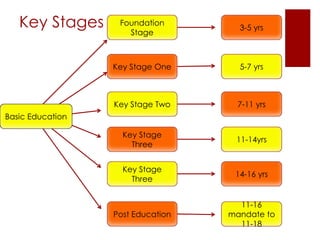
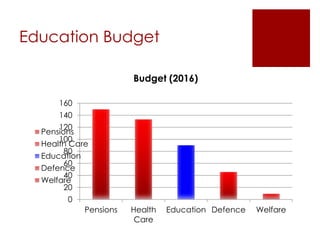
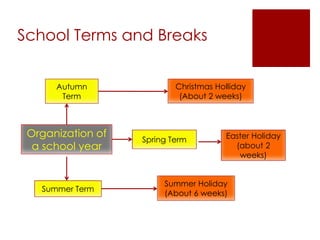
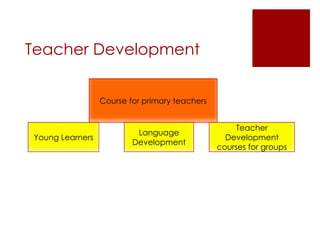
The UK education system has three key stages: primary school from ages 5-11, secondary school from ages 11-16, and post-16 education until age 18. Education is compulsory between ages 5-16, though home schooling is an option. Schools are either comprehensive, which do not use academic selection criteria, or grammar schools, which are selective. Students typically wear school uniforms and the school year runs from September to July. After secondary school, students can pursue higher education at universities, colleges, or arts institutions.