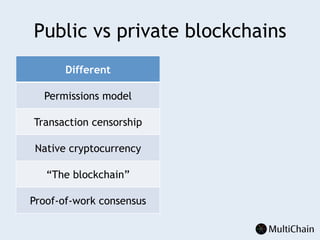
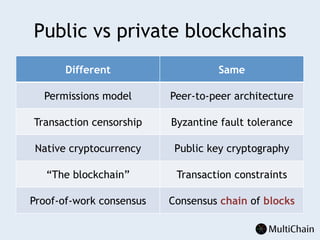
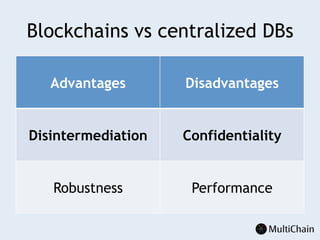
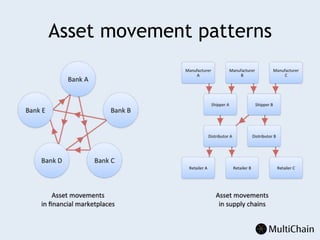
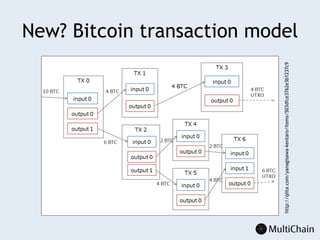
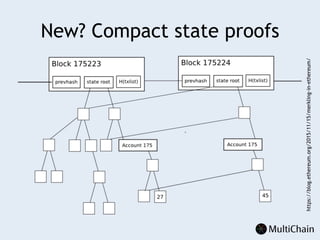
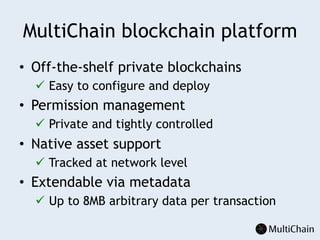
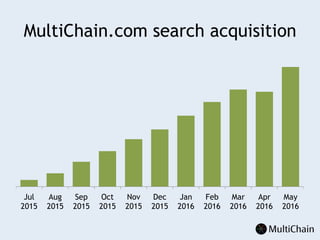
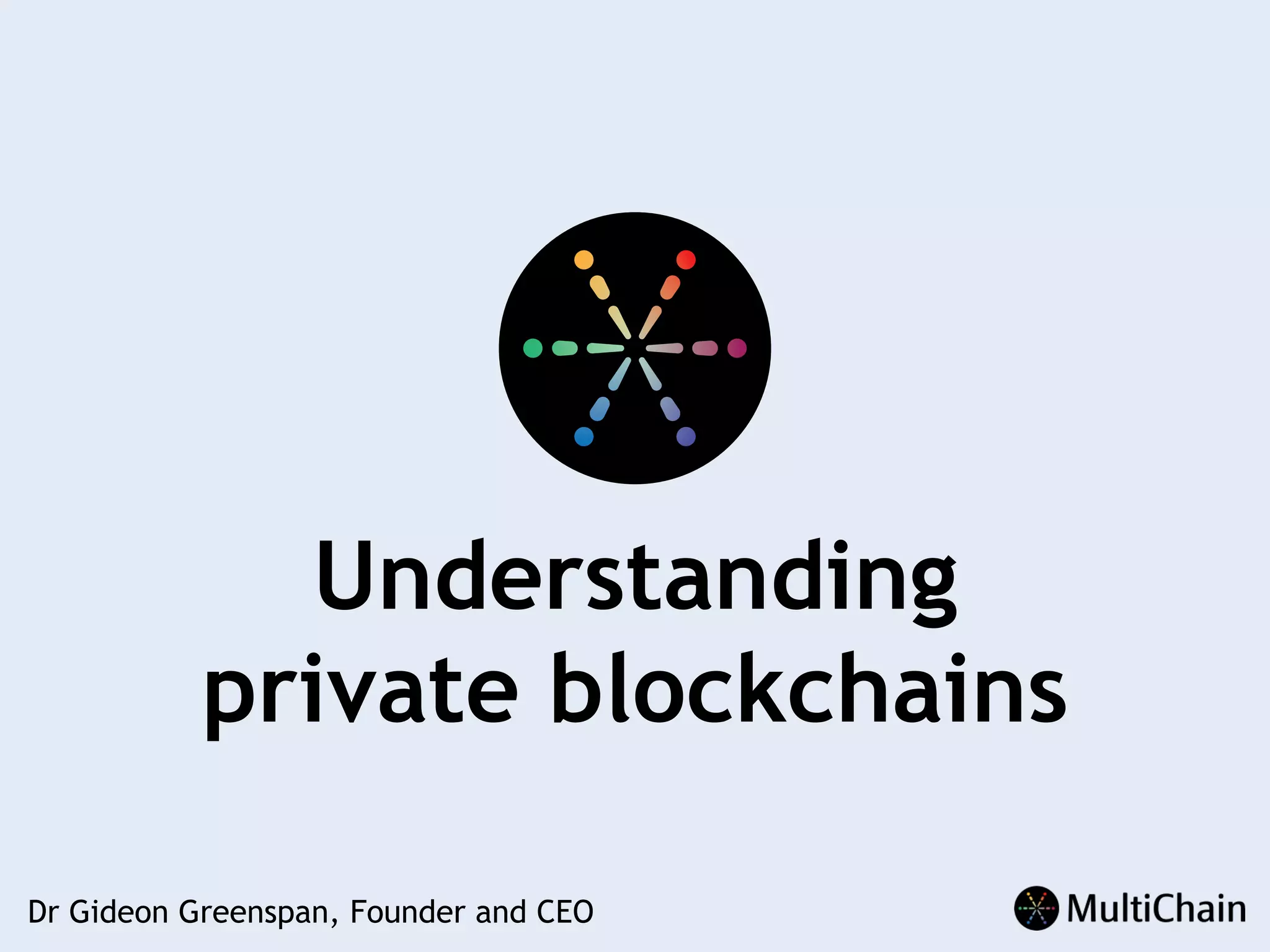
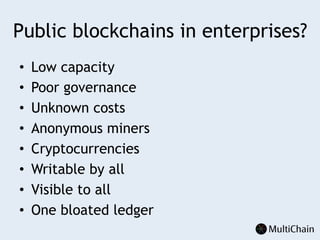
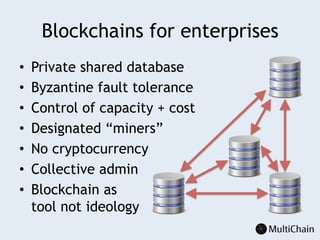
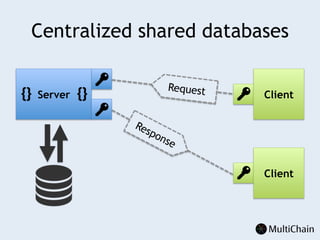
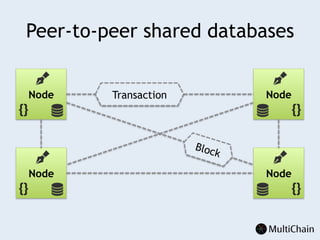
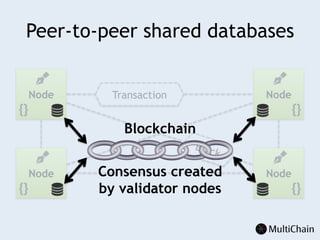
This document discusses private blockchains and how they differ from public blockchains. It explains that private blockchains are permissioned shared databases that use blockchain technology like cryptography and consensus algorithms to provide trust between entities that have limited trust. While they don't have the same properties as public blockchains like immutability and anonymity, private blockchains can enable use cases like financial settlement, provenance tracking, and interorganizational record keeping where a centralized database is not ideal due to lack of trust or need for disintermediation. The document addresses criticisms of private blockchains and blockchain technology in general. It also introduces the MultiChain platform for deploying private blockchains.



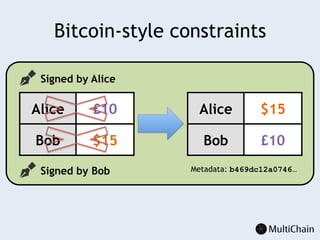
![Ethereum-style constraints
from = msg.sender
fromvalue = contract.storage[from]
to = msg.data[0]
value = msg.data[1]
if fromvalue >= value:
contract.storage[from] -= value
contract.storage[to] += value
return(1)
else:
return(0)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/understandingprivateblockchains-160616123633/85/Understanding-private-blockchains-11-320.jpg)