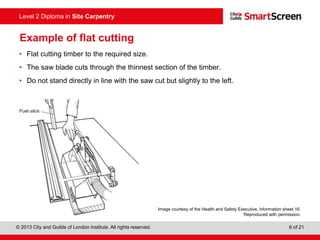
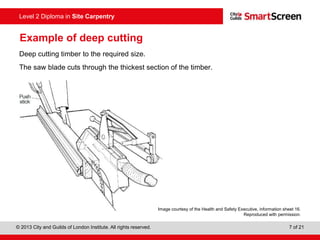
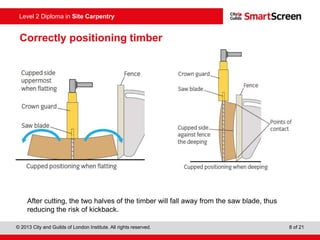
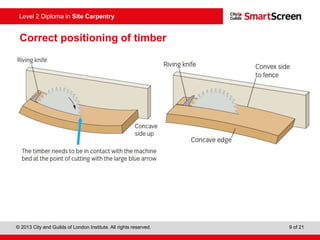
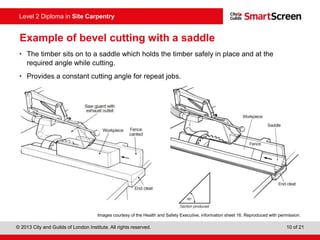
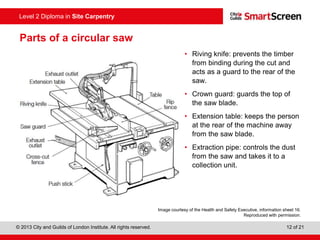
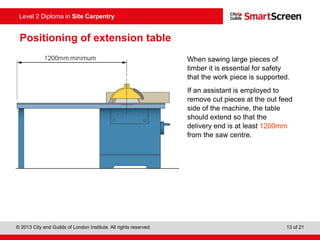
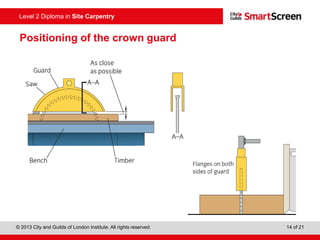
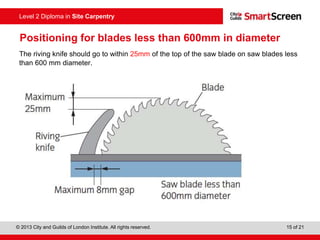
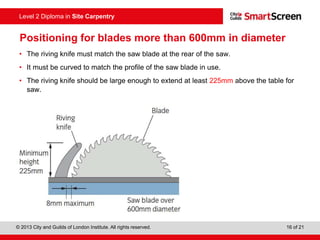
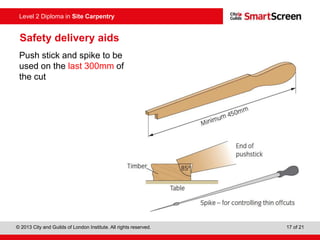
This document provides guidance on safely operating a circular saw. It identifies the key components of a circular saw including the crown guard, riving knife, and extension table. It explains the proper positioning of these components and notes common faults like missing or damaged guards. The document emphasizes following regulations and guidance from the HSE to prevent accidents and ensure all operators are trained, competent, and follow safe working practices.