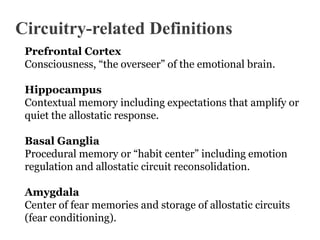
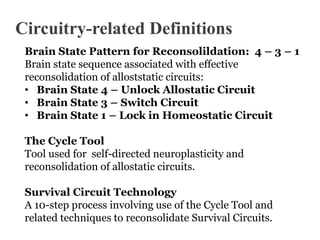
This document defines key terms related to brain circuitry and attachment styles. It discusses action programs, emotions, feelings, homeostatic versus allostatic feelings, secure versus insecure attachment styles. It also outlines the roles of the prefrontal cortex, hippocampus, basal ganglia, and amygdala. Finally, it defines the brain state pattern for reconsolidating allostatic circuits, introduces the Cycle Tool for neuroplasticity, and discusses Survival Circuit Technology.