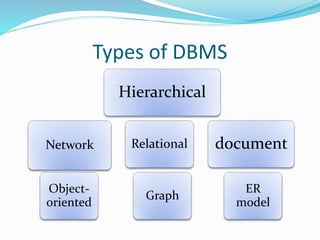
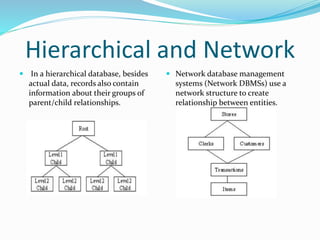
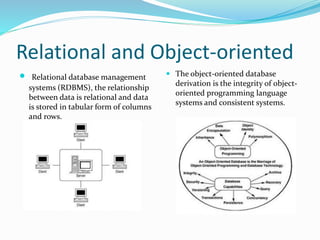
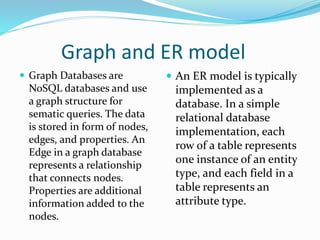
This document defines and describes different types of databases and database management systems (DBMS). It discusses relational databases, object-oriented databases, hierarchical databases, network databases, graph databases, and document databases. It also covers classifications of databases including in-memory, active, cloud, distributed, embedded, federated, mobile, and parallel databases. Popular databases like Oracle, MySQL, SQL Server, PostgreSQL, and MongoDB are mentioned.