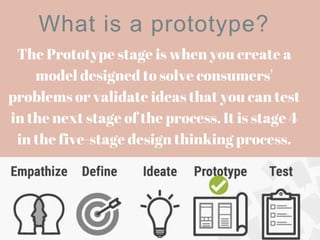
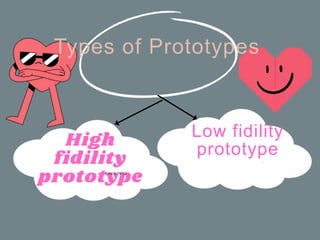
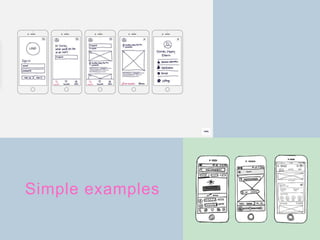
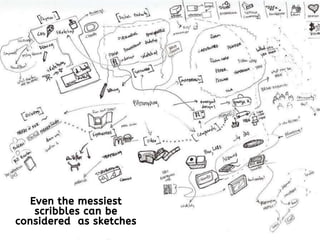
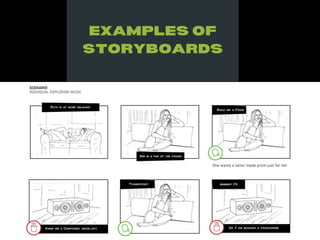
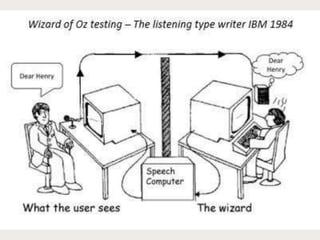
The document discusses the prototype stage in the design thinking process, specifically focusing on low-fidelity and high-fidelity prototypes. Low-fidelity prototypes are quick and inexpensive but lack realism, while high-fidelity prototypes provide more realism but require more time to produce. Various types of low-fidelity prototypes are also described, including sketches, paper interfaces, and role-playing techniques for user experience exploration.