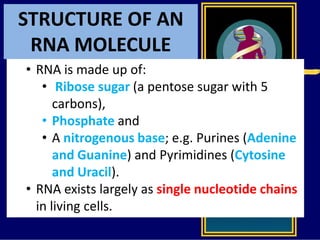
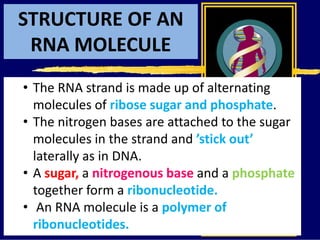
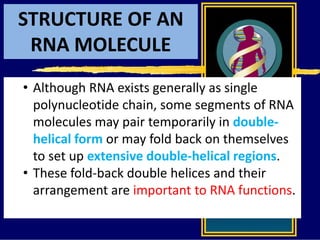
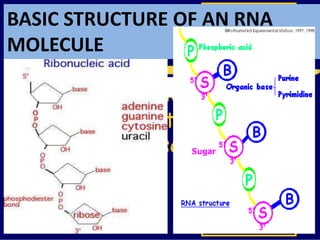
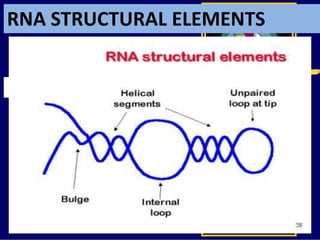
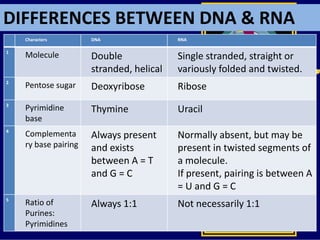
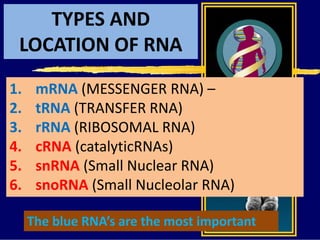
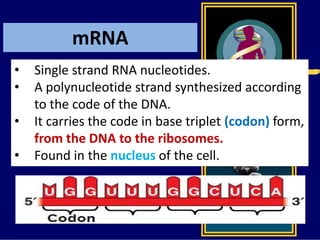
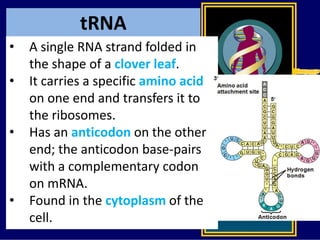
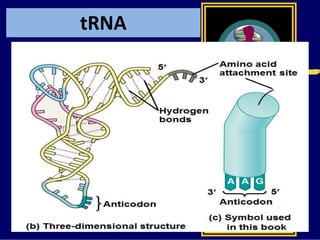
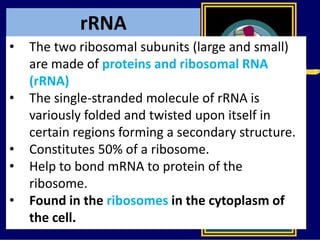
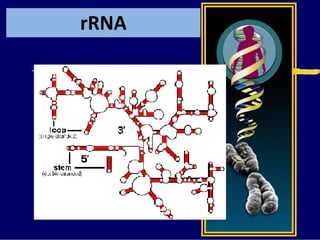
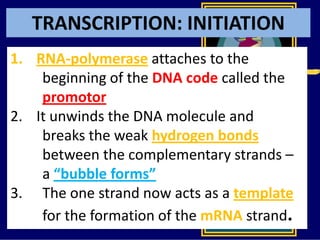
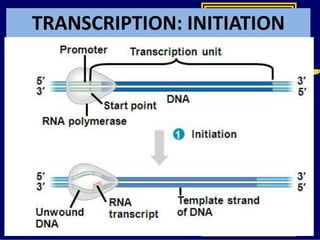
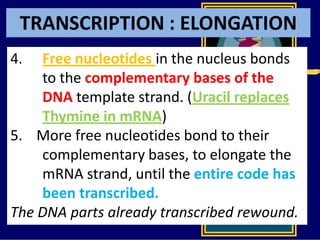
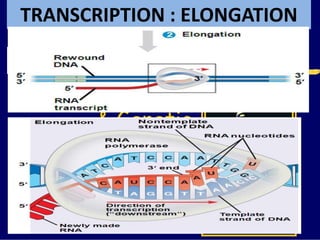
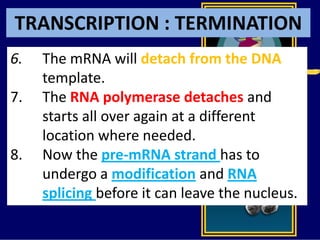
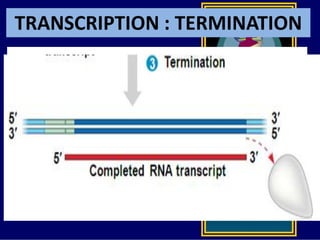
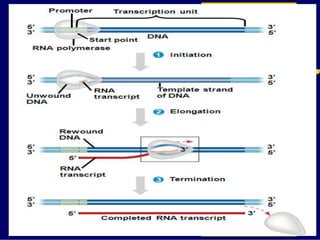
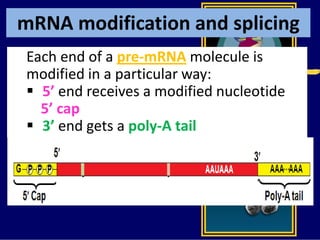
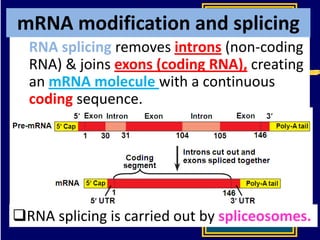
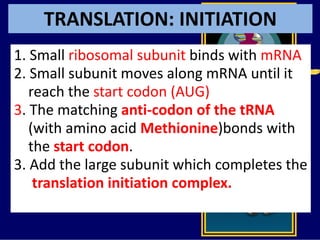
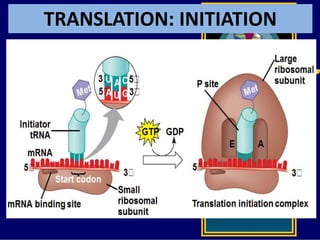
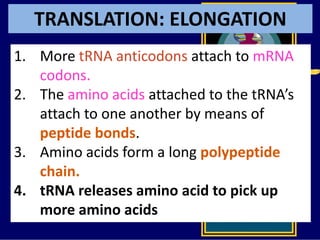
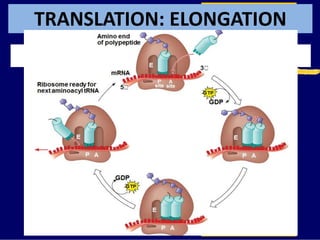
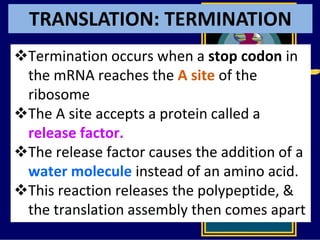
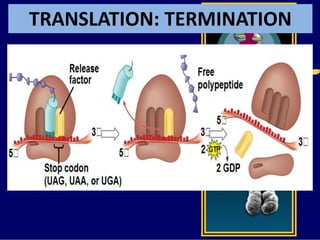
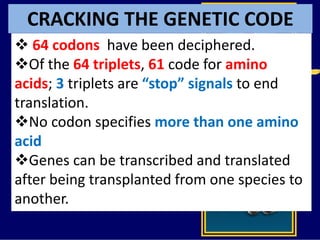
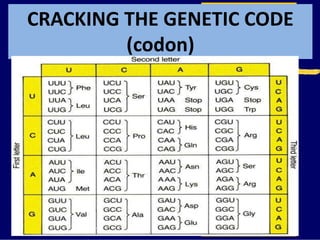
RNA is a single-stranded nucleic acid that plays several roles in protein synthesis. It has a ribose sugar backbone instead of deoxyribose and contains the nitrogenous base uracil instead of thymine. There are several types of RNA, including mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA. mRNA carries the genetic code from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. tRNA transfers amino acids to the ribosome during protein synthesis. rRNA makes up part of the ribosome and helps bind mRNA and proteins together. Protein synthesis involves two main stages - transcription of DNA to mRNA in the nucleus, and translation of mRNA to protein by ribosomes in the cytoplasm.