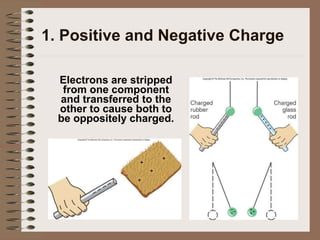
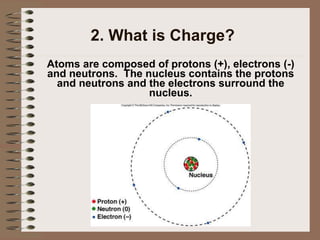
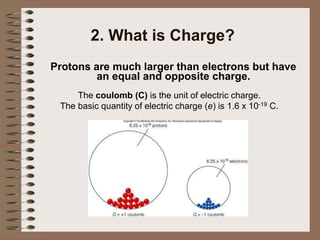
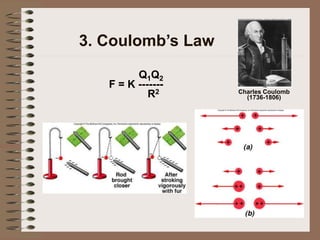
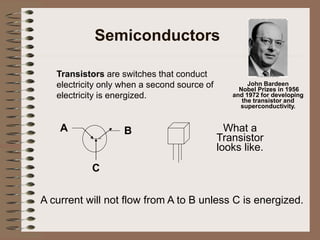
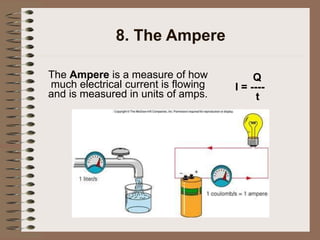
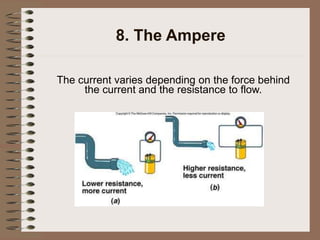
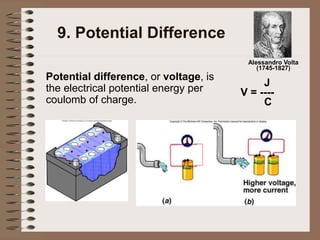
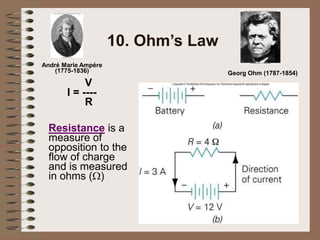
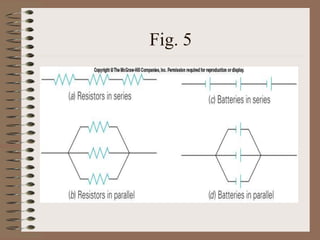
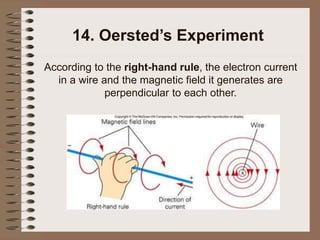
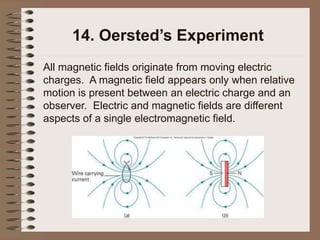
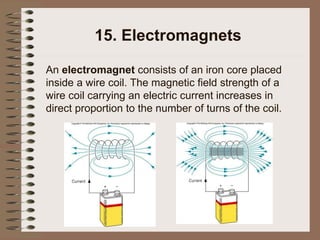
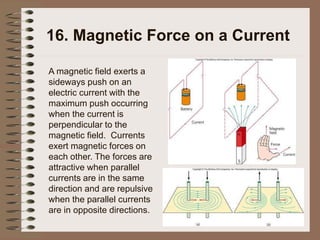
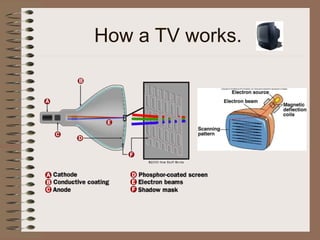
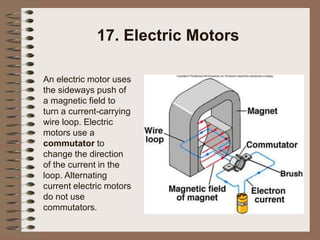
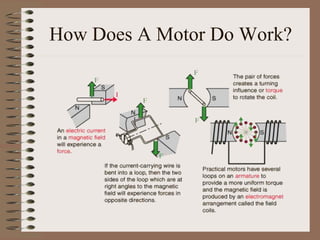
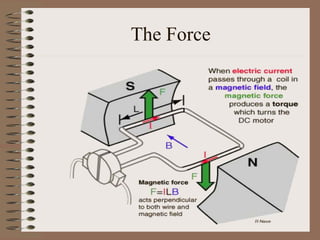
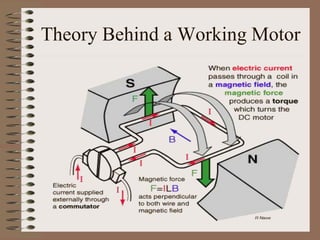
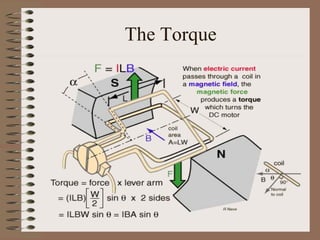
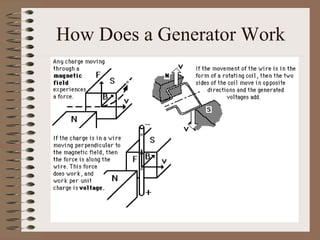
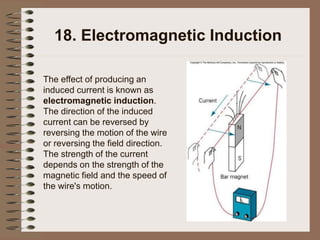
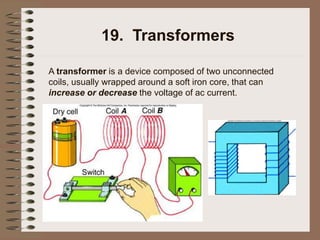
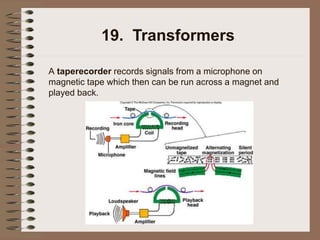
The document outlines fundamental concepts of electricity and magnetism, including electric power, charge types, Coulomb's law, and the principles of conductors, insulators, and superconductivity. It describes the interactions between electric currents and magnetic fields, covering topics such as electromagnets, electric motors, generators, and electromagnetic induction. Key historical figures and experiments in the development of electrical theory and technology are also referenced.