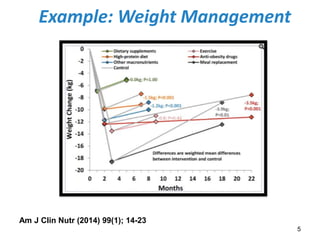
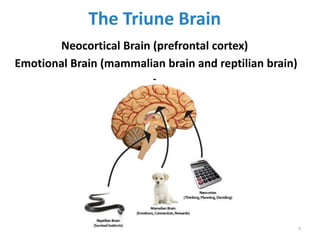
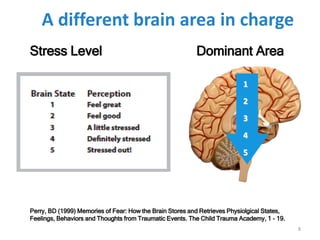
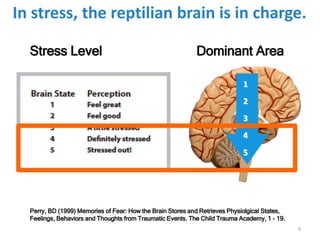
This document discusses the need for EBT (Emotional Brain Training) and how it works. It explains that traditional interventions often do not sustain improvements after treatment ends. It describes how the brain's stress response can encode false associations, leading people to engage in unhealthy behaviors to seek safety and comfort. EBT aims to help rewire these survival circuits through tools and ongoing support so that positive outcomes are sustained long-term.