Embed presentation
Download to read offline


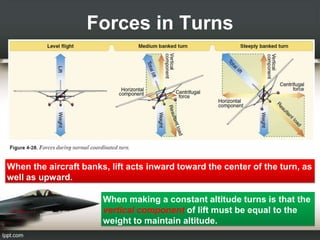

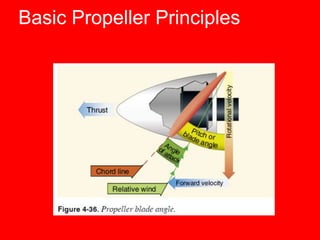

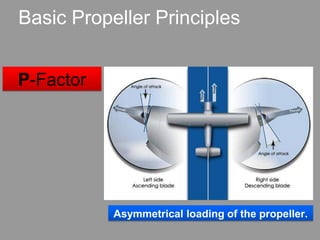




Forces in Turns: When an aircraft banks in a turn, lift acts both inward toward the center of the turn and upward. For constant altitude turns, the vertical component of lift must equal weight. Forces in Climbs: Raising the aircraft's nose increases its angle of attack and temporarily increases lift above weight. Thrust must exceed drag to maintain airspeed during climbs. More power is required at steeper climb angles. Basic Propeller Principles: Several factors cause a left turning tendency in airplanes, including p-factor, gyroscopic effect, corkscrew slipstream, and torque reaction based on Newton's Third Law. Flight instructors remind pilots to "Right rudder,










