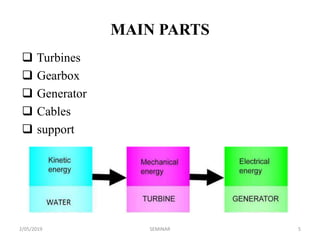
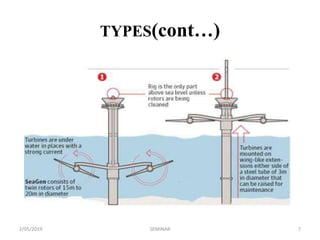
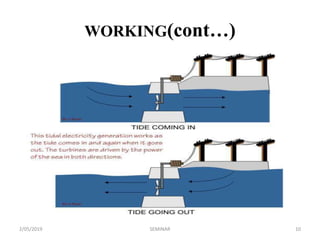
The seminar discusses underwater windmills, devices that harness tidal energy to generate electricity, which is a renewable alternative to fossil fuels. It details the main components, types, working principles, advantages, and disadvantages of this technology, highlighting its potential for clean energy generation. The conclusion emphasizes the competitiveness of tidal energy against conventional energy sources and its low environmental impact.