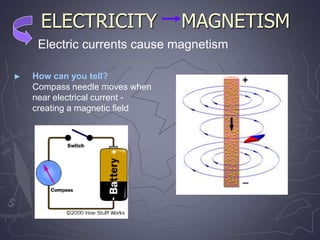
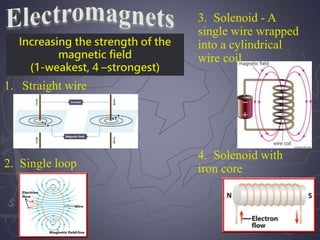
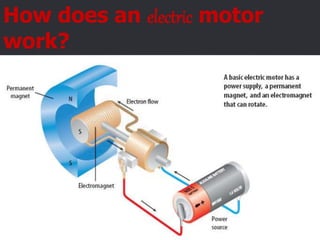
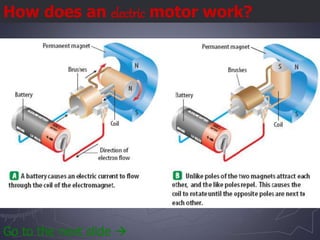
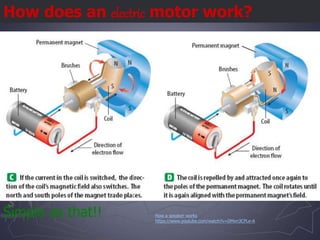
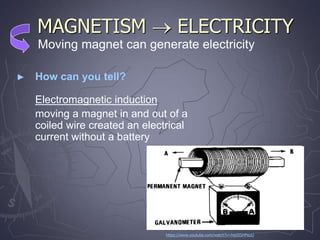
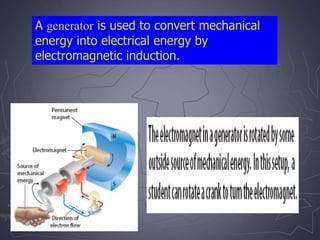
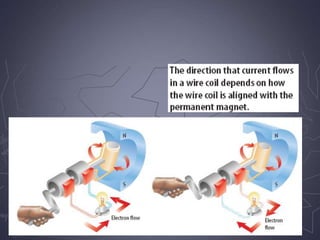
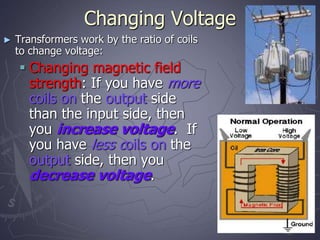
Electricity and magnetism are related phenomena that affect our everyday lives. Charged particles experience electric forces when in electric fields and magnetic forces when moving in magnetic fields. Magnetic forces are proportional to charge, speed, and perpendicular to both velocity and the magnetic field. Electric currents can generate magnetic fields, as seen when a compass needle moves near a current. Conversely, moving a magnet through a coil of wire or vice versa generates an electric current through electromagnetic induction, the principle behind generators and transformers. Electric motors convert electricity into motion via an electromagnet turning inside a permanent magnet.