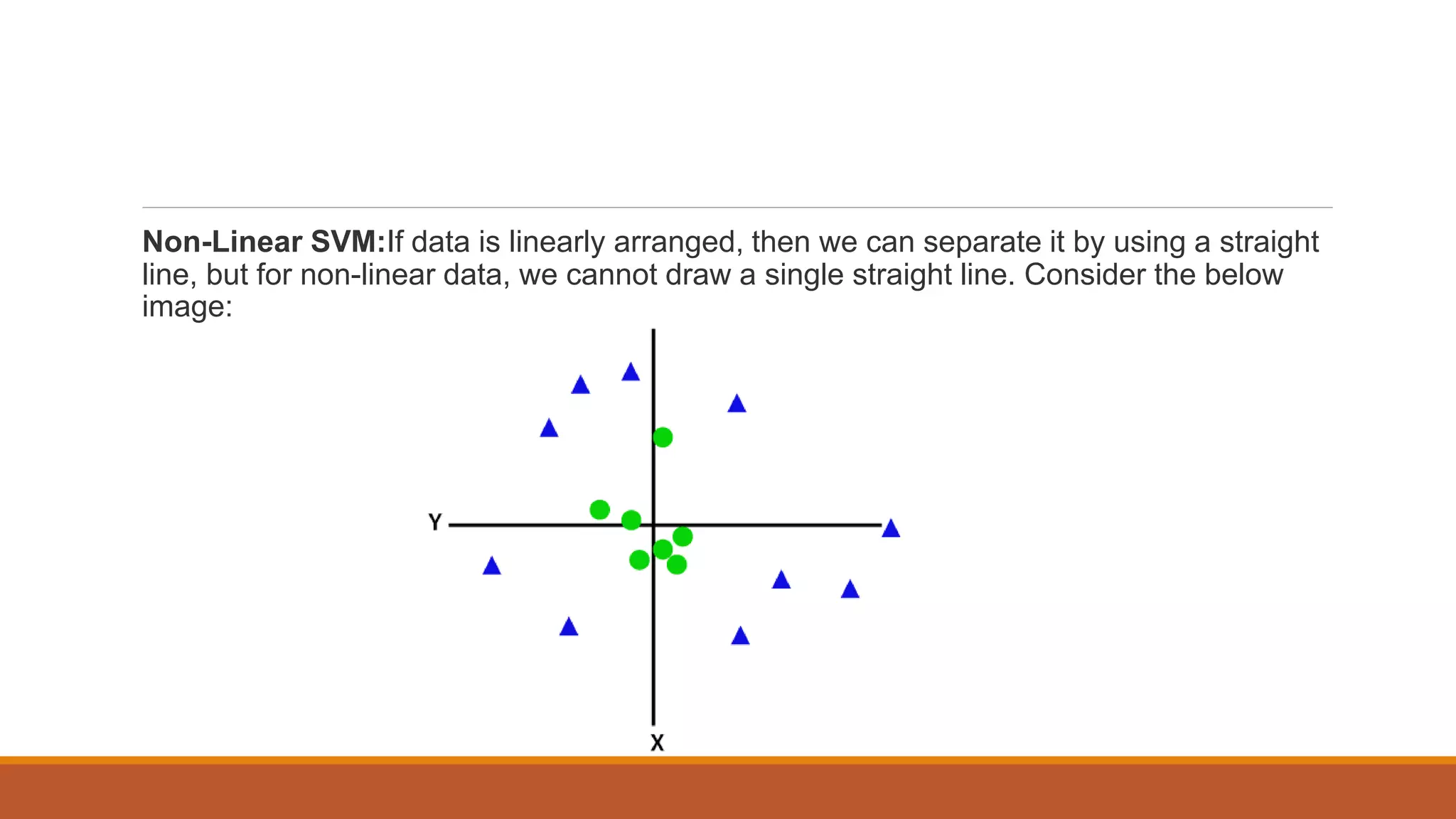
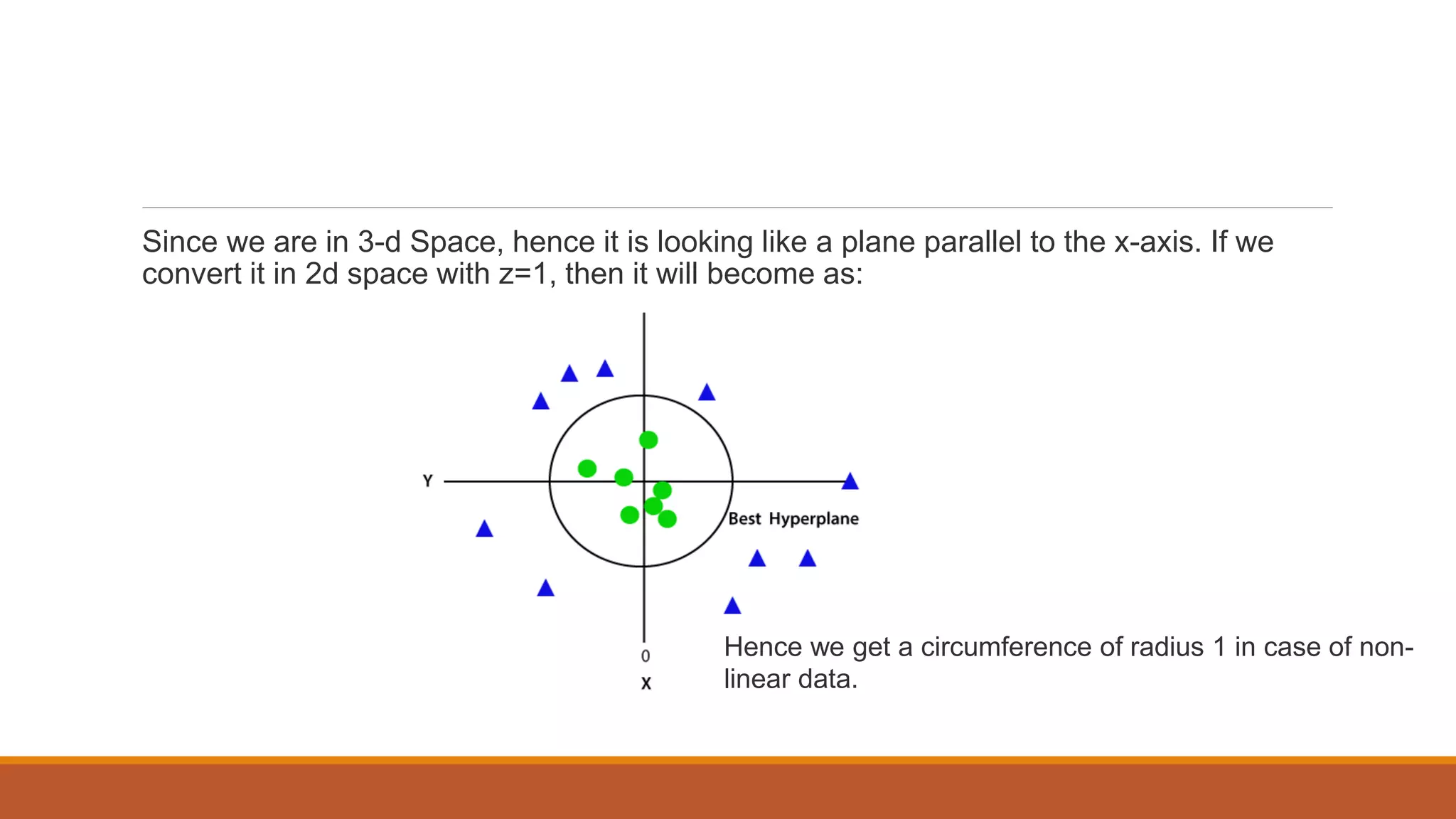
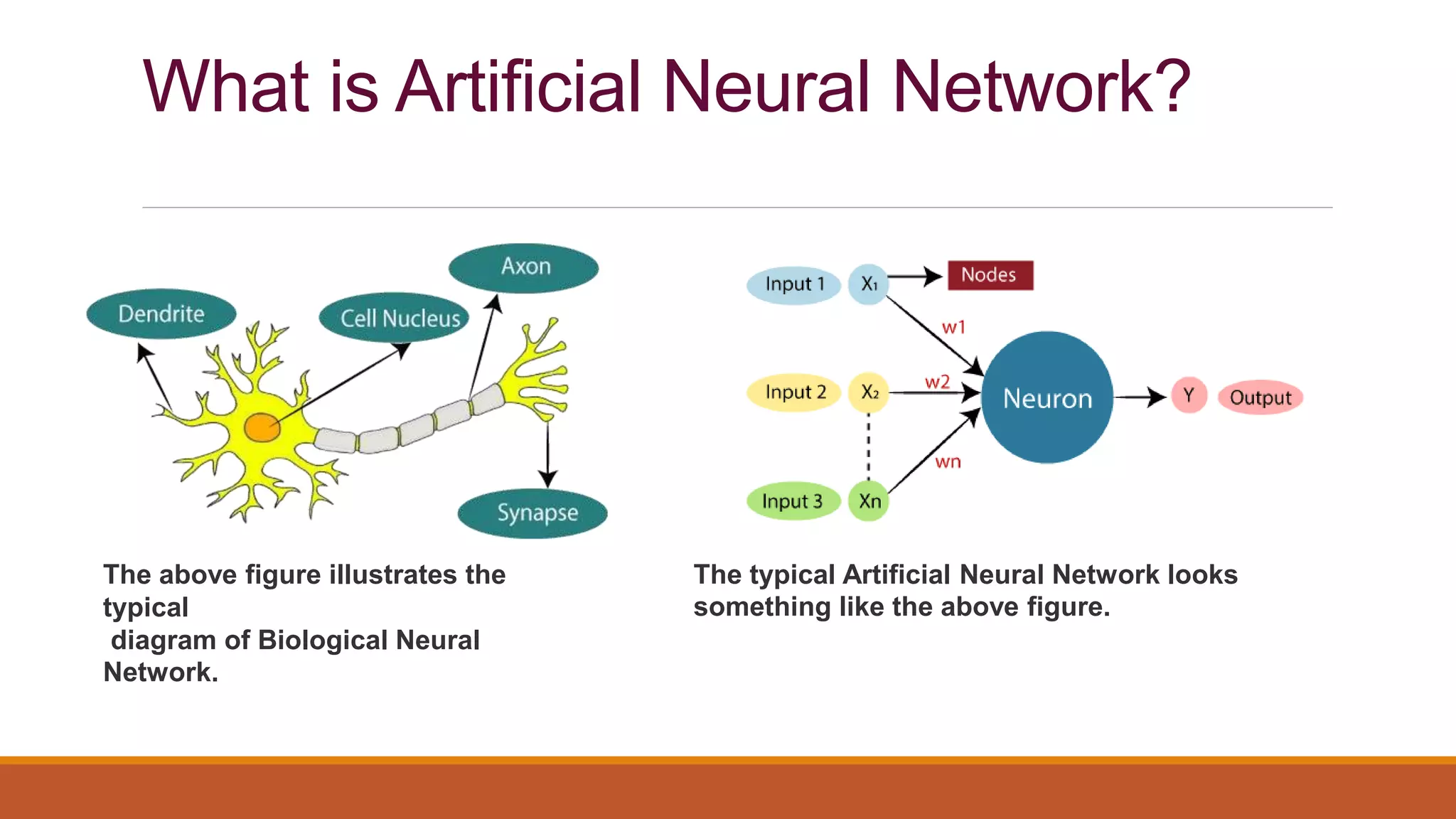
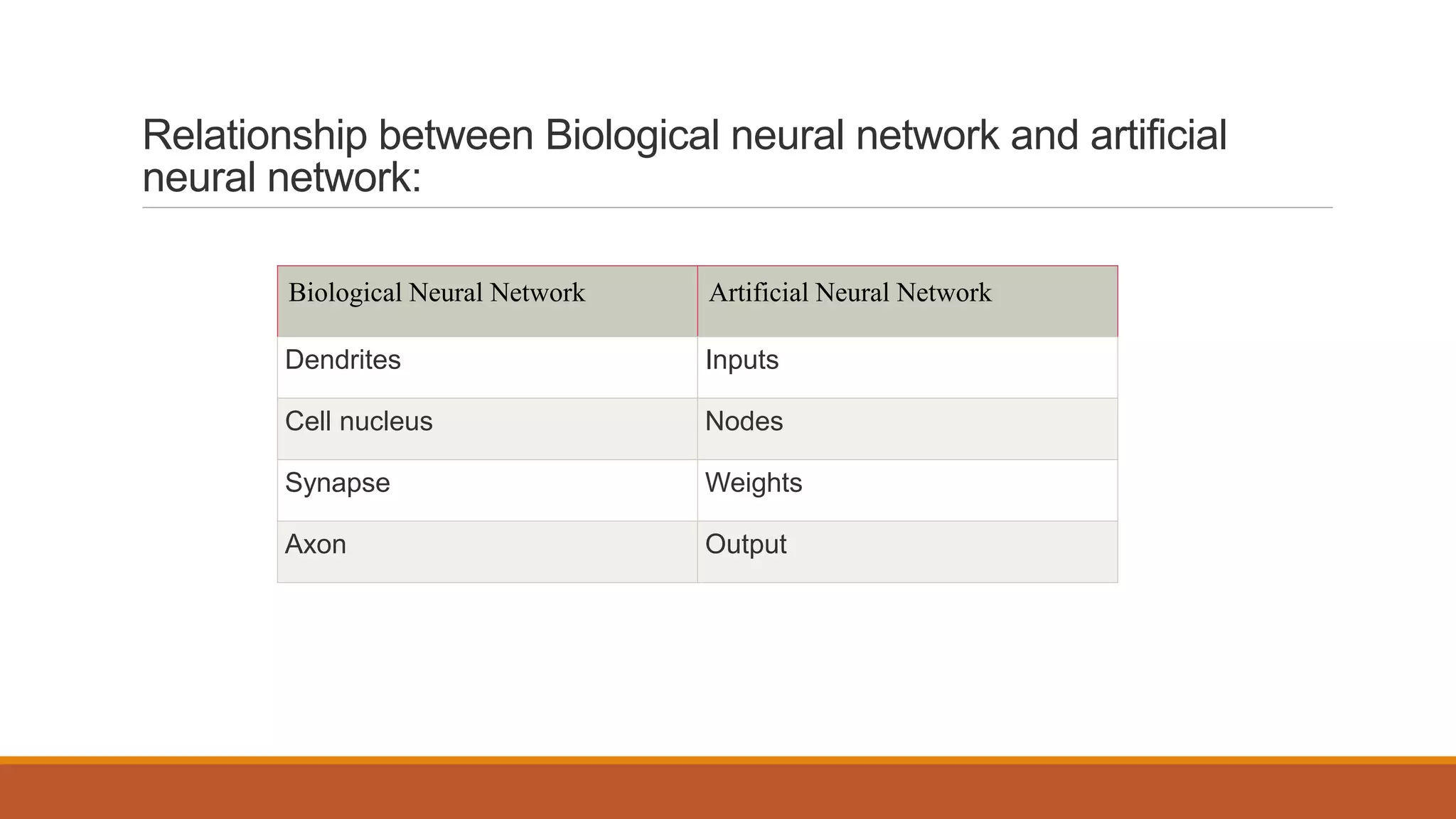
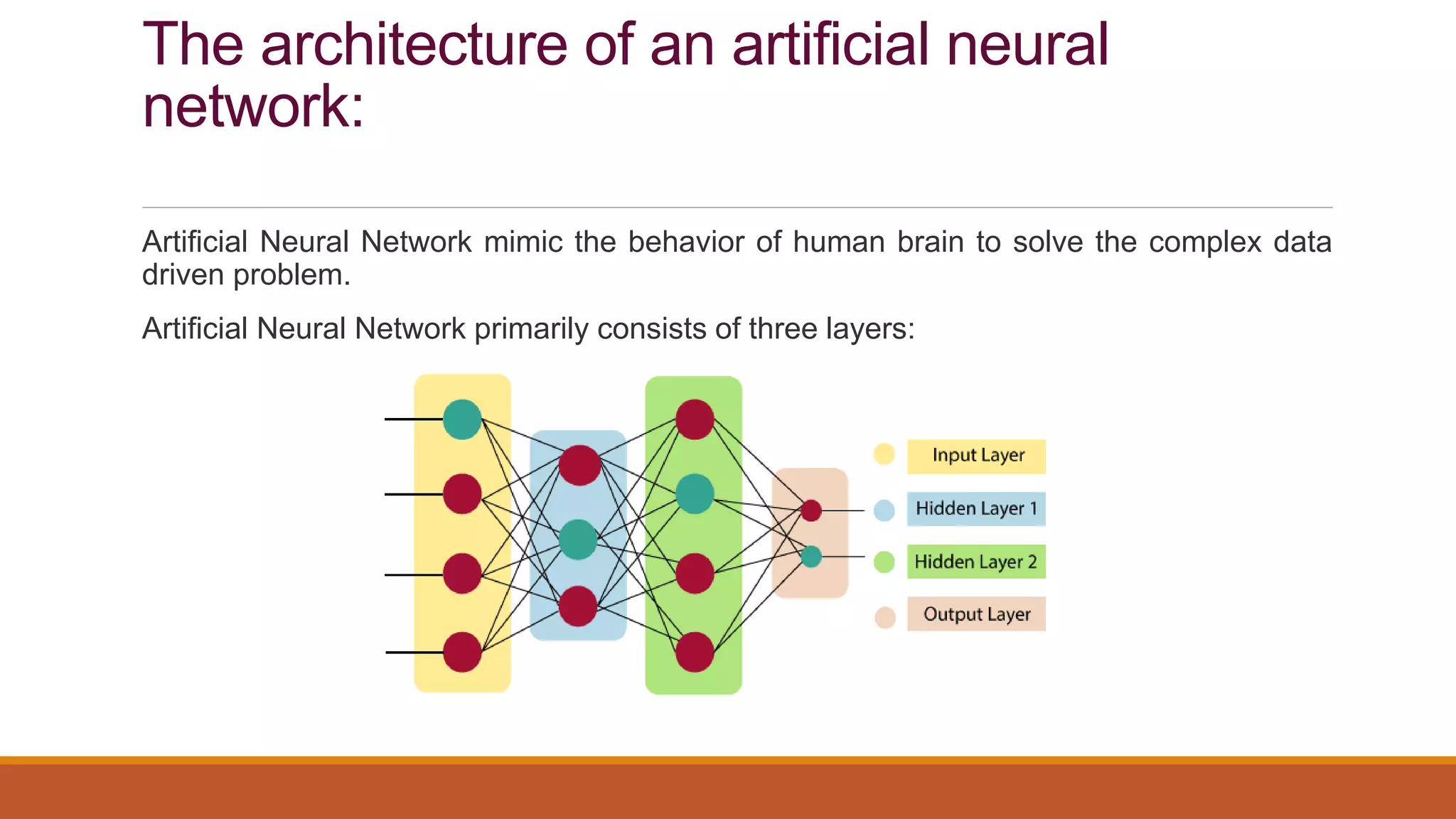
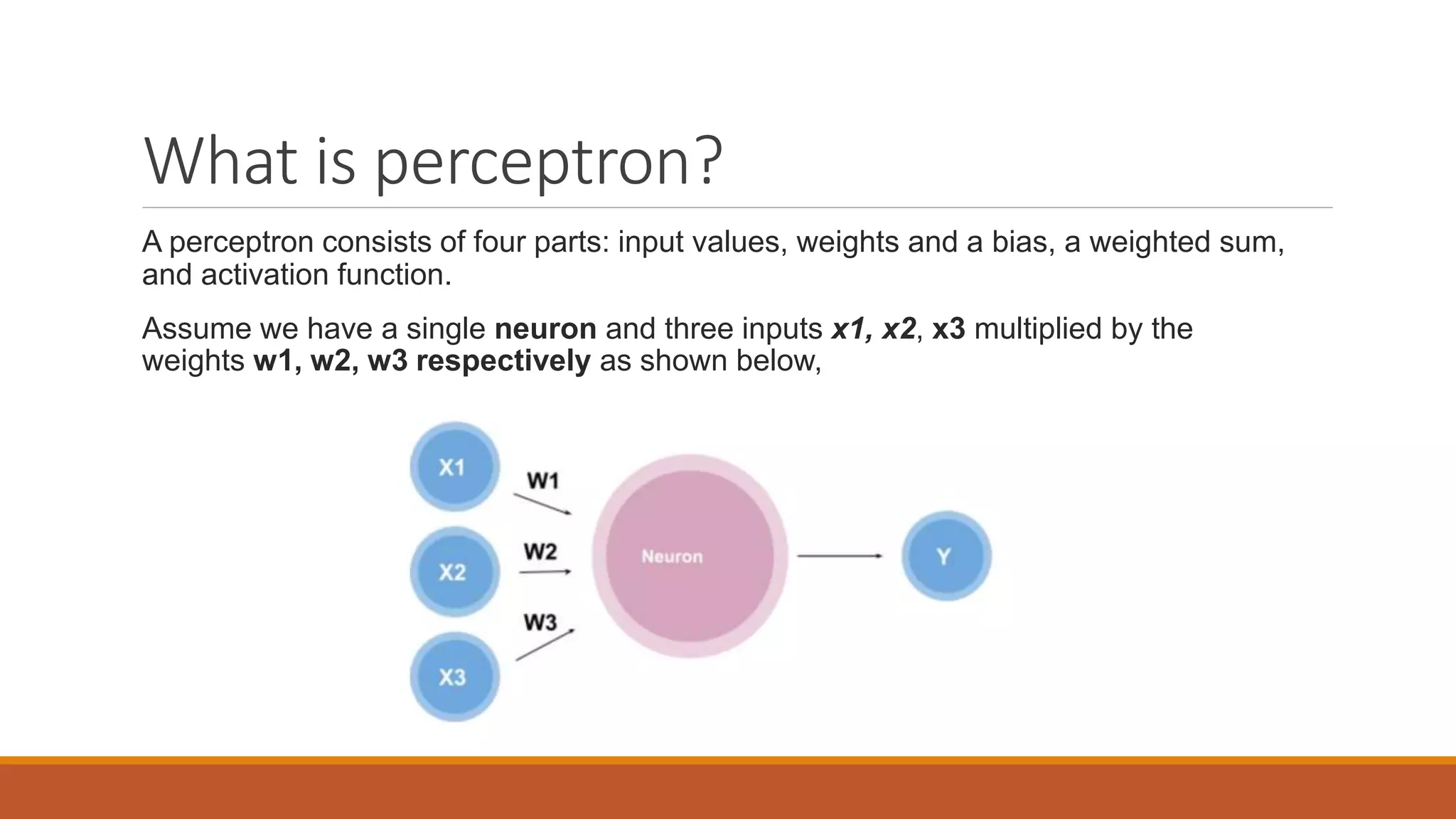
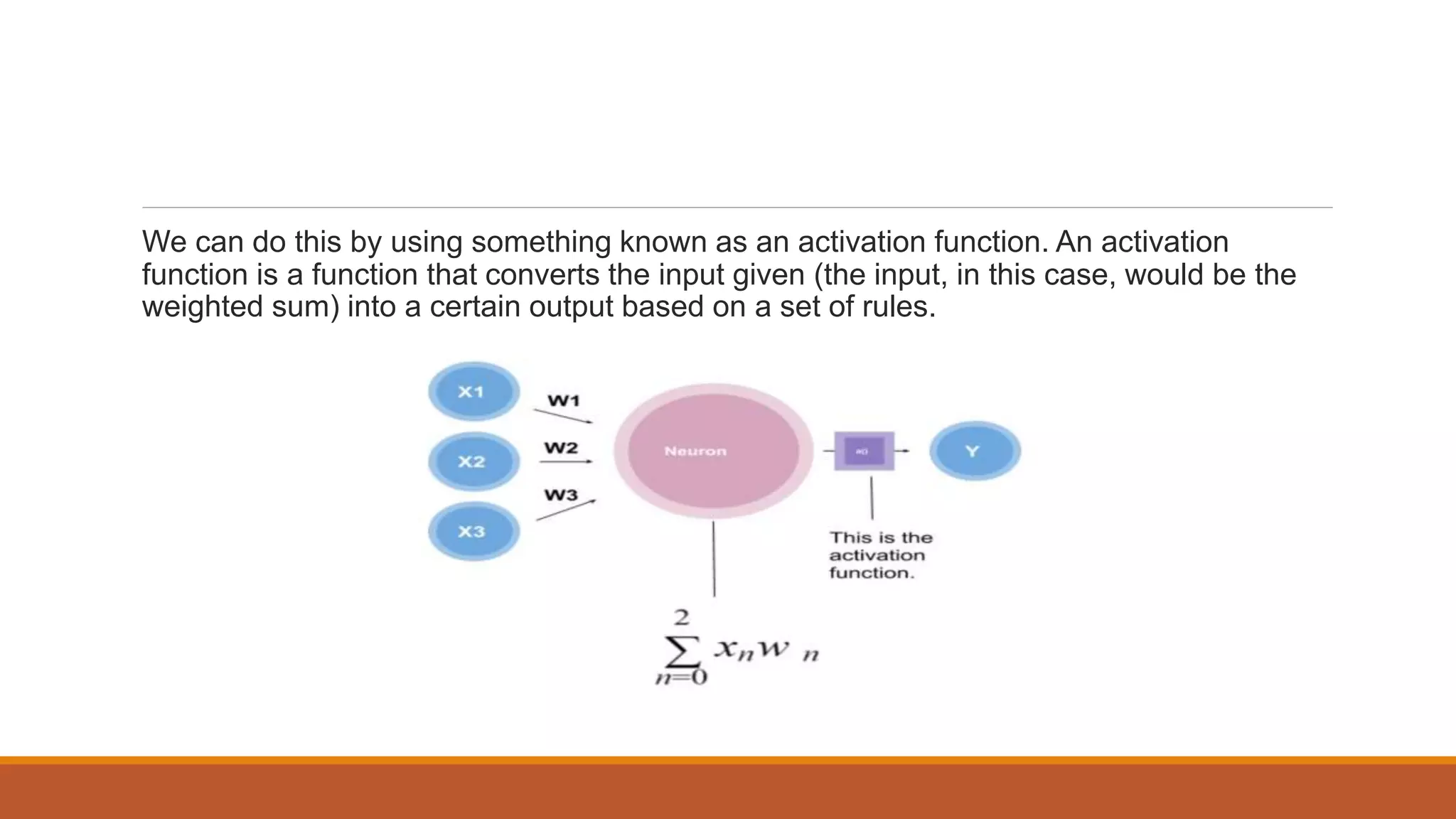
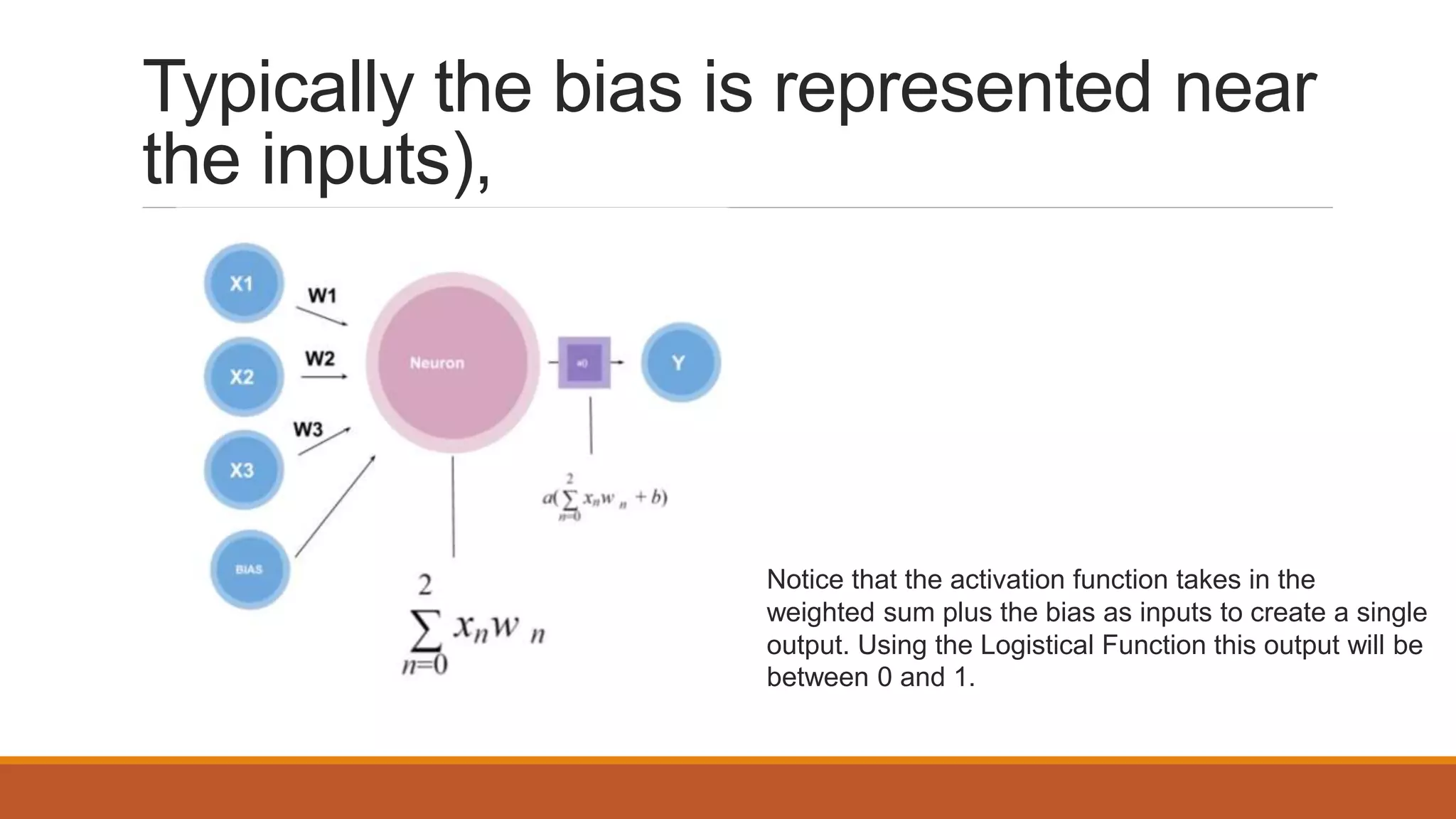
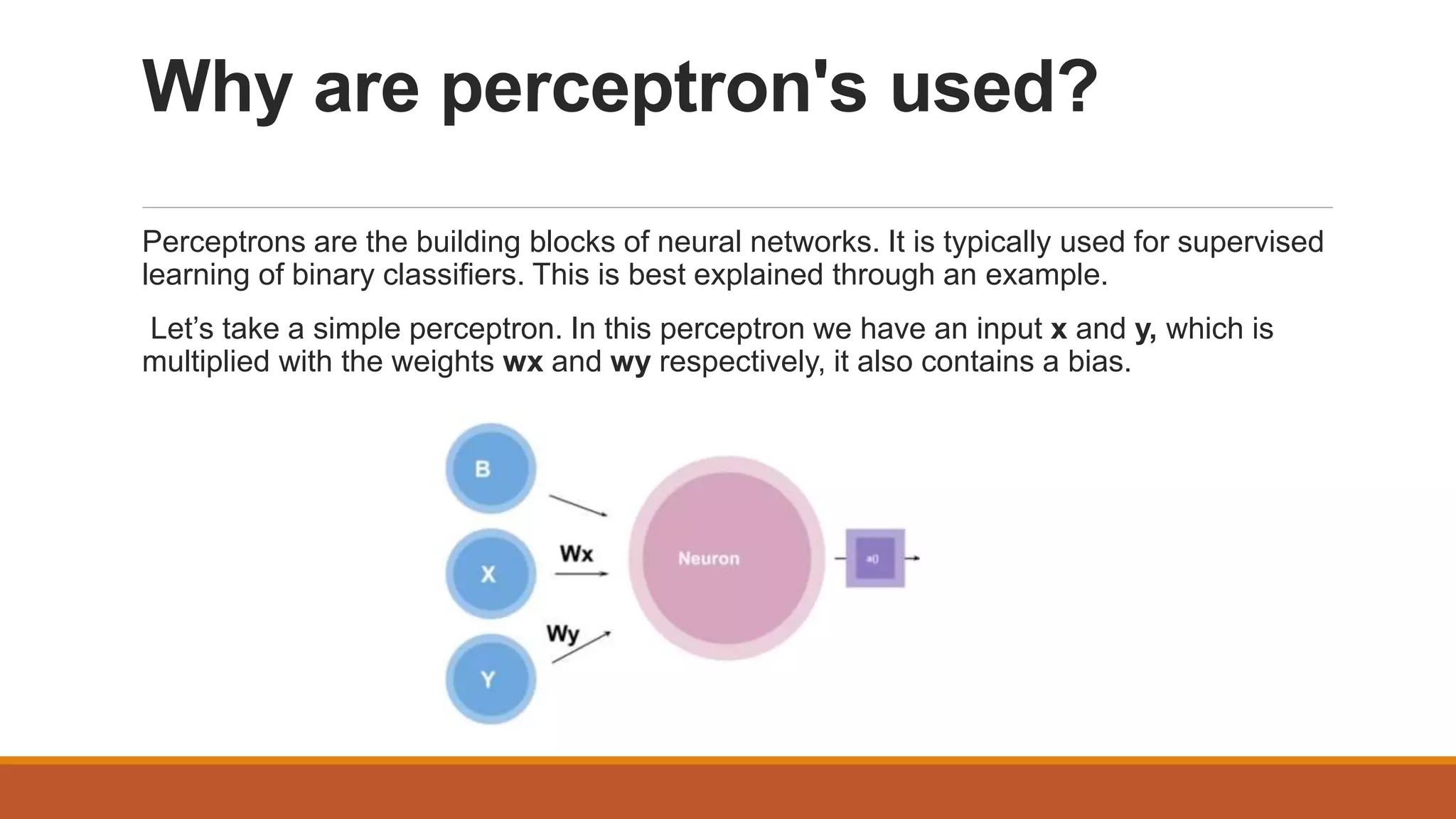
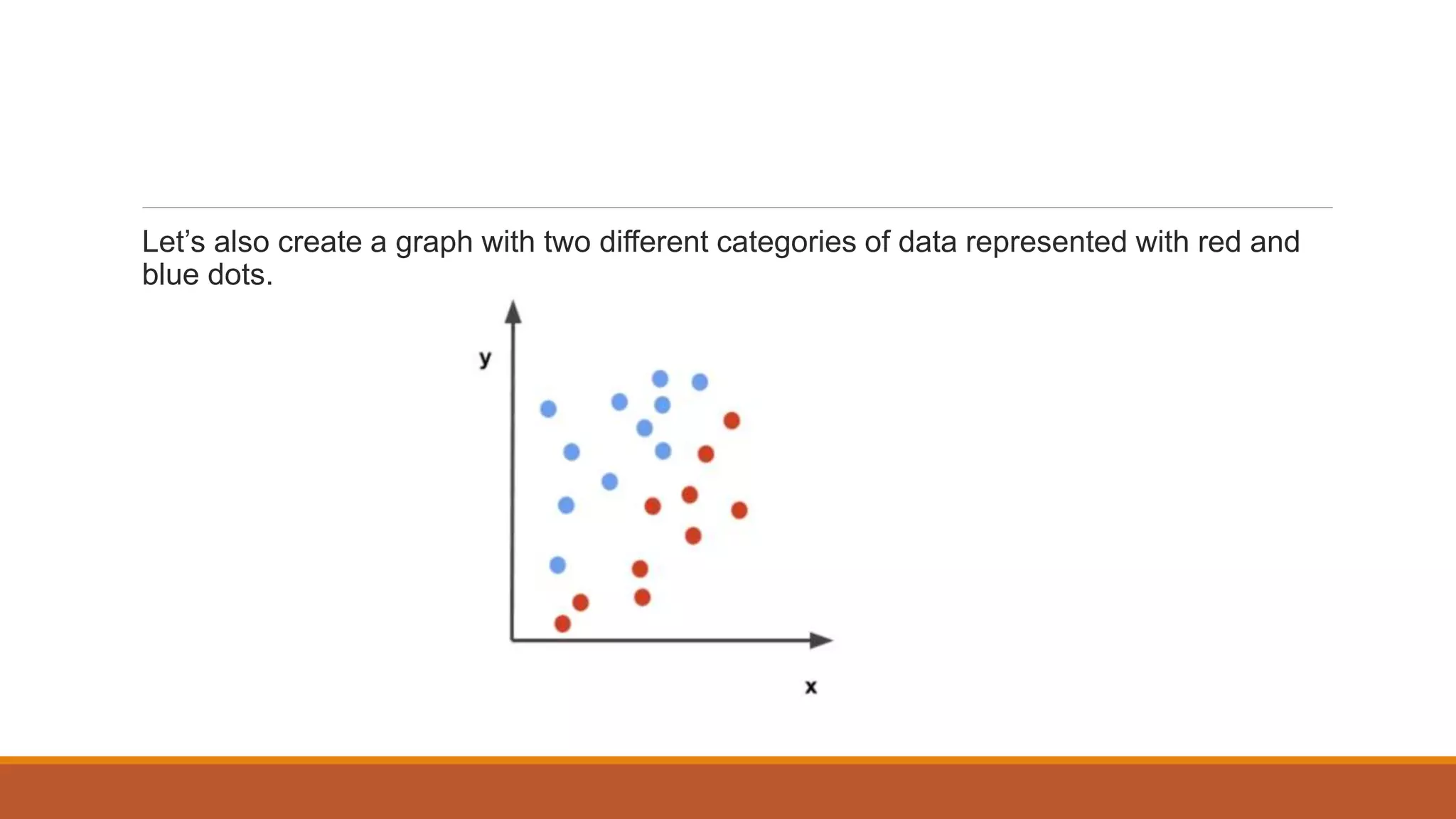
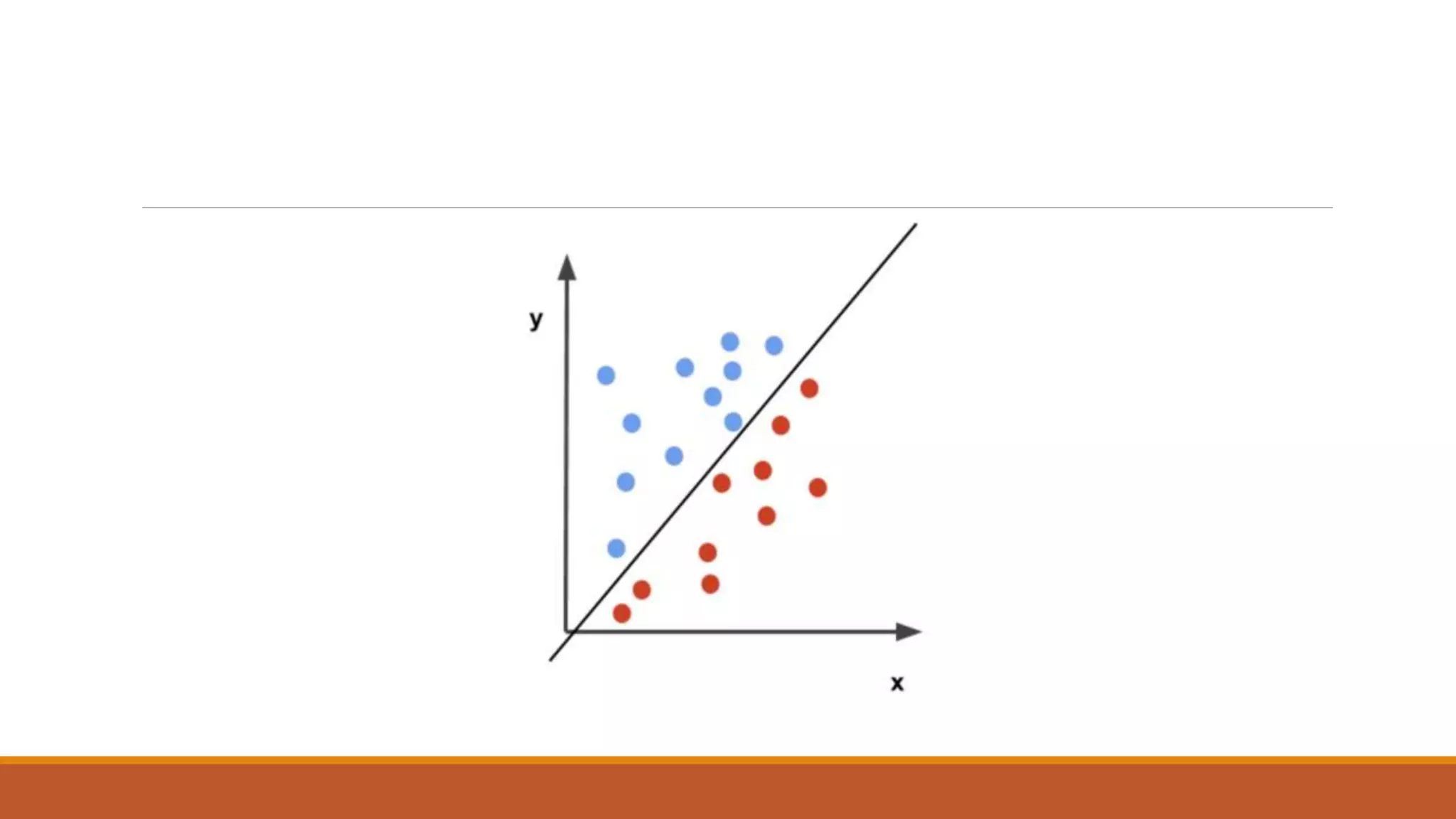
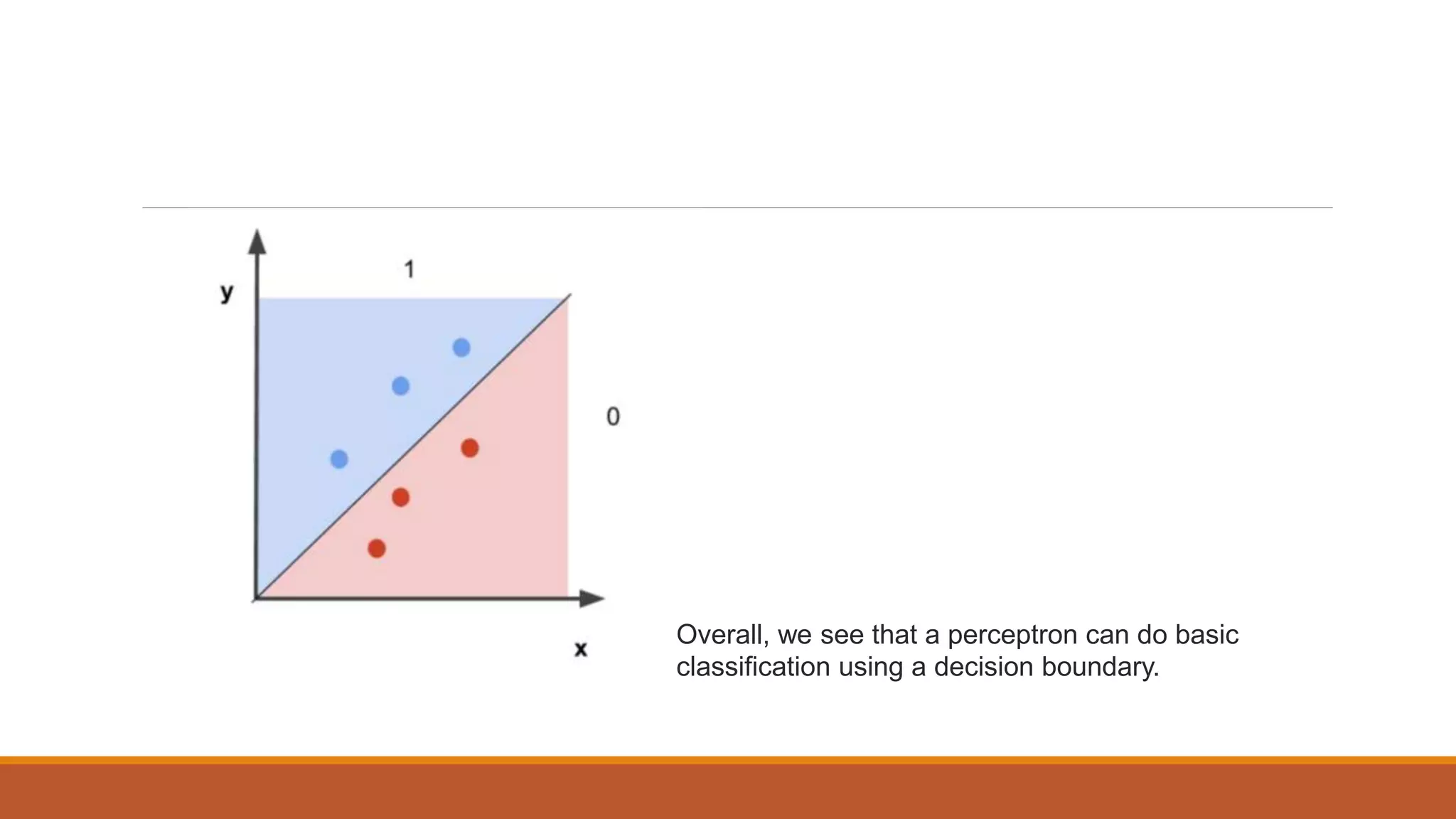
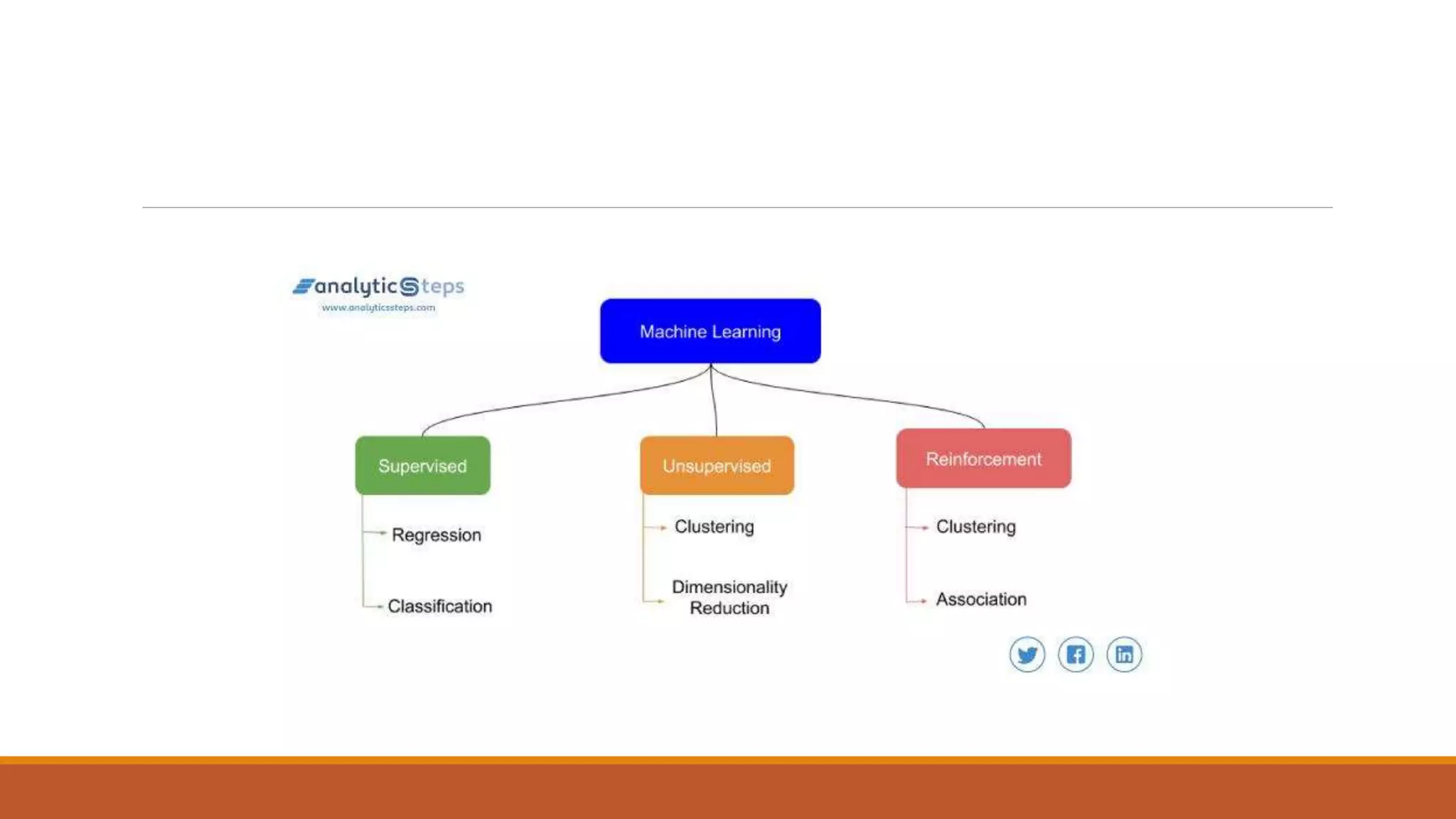
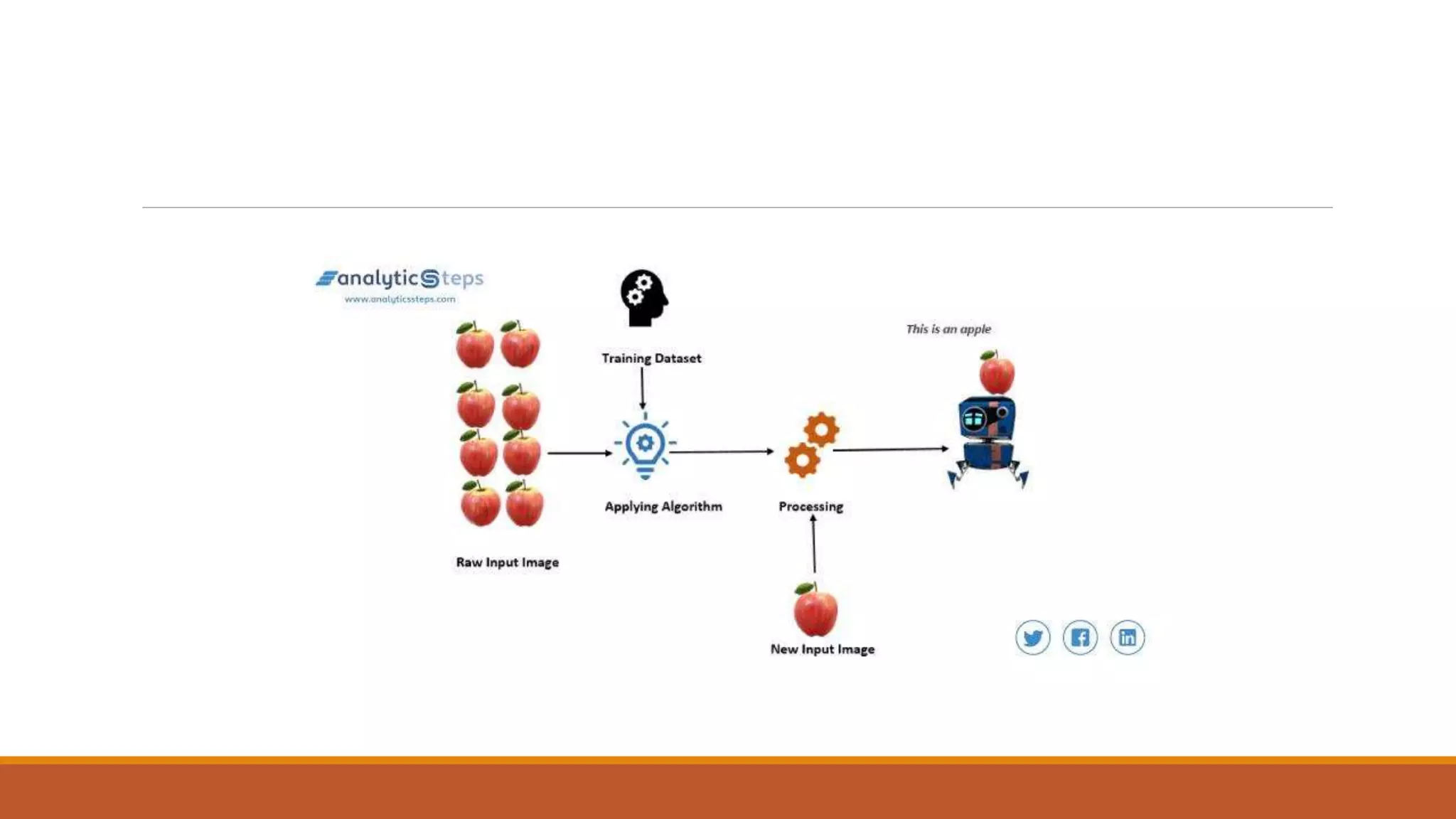
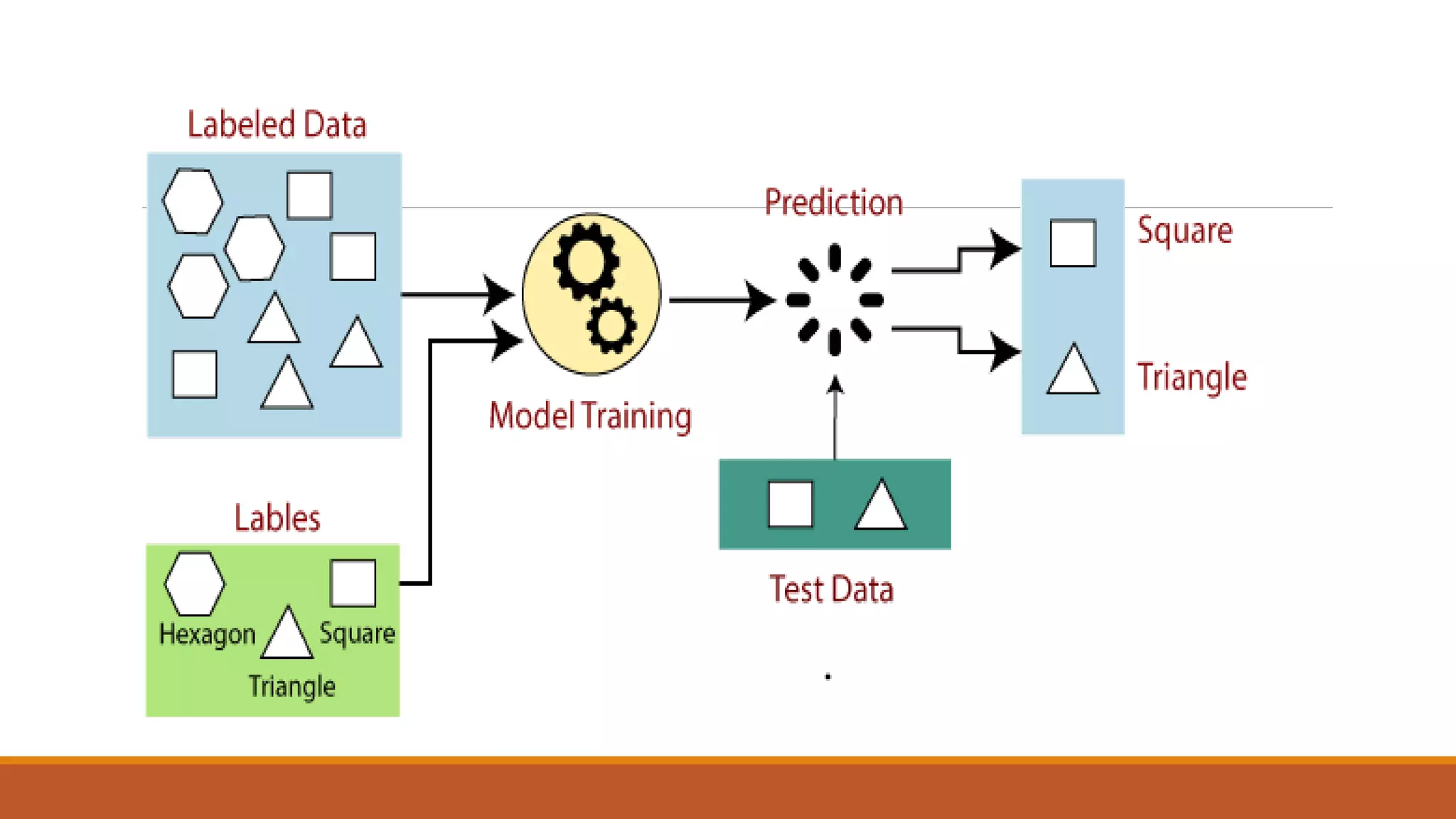
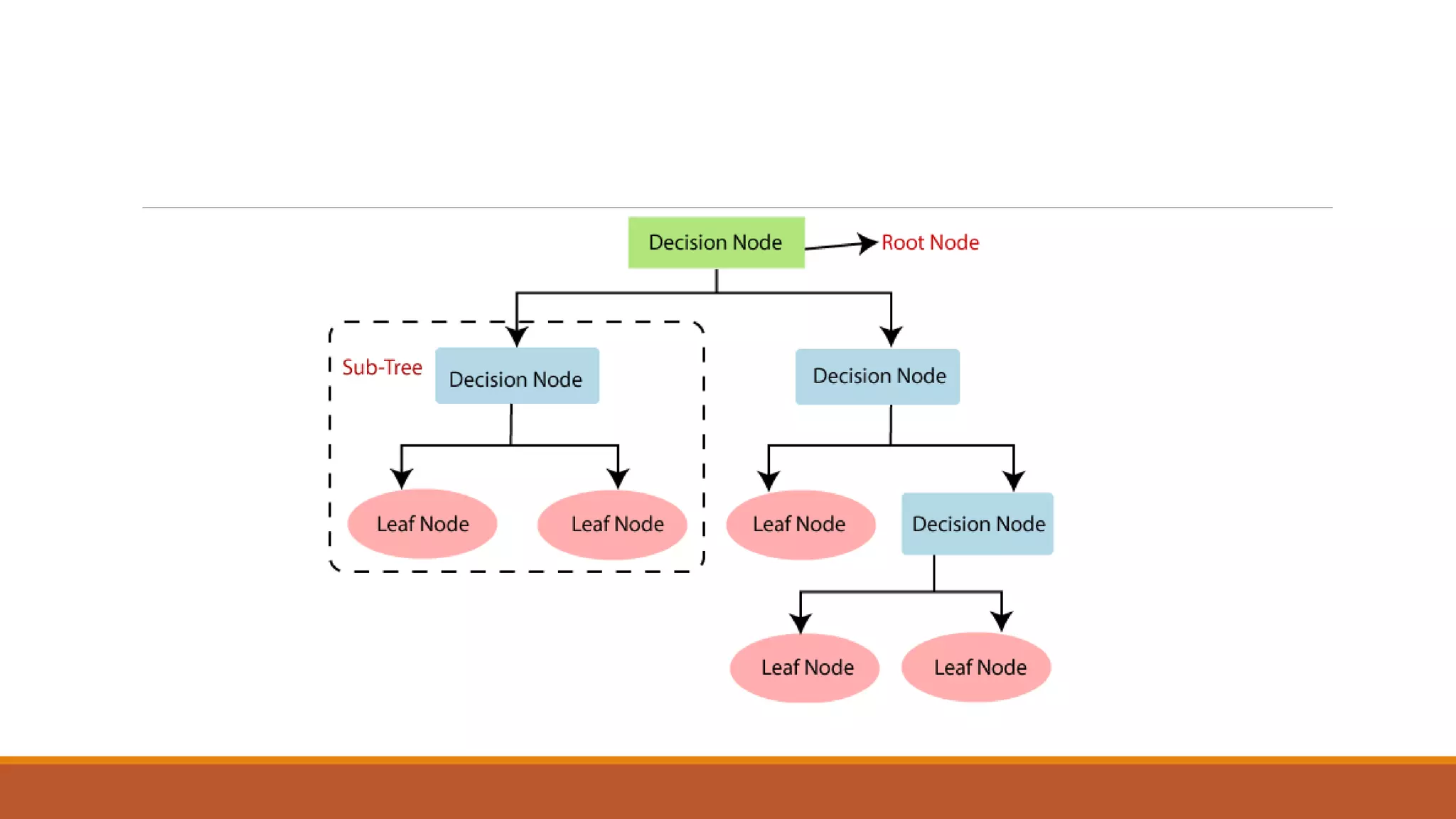
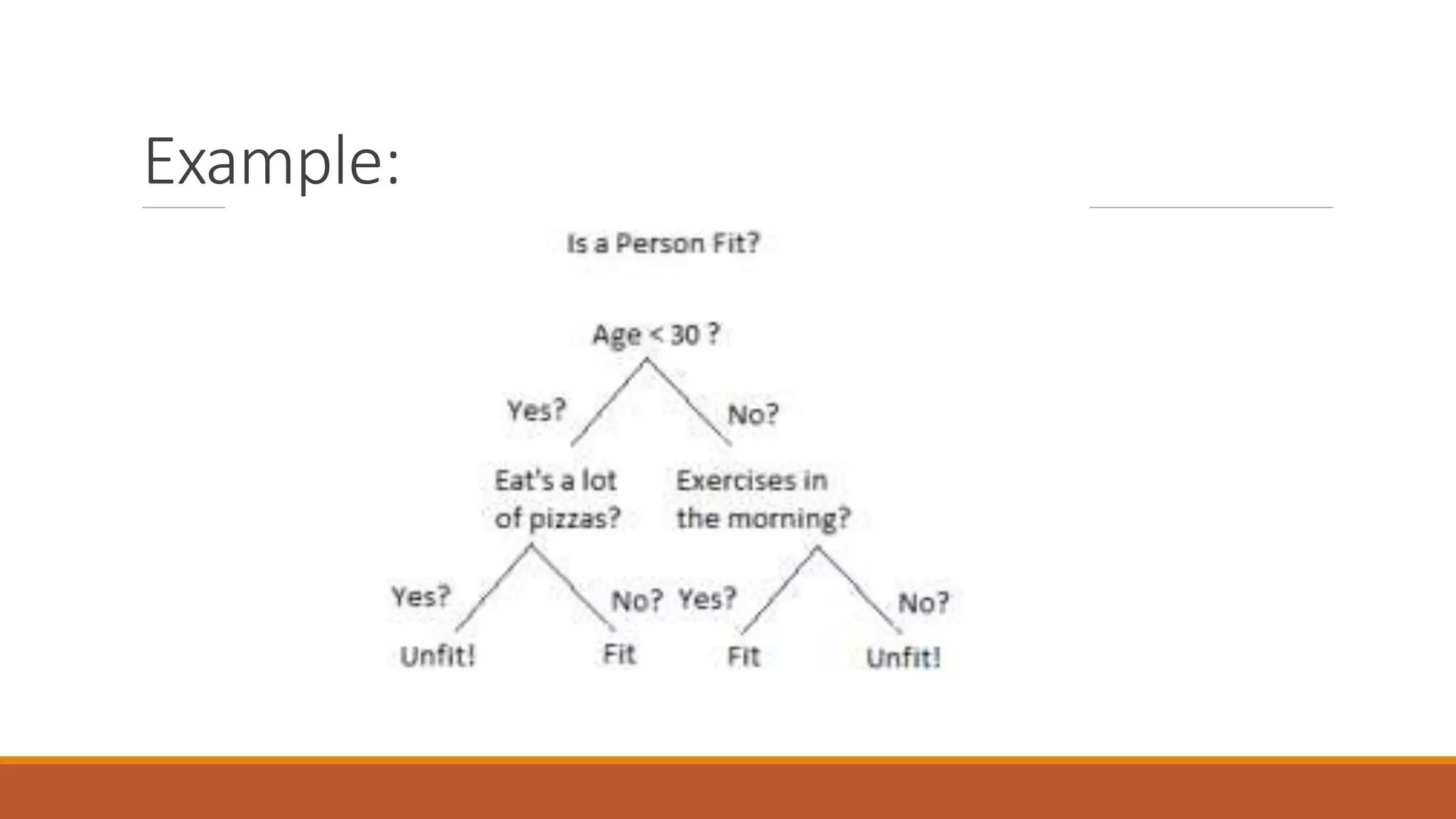
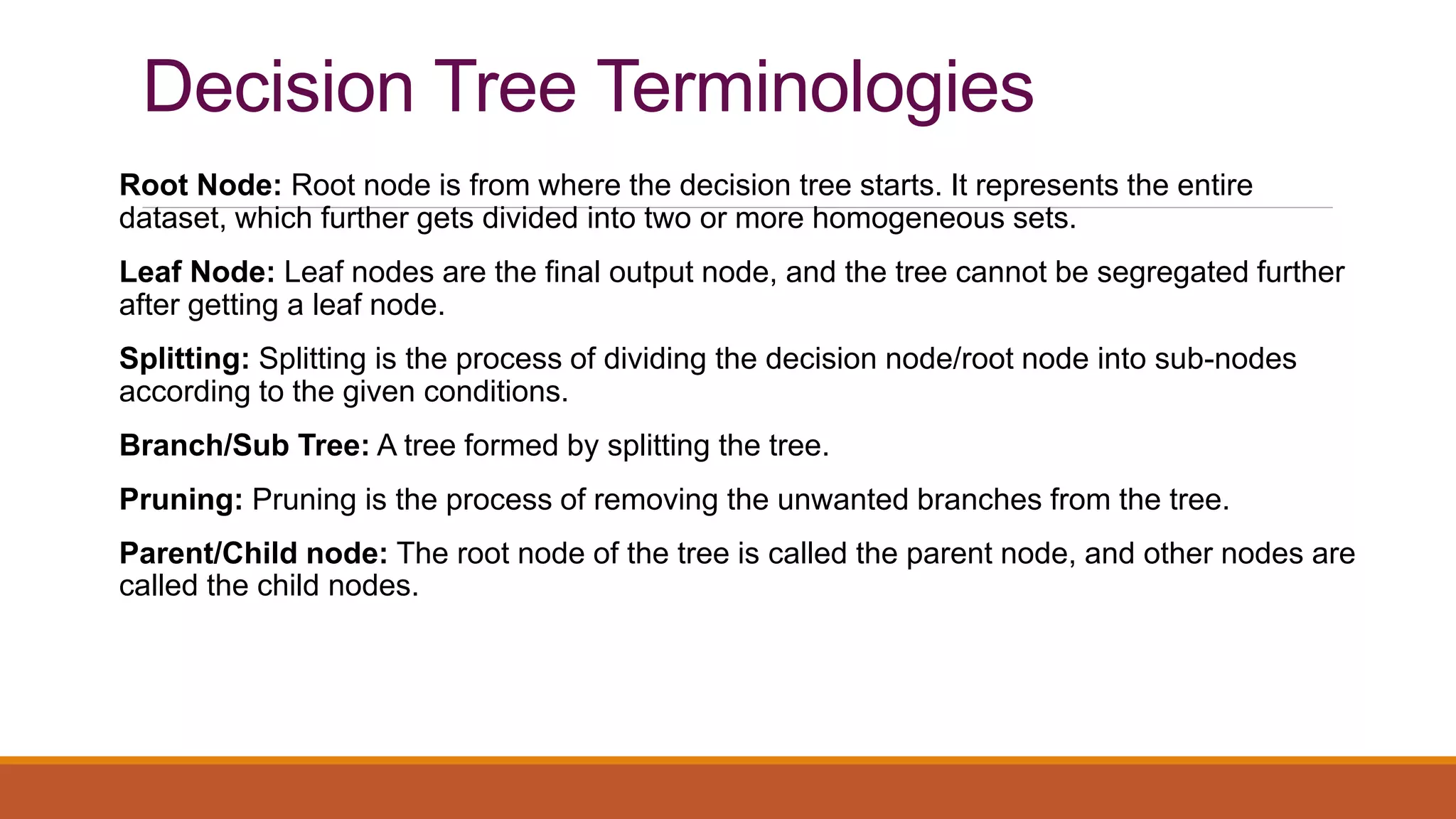
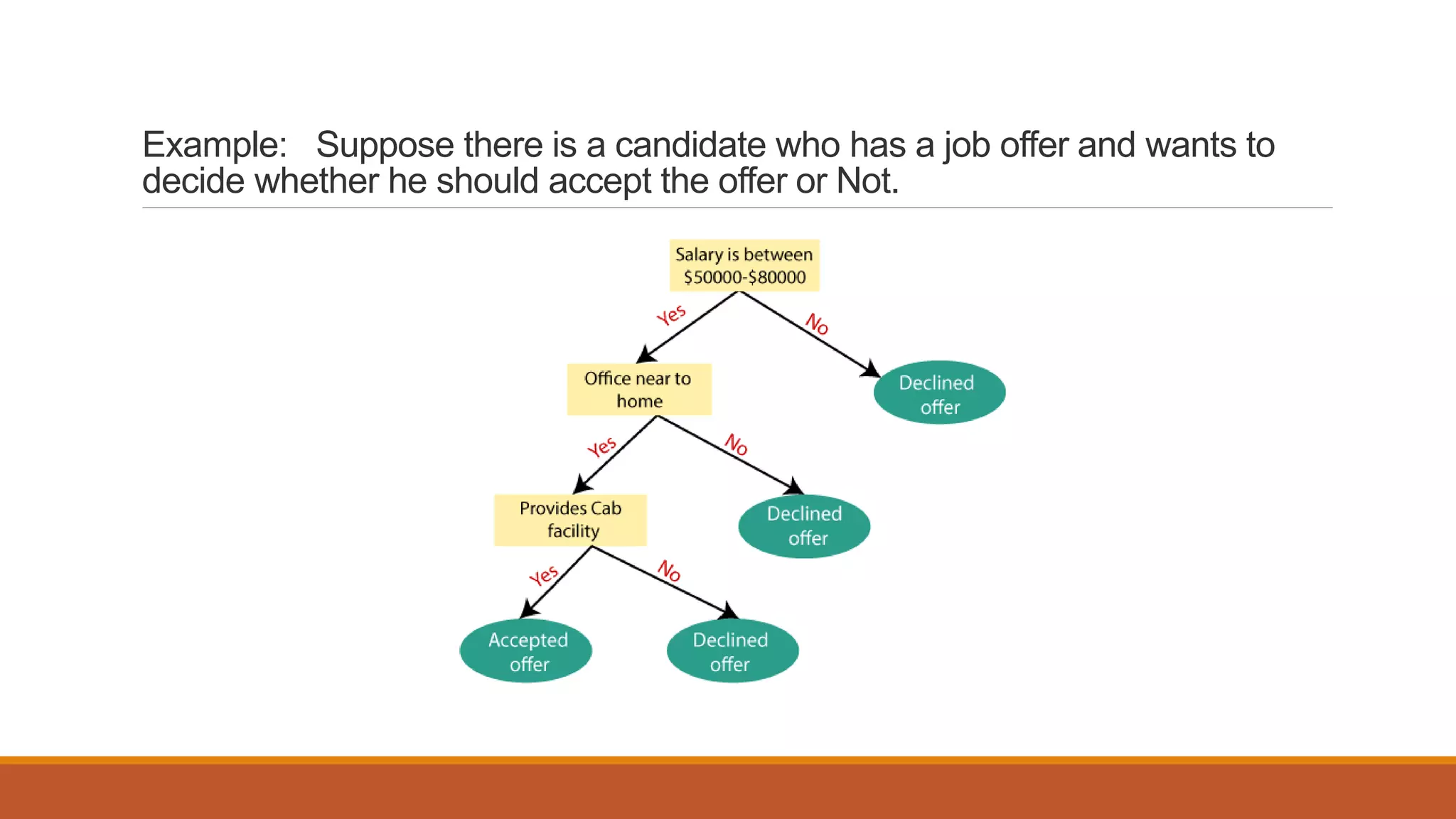
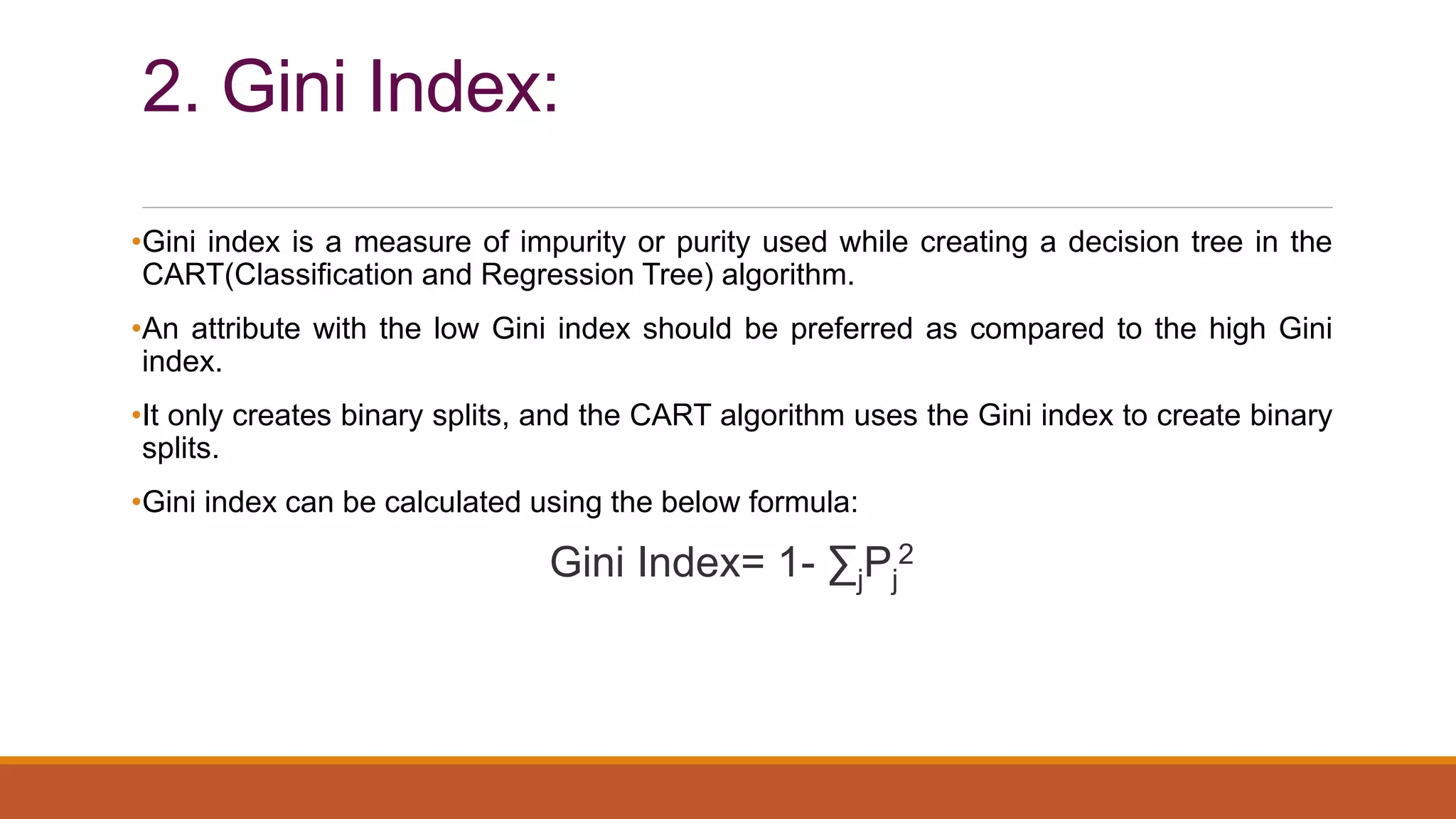
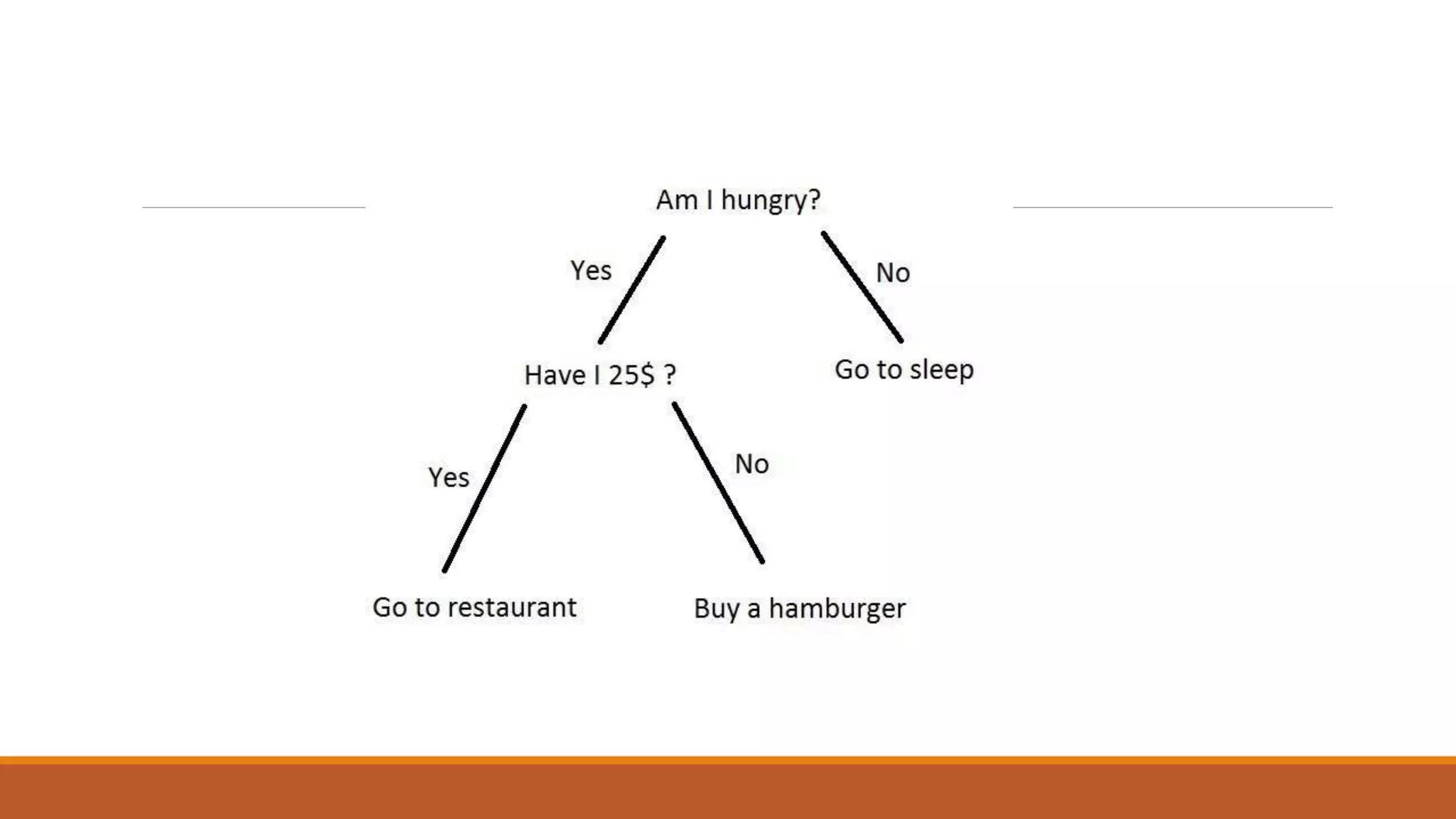
The document provides an introduction to supervised learning. It discusses how supervised learning models are trained on labelled datasets containing both input data and corresponding results or labels. The model learns from these examples to predict accurate results for new, unseen data. Common applications of supervised learning mentioned include sentiment analysis, recommendations, and spam filtration. Decision trees and K-nearest neighbors are discussed as examples of supervised learning algorithms. Decision trees use a top-down approach to split the dataset into more homogeneous subsets. K-nearest neighbors classifies new data based on similarity to labelled examples in the training set.






















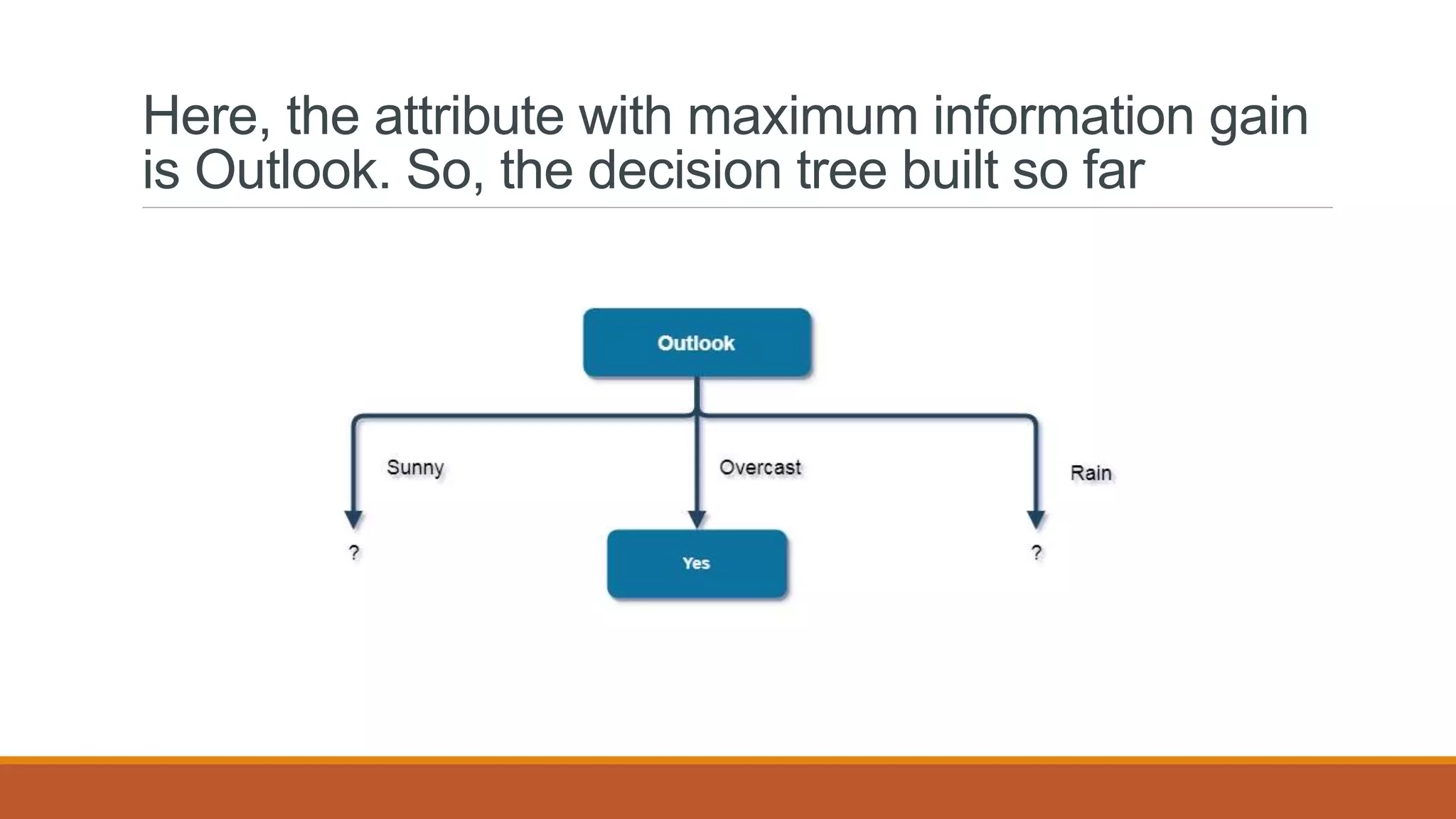
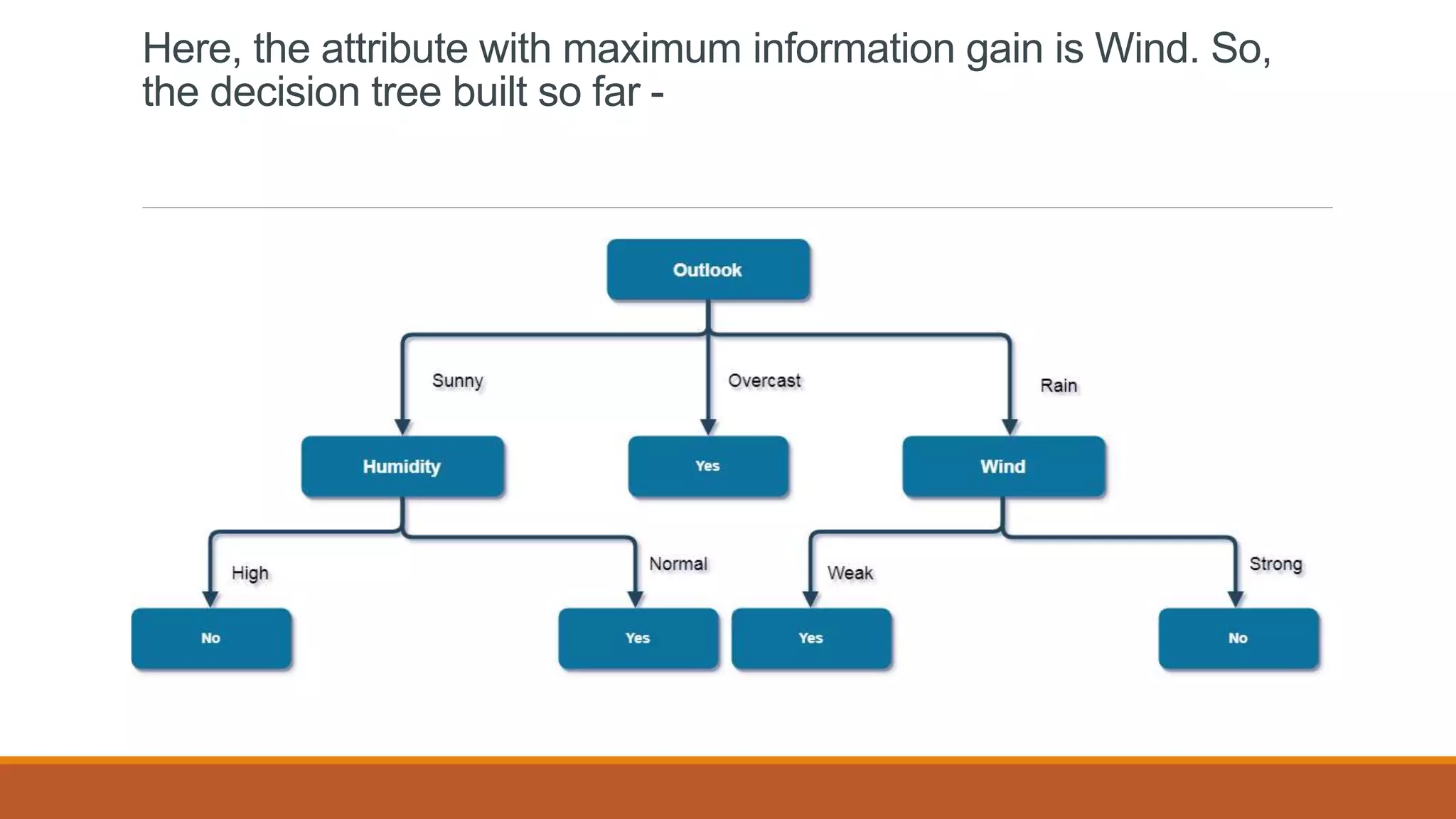
![Here, when Outlook == overcast, it is of pure class(Yes).
Now, we have to repeat same procedure for the data with rows consist of Outlook value
as Sunny and then for Outlook value as Rain.
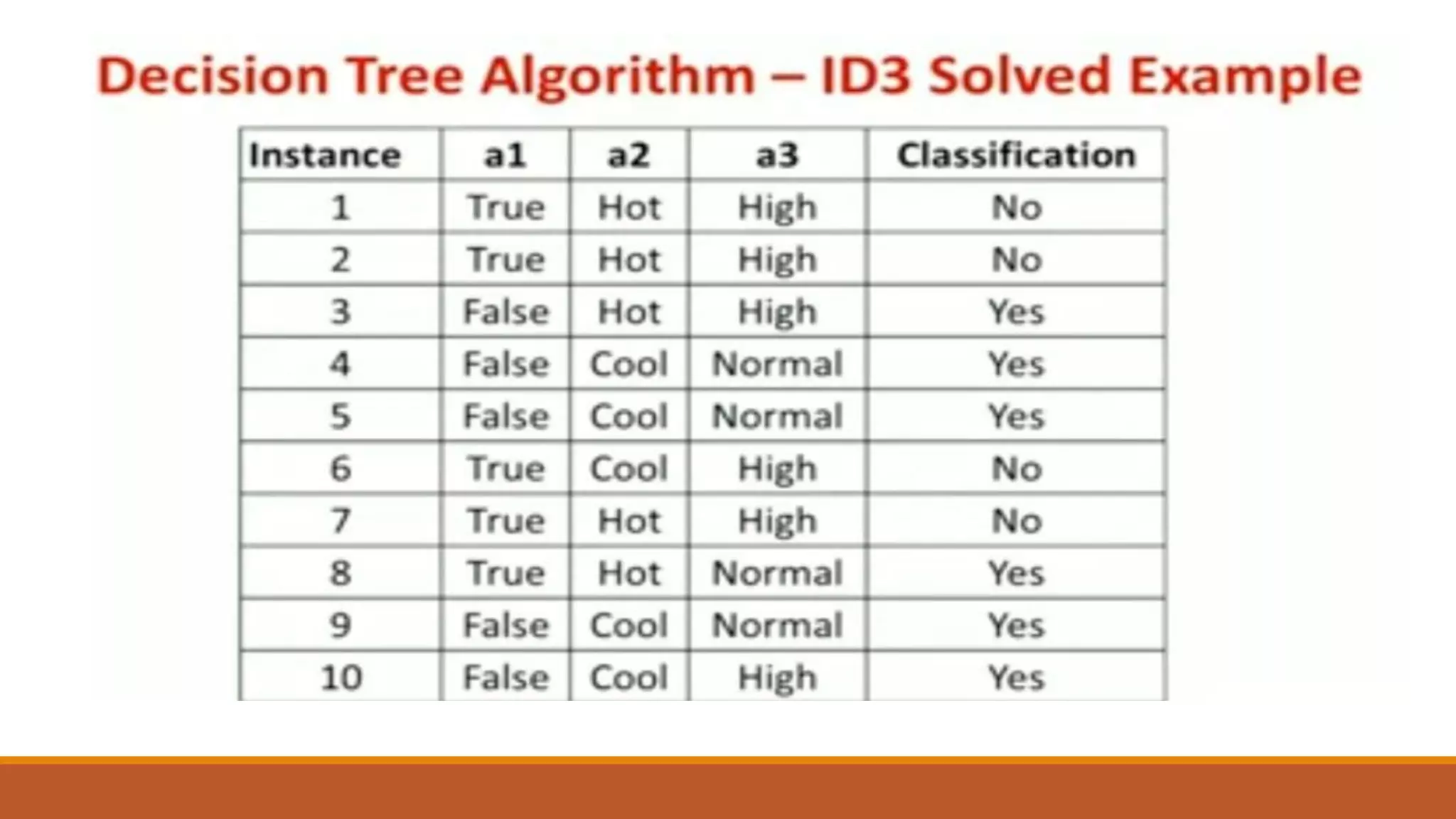
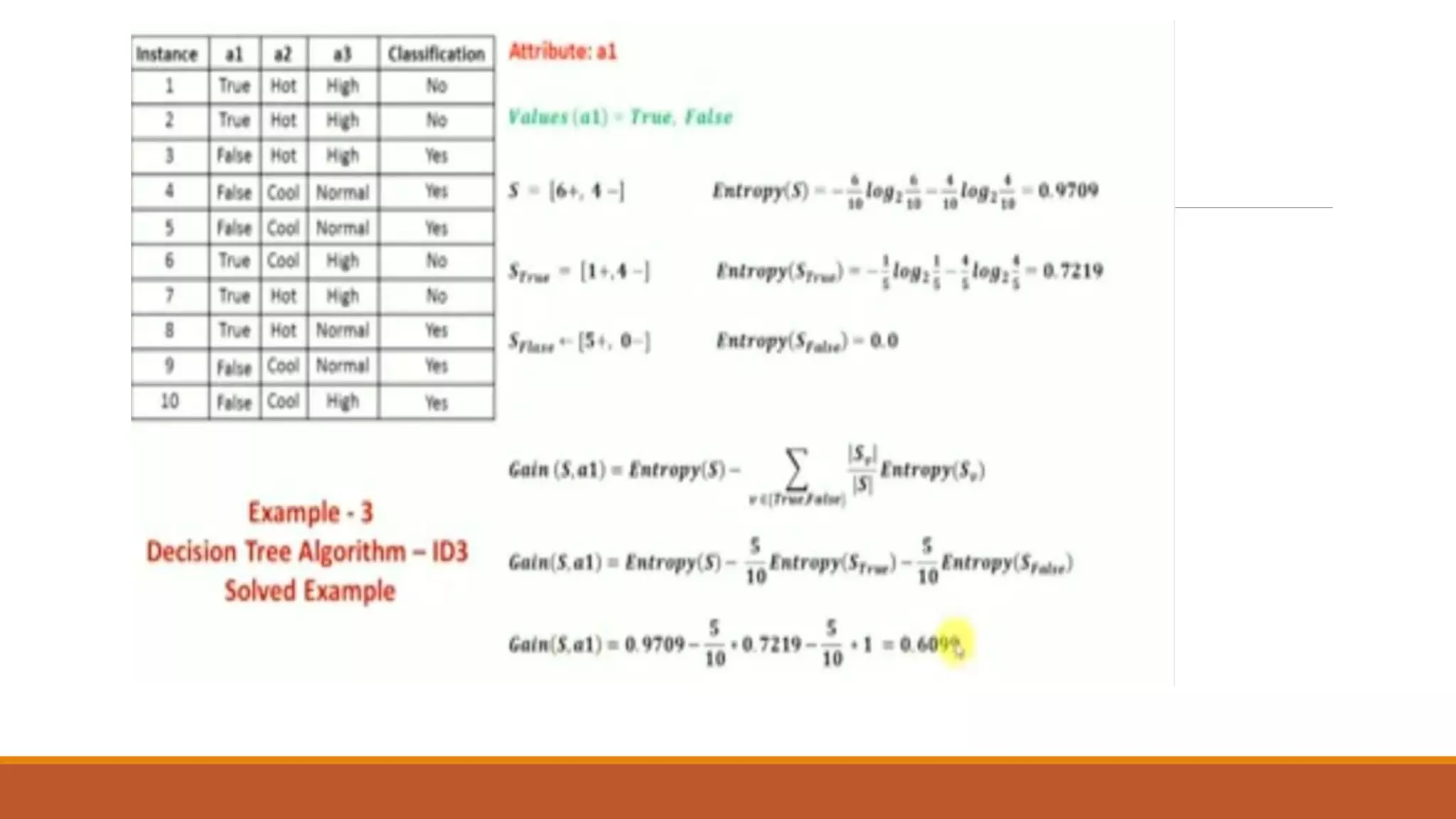
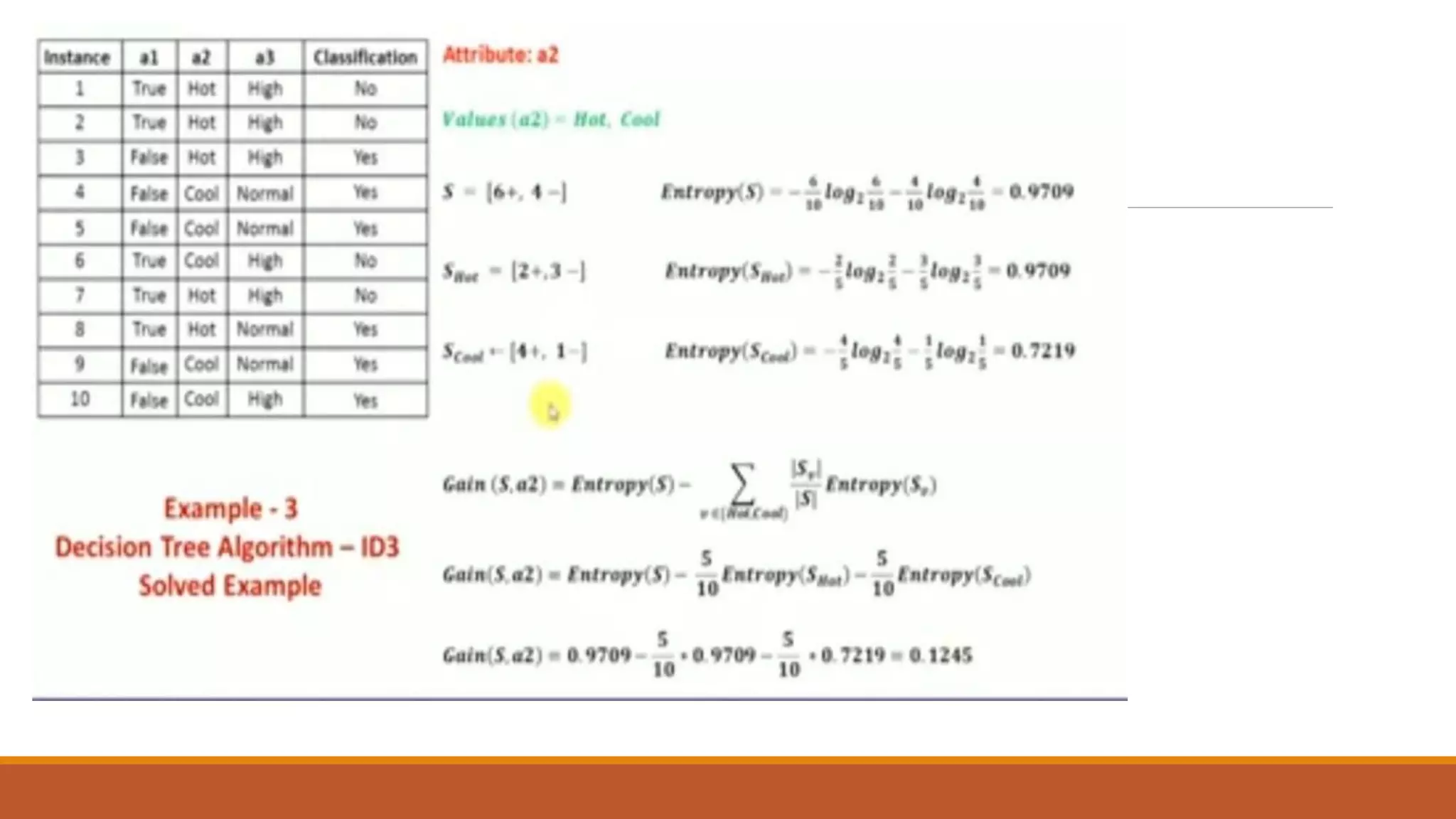
Now, finding the best attribute for splitting the data with Outlook=Sunny values{ Dataset
rows = [1, 2, 8, 9, 11]}.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2-ml-220821090358-39eaa73b/75/Unit-2-ML-pptx-37-2048.jpg)


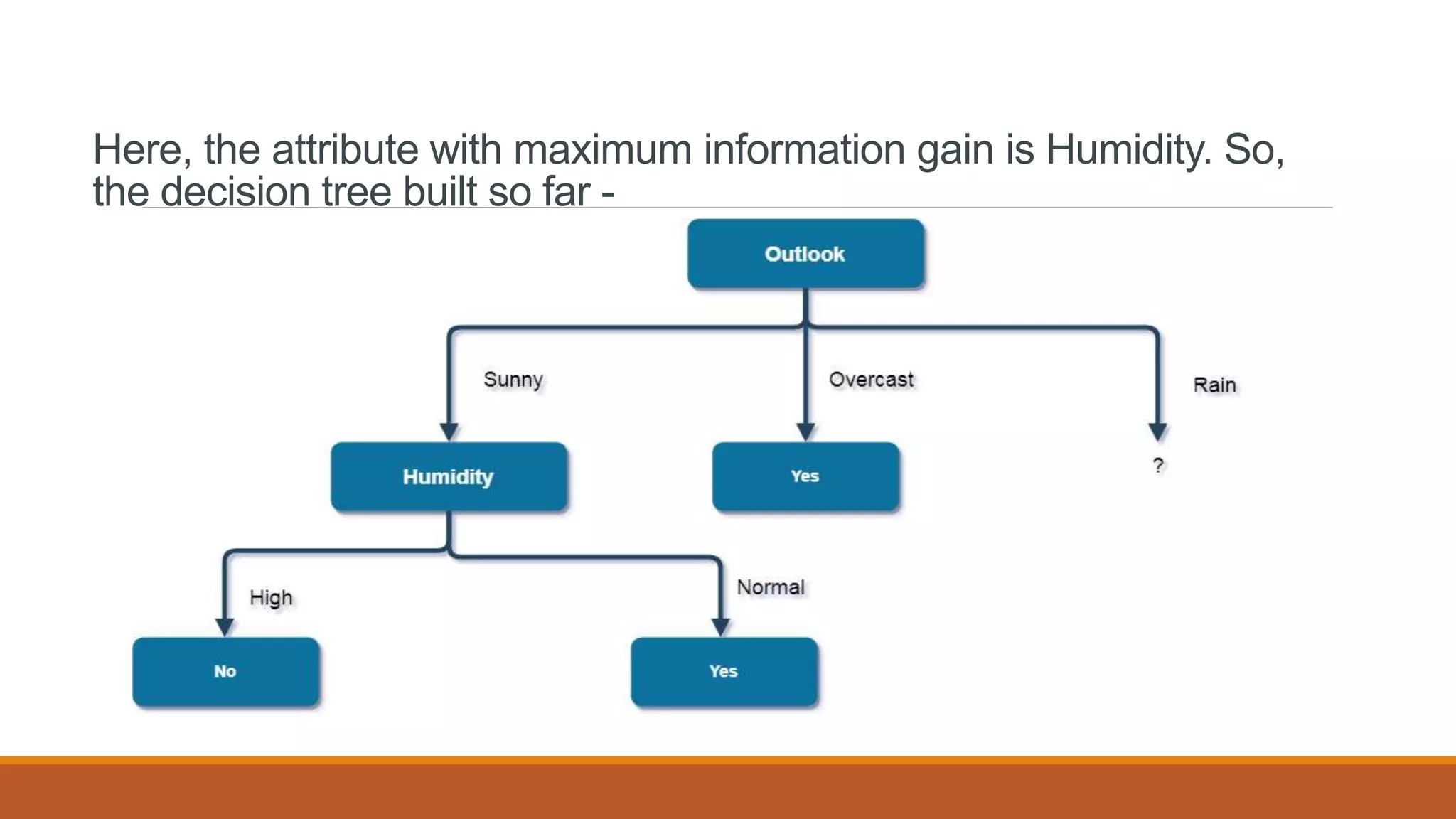
![Here, when Outlook = Sunny and Humidity = High, it is a pure class of category "no". And
When Outlook = Sunny and Humidity = Normal, it is again a pure class of category "yes".
Therefore, we don't need to do further calculations.
Now, finding the best attribute for splitting the data with Outlook=Sunny values{ Dataset
rows = [4, 5, 6, 10, 14]}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2-ml-220821090358-39eaa73b/75/Unit-2-ML-pptx-41-2048.jpg)