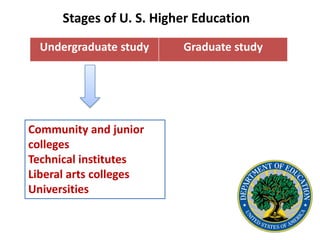
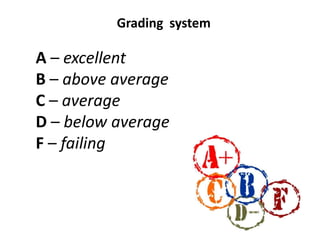
The document outlines the key stages and components of the U.S. higher education system. It discusses the types of institutions including community colleges, technical institutes, liberal arts colleges and universities. It also describes the process for earning degrees based on credit hours completed and courses passed with grades. Degrees are awarded upon completing 120 credit hours typically over a 4 year period within an academic calendar that runs from late August to May.