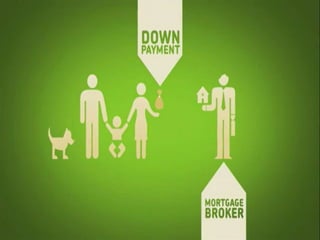
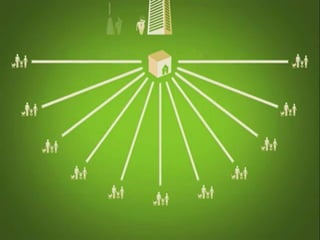
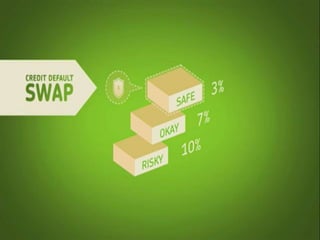
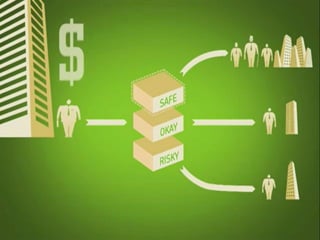
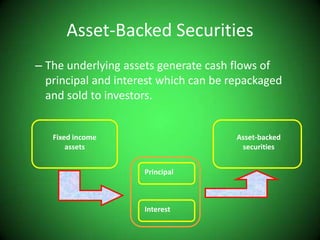
Mortgage-backed securities derive their cash flows from pools of mortgage loans. Asset-backed securities more broadly are financial instruments backed by pools of underlying assets like auto loans, credit cards, or home equity loans that generate cash flows which are repackaged and sold to investors as fixed-income securities. The underlying assets are placed in a trust, and securities representing claims on the cash flows from the asset pool are structured and sold, including pass-through and multi-class structures.