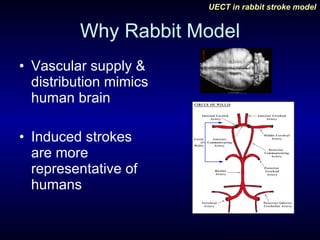
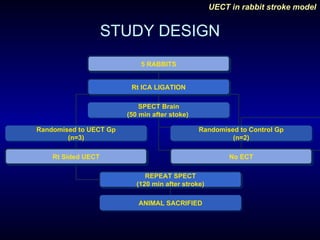
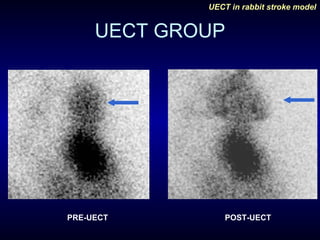
This study evaluated the effects of unilateral electroconvulsive therapy (UECT) on regional cerebral blood flow (rCBF) following experimentally induced stroke in rabbits. Five rabbits underwent right internal carotid artery ligation to induce stroke and were imaged with SPECT scans before and after being randomized to either receive UECT or act as controls. The three rabbits that received UECT showed improvement in rCBF in the affected region on the second SPECT scan, while the two control rabbits showed no improvement, indicating UECT may decrease infarct size following stroke. However, the study was limited by its small sample size.