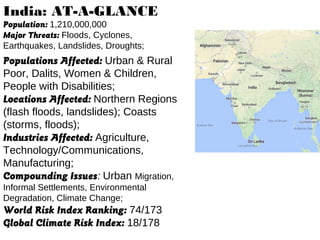
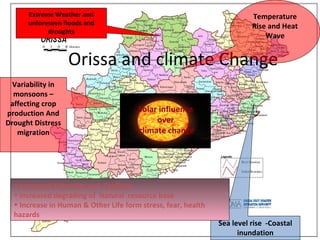
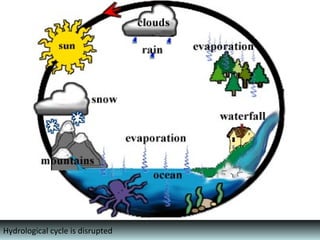
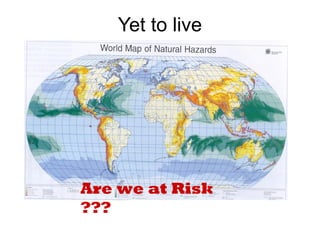
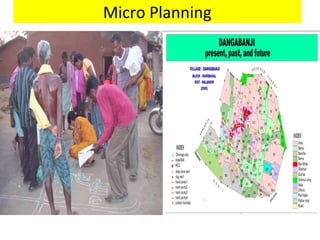
This document provides an overview of the Community Resilience Linking Livelihoods event taking place on February 13-14, 2015 in Patna, Bihar. It discusses key concepts around building community resilience, including local focus, capacity building, adapting from relief to sustainable practices, and linking community efforts to national programs. It also summarizes the work of UDYAMA, an organization working on community resilience and livelihood programs in Odisha, India, including their community interventions, key results, and relationship with local and international partners and initiatives. The document outlines some of the climate change and other risks faced in Odisha and discusses UDYAMA's approach to building resilience through micro-planning, watershed management