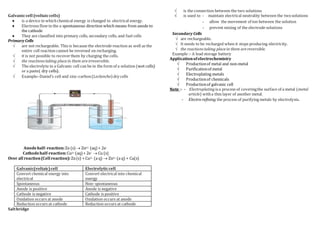
Electrochemistry deals with the relationship between electrical and chemical energy. It studies the interconversion of one form of energy to another. Electrochemical cells like batteries convert chemical energy to electrical energy and vice versa. There are two main types of cells - electrolytic cells which use electrical energy for chemical reactions, and galvanic/voltaic cells which generate electricity from spontaneous chemical reactions. Electrochemistry has many applications including metal production, electrolysis, electroplating and in batteries used in devices and vehicles.