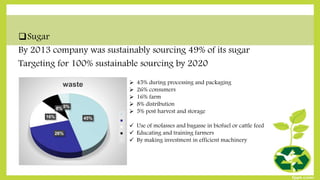
Unilever has taken several steps to combat global food waste within its supply chain and operations. It has focused on reducing waste in three major areas - tomatoes, sugar, and tea. For each commodity, Unilever analyzed where waste occurs most and implemented strategies like improving harvesting techniques, educating farmers, and developing more efficient packaging. Unilever also works with customers and consumers to reduce waste, such as by encouraging the use of leftovers. The company's goal is to have zero waste sent to landfills by 2020 and encourage other stakeholders to do the same across the entire value chain.